
The Indian flapshell turtle is a freshwater species of turtle found in South Asia. The "flap-shelled" name stems from the presence of femoral flaps located on the plastron. These flaps of skin cover the limbs when they retract into the shell. It is unclear what protection the flaps offer against predators. Indian flapshell turtles are widespread and common in the South Asian provinces. It is morphologically an evolutionary link between the softshell and hardshell aquatic turtles. Exploitation for profit and habitat change are threats to their survival.

Phyllorhiza punctata is a species of jellyfish, also known as the floating bell, Australian spotted jellyfish, brown jellyfish or the white-spotted jellyfish. It is native to the western Pacific from Australia to Japan, but has been introduced widely elsewhere. It feeds primarily on zooplankton. P. punctata generally can reach up to 50 centimetres (20 in) in bell diameter, but in October 2007, one 74 cm (29 in) wide, perhaps the largest ever recorded, was found on Sunset Beach, North Carolina.

Lissemys is a genus of softshell turtles in the subfamily Cyclanorbinae of the family Trionychidae. The genus is indigenous to southern Asia.
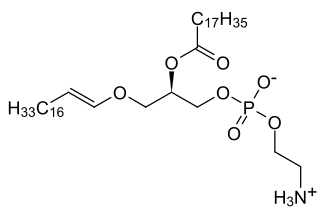
Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata is a rare developmental brain disorder characterized by abnormally short arms and legs (rhizomelia), seizures, recurrent respiratory tract infections and congenital cataracts.
Conradi–Hünermann syndrome is a rare type of chondrodysplasia punctata. It is associated with the EBP gene and affects between one in 100,000 and one in 200,000 babies.
Chondrodysplasia punctata is a clinically and genetically diverse group of rare diseases, first described by Erich Conradi (1882–1968), that share the features of stippled epiphyses and skeletal changes.
The European White Elm cultivar Ulmus laevis 'Punctata' was mentioned in 1873, 1889, and later in 1903 as U. effusa f. punctata, but without description.
The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Folia Alba-Punctata' was first identified by C. de Vos in 1867, as Ulmus campestris fol. albo punctatis. The tree is assumed to be U. minor by Green.
X-linked recessive chondrodysplasia punctata is a type of chondrodysplasia punctata that can involve the skin, hair, and cause short stature with skeletal abnormalities, cataracts, and deafness.

Arylsulfatase L is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ARSL gene.

The Noronha skink is a species of skink from the island of Fernando de Noronha off northeastern Brazil. It is covered with dark and light spots on the upperparts and is usually about 7 to 10 cm in length. The tail is long and muscular, but breaks off easily. Very common throughout Fernando de Noronha, it is an opportunistic feeder, eating both insects and plant material, including nectar from the Erythrina velutina tree, as well as other material ranging from cookie crumbs to eggs of its own species. Introduced predators such as feral cats prey on it and several parasitic worms infect it.

Ransoniella punctata, common name the brown-spotted cowry, is a species of sea snail, a cowry, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Cypraeidae, the cowries.

Colobotheini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae.

Colobothea is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae.
Colobothea grallatrix is a species in the longhorn beetle family Cerambycidae. It was described by Bates in 1865. It is known from French Guiana, Brazil, and Ecuador.
Colobothea destituta is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Bates in 1865.
Colobothea seminalis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Henry Walter Bates in 1865. It is known from Brazil.
Colobothea fasciatipennis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Linsley in 1935. It is known from Honduras and Panama.
Colobothea flavimacula is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Voet in 1806. It is known from South America.
The field elm cultivar 'Punctata' ['spotted', the leaf] first appeared in the 1886–87 catalogue of Simon-Louis of Metz, France, as U. campestris punctata. It was distributed by the Späth nursery, Berlin, in the 1890s and early 1900s as U. campestris punctataSim.-Louis, the Späth catalogue listing it separately from U. campestris fol. argenteo-variegata and from U. campestris fol. argenteo-marginata. Green considered it possibly a synonym of the Field Elm cultivar 'Argenteo-Variegata'.








