
A concept is defined as an abstract idea. It is understood to be a fundamental building block underlying principles, thoughts and beliefs. Concepts play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied within such disciplines as linguistics, psychology, and philosophy, and these disciplines are interested in the logical and psychological structure of concepts, and how they are put together to form thoughts and sentences. The study of concepts has served as an important flagship of an emerging interdisciplinary approach, cognitive science.

A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term. Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions, and extensional definitions. Another important category of definitions is the class of ostensive definitions, which convey the meaning of a term by pointing out examples. A term may have many different senses and multiple meanings, and thus require multiple definitions.

Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as:
Universal algebra is the field of mathematics that studies algebraic structures themselves, not examples ("models") of algebraic structures. For instance, rather than take particular groups as the object of study, in universal algebra one takes the class of groups as an object of study.
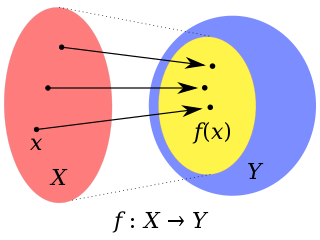
In mathematics, the domain of a function is the set of inputs accepted by the function. It is sometimes denoted by or , where f is the function. In layman's terms, the domain of a function can generally be thought of as "what x can be".

In mathematics, a codomain or set of destination of a function is a set into which all of the output of the function is constrained to fall. It is the set Y in the notation f: X → Y. The term range is sometimes ambiguously used to refer to either the codomain or the image of a function.

An image is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a projection on a surface, activation of electronic signals, or digital displays; they can also be reproduced through mechanical means, such as photography, printmaking, or photocopying. Images can also be animated through digital or physical processes.
A proposition is a central concept in the philosophy of language, semantics, logic, and related fields, often characterized as the primary bearer of truth or falsity. Propositions are also often characterized as being the kind of thing that declarative sentences denote. For instance the sentence "The sky is blue" denotes the proposition that the sky is blue. However, crucially, propositions are not themselves linguistic expressions. For instance, the English sentence "Snow is white" denotes the same proposition as the German sentence "Schnee ist weiß" even though the two sentences are not the same. Similarly, propositions can also be characterized as the objects of belief and other propositional attitudes. For instance if one believes that the sky is blue, what one believes is the proposition that the sky is blue. A proposition can also be thought of as a kind of idea: Collins Dictionary has a definition for proposition as "a statement or an idea that people can consider or discuss whether it is true."
In mathematics, a function from a set X to a set Y assigns to each element of X exactly one element of Y. The set X is called the domain of the function and the set Y is called the codomain of the function.
In algebra, ring theory is the study of rings—algebraic structures in which addition and multiplication are defined and have similar properties to those operations defined for the integers. Ring theory studies the structure of rings, their representations, or, in different language, modules, special classes of rings, as well as an array of properties that proved to be of interest both within the theory itself and for its applications, such as homological properties and polynomial identities.
In category theory, a branch of mathematics, a subobject is, roughly speaking, an object that sits inside another object in the same category. The notion is a generalization of concepts such as subsets from set theory, subgroups from group theory, and subspaces from topology. Since the detailed structure of objects is immaterial in category theory, the definition of subobject relies on a morphism that describes how one object sits inside another, rather than relying on the use of elements.
Identity is the set of qualities, beliefs, personality traits, appearance, and/or expressions that characterize a person or a group.
In mathematics, 0.999... is a notation for the repeating decimal consisting of an unending sequence of 9s after the decimal point. This repeating decimal is a numeral that represents the smallest number no less than every number in the sequence ; that is, the supremum of this sequence. This number is equal to 1. In other words, "0.999..." is not "almost exactly 1" or "very, very nearly but not quite 1"; rather, "0.999..." and "1" represent exactly the same number.
Digital topology deals with properties and features of two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) digital images that correspond to topological properties or topological features of objects.
In control theory, affect control theory proposes that individuals maintain affective meanings through their actions and interpretations of events. The activity of social institutions occurs through maintenance of culturally based affective meanings.
Positive deconstruction, in relation to Christian apologetics, is a term first used by Nick Pollard in Evangelism Made Slightly Less Difficult, to describe a methodology for engaging with worldviews in Christian apologetics. The process is one of deconstruction because it involves 'dismantling' the worldview in order to identify areas of conflict with a Christian worldview. It is positive because the intention is not to destroy a person's ideas and belief system, but to build on areas of agreement between the two worldviews in order to argue for the truth of the Christian worldview.

In mathematics, more specifically algebra, abstract algebra or modern algebra is the study of algebraic structures. Algebraic structures include groups, rings, fields, modules, vector spaces, lattices, and algebras over a field. The term abstract algebra was coined in the early 20th century to distinguish it from older parts of algebra, and more specifically from elementary algebra, the use of variables to represent numbers in computation and reasoning. The abstract perspective on algebra has become so fundamental to advanced mathematics that it is simply called "algebra", while the term "abstract algebra" is seldom used except in pedagogy.
David Orme Tall is Emeritus Professor in Mathematical Thinking at the University of Warwick. One of his early influential works is the joint paper with Vinner "Concept image and concept definition in mathematics with particular reference to limits and continuity". The "concept image" is a notion in cognitive theory. It consists of all the cognitive structure in the individual's mind that is associated with a given concept. Tall and Vinner point out that the concept image may not be globally coherent, and may have aspects which are quite different from the formal concept definition. They study the development of limits and continuity, as taught in secondary school and university, from the cognitive viewpoint, and report on investigations which exhibit individual concept images differing from the formal theory, and containing factors which cause cognitive conflict.
In mathematics, a topos is a category that behaves like the category of sheaves of sets on a topological space. Topoi behave much like the category of sets and possess a notion of localization; they are a direct generalization of point-set topology. The Grothendieck topoi find applications in algebraic geometry; the more general elementary topoi are used in logic.

A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of color – whether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names, or structured with mathematical rigor. A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised.






