Scaling methods
An image size can be changed in several ways. Consider resizing a 160x160 pixel photo to the following 40x40 pixel thumbnail and then scaling the thumbnail to a 160x160 pixel image. Also consider doubling the size of the following image containing text.
| Thumbnail | Text |
|---|---|
| | |
| Original photo | Upscaled thumbnail | Upscaled text | Algorithm and description |
|---|---|---|---|
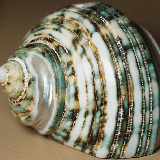 |  | 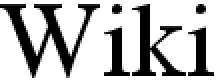 | Nearest-neighbor interpolationOne of the simpler ways of increasing the size, replacing every pixel with a number of pixels of the same color. The resulting image is larger than the original, and preserves all the original detail, but has (possibly undesirable) jaggedness. The diagonal lines of the "W", for example, now show the "stairway" shape characteristic of nearest-neighbor interpolation. Other scaling methods below are better at preserving smooth contours in the image. |
 |  | 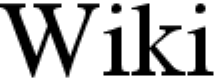 | Bilinear interpolationLinear (or bilinear, in two dimensions) interpolation is typically good for changing the size of an image, but causes some undesirable softening of details and can still be somewhat jagged. |
 |  | 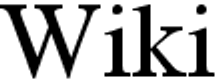 | Bicubic interpolationBetter scaling methods include Lanczos resampling and Mitchell-Netravali filters. |
 |  |  | Fourier-based interpolationSimple Fourier based interpolation based on padding of the frequency domain with zero components (a smooth-window-based approach would reduce the ringing). Beside the good conservation of details, notable is the ringing and the circular bleeding of content from the left border to right border (and way around). |
 |  |  | Edge-directed interpolationEdge-directed interpolation algorithms aim to preserve edges in the image after scaling, unlike other algorithms which can produce staircase artifacts around diagonal lines or curves. Examples of algorithms for this task include New Edge-Directed Interpolation (NEDI), [1] [2] Edge-Guided Image Interpolation (EGGI), [3] Iterative Curvature-Based Interpolation (ICBI),[ citation needed ] and Directional Cubic Convolution Interpolation (DCCI). [4] A study found that DCCI had the best scores in PSNR and SSIM on a series of test images. [5] |
 |  |  | Pixel art scaling algorithms (hqx)For magnifying computer graphics with low resolution and few colors (usually from 2 to 256 colors), better results will be achieved by pixel art scaling algorithms such as hqx or xbr. These produce sharp edges and maintain high level of detail. Unfortunately due to the standardized size of 218x80 pixels, the "Wiki" image cannot use HQ4x or 4xBRZ to better demonstrate the artifacts they may produce such as row shifting.
|
 |  |  | Pixel art scaling algorithms (xbr)The xbr family is very useful for creating smooth edges. It will however deform the shape significantly, which in many cases creates a very appealing result. However it will create an effect similar to posterization by grouping together local areas into a single colour. It will also remove small details if in-between larger ones which connect together. The example images use 4xBRZ and 2xBRZ respectively. |
  |   | 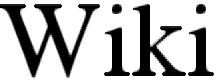 | Pixel art scaling algorithms (GemCutter)An adaptable technique which can deliver variable amounts of detail or smoothness. It aims to preserve the shape and coordinates of original details, without blurring those details into neighboring ones. It will avoid blending pixels which directly touch each other, and instead only blend pixels with their diagonal neighbors. The "Cutter" name comes from its tendency to cut corners of squares and turn them into diamonds, as well as create distinct faces along stair-stepped pixels, i.e. those which exist on along the angles of edges found on a diamond. The "Gem" prefix both refers to the diamond cut, and also many traditional gem cuts which involve cutting corners at a 45-degree angle.
|
 |  |  | Image tracingVectorization first creates a resolution-independent vector representation of the graphic to be scaled. Then the resolution-independent version is rendered as a raster image at the desired resolution. This technique is used by Adobe Illustrator Live Trace, Inkscape, and several recent papers. [6] Scalable Vector Graphics are well suited to simple geometric images, while photographs do not fare well with vectorization due to their complexity.
|
 |  |  | Deep convolutional neural networksUsing machine learning, convincing details are generated as best guesses by learning common patterns from a training data set. The upscaled result is sometimes described as a hallucination because the information introduced may not correspond to the content of the source. Enhanced deep residual network (EDSR) methods have been developed by optimizing conventional residual neural network architecture. [7] Programs that use this method include waifu2x, Imglarger and Neural Enhance. |
 |  | 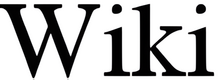 | Deep convolutional neural networks using perceptual lossDeveloped on the basis of the super-resolution generative adversarial network (SRGAN) method, [8] enhanced SRGAN (ESRGAN) [9] is an incremental tweaking of the same generative adversarial network basis. Both methods rely on a perceptual loss function [10] to evaluate training iterations. |
















