Drawing is a form of visual art in which a person uses various drawing instruments to mark paper or another two-dimensional medium. Instruments include graphite pencils, pen and ink, various kinds of paints, inked brushes, colored pencils, crayons, charcoal, chalk, pastels, various kinds of erasers, markers, styluses, and various metals. Digital drawing is the act of using a computer to draw. Common methods of digital drawing include a stylus or finger on a touchscreen device, stylus- or finger-to-touchpad, or in some cases, a mouse. There are many digital art programs and devices.
Relief printing is a family of printing methods where a printing block, plate or matrix that has had ink applied to its surface, but not to any recessed areas, is brought into contact with paper. The areas of the printing plate with ink will leave ink on the paper, whereas the recessed areas of the printing plate will leave the paper ink-free. A printing press may not be needed, as the back of the paper can be rubbed or pressed by hand with a simple tool such as a brayer or roller.
Décollage, in art, is the opposite of collage; instead of an image being built up of all or parts of existing images, it is created by cutting, tearing away or otherwise removing, pieces of an original image. The French word "décollage" translates into English literally as "take-off" or "to become unglued" or "to become unstuck". Examples of décollage include etrécissements and cut-up technique. A similar technique is the lacerated poster, a poster in which one has been placed over another or others, and the top poster or posters have been ripped, revealing to a greater or lesser degree the poster or posters underneath.

The Chavín culture is an extinct, pre-Columbian civilization, named for Chavín de Huantar, the principal archaeological site at which its artifacts have been found. The culture developed in the northern Andean highlands of Peru from 900 BCE to 200 BCE. It extended its influence to other civilizations along the coast. The Chavín people were located in the Mosna Valley where the Mosna and Huachecsa rivers merge. This area is 3,150 metres (10,330 ft) above sea level and encompasses the quechua, suni, and puna life zones. In the periodization of pre-Columbian Peru, the Chavín is the main culture of the Early Horizon period in highland Peru, characterized by the intensification of the religious cult, the appearance of ceramics closely related to the ceremonial centers, the improvement of agricultural techniques and the development of metallurgy and textiles.

Haboku (破墨) and Hatsuboku (溌墨) are both Japanese painting techniques employed in suiboku, as seen in landscape paintings, involving an abstract simplification of forms and freedom of brushwork. The two terms are often confused with each other in ordinary use. Generally, haboku relies on a layered contrast black, gray and white, whereas hatsuboku utilizes "splashes" of ink, without leaving clear contours or outlines. In Japan, these styles of painting were firmly founded and spread by the Japanese painter Sesshū Tōyō.

Paper craft is a collection of crafts using paper or card as the primary artistic medium for the creation of one, two or three-dimensional objects. Paper and card stock lend themselves to a wide range of techniques and can be folded, curved, bent, cut, glued, molded, stitched, or layered. Papermaking by hand is also an important paper craft.

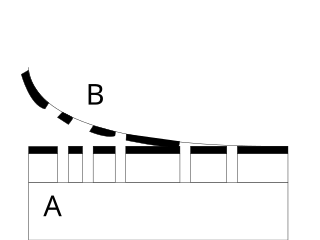
Hatching is an artistic technique used to create tonal or shading effects by drawing closely spaced parallel lines. When lines are placed at an angle to one another, it is called cross-hatching.

The Lanzón is a granite stella associated with the Chavín culture. It is located in the Old Temple of Chavin de Huantar which rests in the central highlands of Peru. The Chavín religion was the first major religious and cultural movement in the Andes mountains, flourishing between 900 and 200 BCE. The Lanzón itself was erected during the Early Horizon period of Andean art circa 500 BCE and takes its name from the Spanish word for "lance," an allusion to the shape of the sculpture. The name is deceiving, as its form more closely resembles a highland plow which would have been used for agricultural purposes at the time. It is suspected because of this that the deity depicted is linked to agrarian worship.

Fresco-secco is a wall painting technique where pigments mixed with an organic binder and/or lime are applied onto a dry plaster. The paints used can e.g. be casein paint, tempera, oil paint, silicate mineral paint. If the pigments are mixed with lime water or lime milk and applied to a dry plaster the technique is called lime secco painting. The secco technique contrasts with the fresco technique, where the painting is executed on a layer of wet plaster.

Gongbi is a careful realist technique in Chinese painting, the opposite of the interpretive and freely expressive xieyi style.

Pre-Columbian art refers to the visual arts of indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, North, Central, and South Americas until the late 15th and early 16th centuries, and the time period marked by Christopher Columbus' arrival in the Americas.

The Raimondi Stele is a sacred object and significant piece of art of the Chavín culture of the central Andes in present-day Peru. The Chavín were named after Chavín de Huantar, the main structure found in ruin at this archaeological site. The Chavín are believed to have occupied this space from 900 BCE to 200 BCE, which places them in the Early Horizon period of Andean cultures. The Early Horizon came to rise after the spread and domination of Chavín art styles, namely the hanging pendant eye and anthropomorphism/zoomorphism of feline, serpent, and crocodilian creatures. The stele is seven feet high, made of highly polished granite, with a lightly incised design featuring these key artistic choices shown in the depiction of the Staff God. After not being found in situ, the stele now is housed in the courtyard of the Museo Nacional de Arqueología Antropología e Historia del Perú in Lima.
Froissage is a method of collage developed by Czech artist Ladislav Novák in which the lines made by crumpling up a piece of paper are used to create a drawing. One major exponent of the art of froissage is Jiří Kolář.

Drybrush is a painting technique in which a paint brush that is relatively dry, but still holds paint, is used. Load is applied to a dry support such as paper or primed canvas. The resulting brush strokes have a characteristic scratchy look that lacks the smooth appearance that washes or blended paint commonly have.
Pholage is an artistic technique and method of graphic reproduction invented by Manuel Bennett in 1959.
Cerography or glyphography is a printmaking technique related to engraving, using a layer of wax over a metal substrate. After the image is engraved into the wax, a positive plate is produced through stereotyping or electrotyping. This plate can be used with conventional letterpress equipment.
Tarashikomi is a Japanese painting technique, in which a second layer of paint is applied before the first layer is dry. This effect creates a dripping form for fine details such as ripples in water or flower petals on a tree. Japanese paintings in the past were usually done on paper with watercolors. The paintings in the Tomb of Kyushu are some of the earliest Japanese art, painted on the tomb’s walls between the fifth and seventh centuries AD. Silk and paper came from China, and in the seventh century was used primarily for writing; however, it began to be used for art during the eighth century. Silk was most common for hanging scroll paintings, while paper was used for calligraphy on handscrolls. Nikawa was used for paint; the glue was made from cowhide or other animal skins.

Cast Paper is a paper crafting technique in which paper fiber or pulp, such as cotton fiber paper, is formed using a mold. The pulp may consist of pure fiber, or be an amalgam of fiber, binder, and filler, such as Papier-mâché. The technique is employed for in-the-round sculpture as well as bas-relief.
Pouncing is an art technique used for transferring an image from one surface to another. It is similar to tracing, and is useful for creating copies of a sketch outline to produce finished works.













