
Cleeve Toot is an Iron Age univallate hillfort above Goblin Combe, Cleeve, Somerset, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument.

Norton Camp is a Bronze Age hill fort at Norton Fitzwarren near Taunton in Somerset, England.

Blacker's Hill is an Iron Age hill fort at Chilcompton, 4.5 kilometres (3 mi) south west of Radstock, Somerset, England. It has been designated as a Scheduled Ancient Monument.

Clatworthy Camp is an Iron Age hill fort 3 miles (4.8 km) North West of Wiveliscombe, Somerset, England. It has been scheduled as an Ancient Monument. Due to the vulnerability to scrub and tree growth it has been added to the Heritage at Risk Register.

Cow Castle is an Iron Age hill fort 5.75 kilometres (4 mi) West South West of Exford, Somerset, England within the Exmoor National Park. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. It has been added to the heritage at Risk register because of the risk from bracken.

Kenwalch's Castle is probably an Iron Age hill fort that may have been converted into a Roman fortress in Penselwood, Somerset, England, 6.6 kilometres (4 mi) East South East of Bruton at grid reference ST747335. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. It is believed to be named after Cenwalh of Wessex.

Kingsdown Camp is an Iron Age hill fort at Buckland Dinham 4.5 kilometres (3 mi) South East of Radstock, Somerset, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument.

Sweetworthy is the site of two Iron Age hill forts or enclosures at Luccombe, 4 kilometres (2 mi) south of Porlock, Somerset, England. They are on the north-facing slope of Dunkery Hill. One has a single rampart and external ditch, enclosing 0.25 hectares. The rampart is still visible and the ditch on the east side is used as a trackway. There was a defended settlement above the main site.
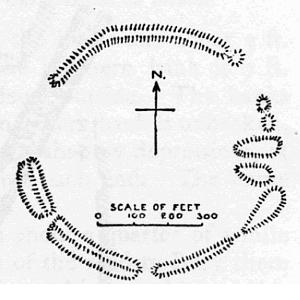
Elworthy Barrows is an unfinished Iron Age hill fort, rather than Bronze Age barrows, which is designated a scheduled ancient monument (No:188401). It is located in the civil parish of Brompton Ralph near Wiveliscombe, Somerset, England. It covers an area of 3.5 hectares and is surrounded by a bank and ditch.

Stantonbury Camp is the site of an Iron Age hill fort near Stanton Prior within the parish of Marksbury in Somerset, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument.

King's Castle is a Neolithic hillfort 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) east of Wiveliscombe in Somerset, England. It is surrounded by two banks with a ditch between them. The inner wall ranges up to 2.5 metres (8.2 ft) high and the outer wall gets up to 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) high. Arrowheads, scrapers, and borers have been found at the site. A coin hoard of 1139 coins was found in a pot buried 0.30 metres (1 ft) deep.

Curdon Camp is a univallate Iron Age hill fort in the West Somerset district of Somerset, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument.

Roddenbury Hillfort is a univallate Iron Age hillfort in the parish of Selwood, Somerset, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument and on the Heritage at Risk Register. It is close to the later Hales Castle.

Taps Combe Camp is an Iron Age hill fort in North Somerset, England. The hill fort is situated approximately 1.8 miles (2.9 km) east from the village of Brockley. The hill fort is shaped a lot like a "D", and is approximately 50 metres (160 ft) by 50 metres (160 ft) wide.

Highbury Hill in Clutton, Somerset, England is the site of the earthwork remains of an Iron Age univallate hillfort. It occupies an area of woodland at the end of a narrow ridge. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument, meaning that it is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.

Tunley Camp is an vallate Iron Age hill fort situated approximately 0.8 miles (1.3 km) north-east from the small village of Camerton in the Bath and North East Somerset district of Somerset, England. The hill fort comprises the slight earthwork remains of a univallate Iron Age hillfort which now nearly ploughed down.

Wain's Hill is an univallate Iron Age hill fort situated approximately 1 mile (1.6 km) south-west from the town of Clevedon in the North Somerset district of Somerset, England. The hillfort is defined by a steep, natural slope from the south and north with two ramparts to the east.

Berry Castle is an early Roman hillslope enclosure in the West Somerset district of Somerset, England. The hill fort is situated approximately 3.2 miles (5.1 km) west from the village of Luccombe. A series of earthworks survive in Berry Castle; it dates from the late Iron Age or early Romano British period. It has been scheduled as an ancient monument.

Broomfield Camp is a univallate Iron Age hill fort in the Taunton Deane district of Somerset, England. The hill fort is situated approximately 0.6 miles (0.97 km) south-east from the village of Broomfield. Broomfield Camp dates from late prehistoric or Roman times. The camp was searched in 1968 and the result uncovered a trench through a bank and ditch which produced Iron Age pottery.

Castles Camp is a univallate Iron Age hill fort in the Taunton Deane district of Somerset, England. The hill fort is situated approximately 1 mile (1.6 km) west from the village of Bathealton. A few trees a scattered around the camp's defences along with Roman coins being found in previous years.












