
Priapulida, sometimes referred to as penis worms, is a phylum of unsegmented marine worms. The name of the phylum relates to the Greek god of fertility, because their general shape and their extensible spiny introvert (eversible) proboscis may resemble the shape of a human penis. They live in the mud and in comparatively shallow waters up to 90 metres (300 ft) deep. Some species show a remarkable tolerance for hydrogen sulfide and anoxia. They can be quite abundant in some areas. In an Alaskan bay as many as 85 adult individuals of Priapulus caudatus per square meter has been recorded, while the density of its larvae can be as high as 58,000 per square meter.

The Maotianshan Shales are a series of Early Cambrian deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their Konservat Lagerstätten, deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.
Markuelia is a genus of fossil worm-like bilaterian animals allied to Ecdysozoa and known from strata of Lower Cambrian to Lower Ordovician age containing five species.

Ottoia is a stem-group archaeopriapulid worm known from Cambrian fossils. Although priapulid-like worms from various Cambrian deposits are often referred to Ottoia on spurious grounds, the only clear Ottoia macrofossils come from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, which was deposited 508 million years ago. Microfossils extend the record of Ottoia throughout the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin, from the mid- to late- Cambrian. A few fossil finds are also known from China.
Fieldia is a genus of worms known from the Cambrian Burgess Shale, and assigned to the priapulids. It was originally interpreted as an arthropod; its trunk bears a dense covering of spines, and its proboscis is small. It fed on sea-floor mud, evidenced by the frequent presence of sediments preserved in its gut.

Facivermis is a genus of sessile lobopodian from the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shales of China

Ancalagon minor is an extinct priapulid worm known from the Cambrian Burgess Shale.
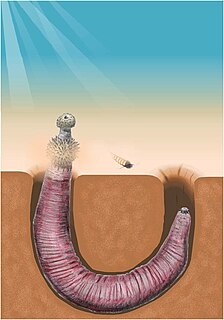
Archaeopriapulida is a group of priapulid-like worms known from Cambrian lagerstätte. The group is closely related to, and very similar to, the modern Priapulids. It is unclear whether it is mono- or polyphyletic. Despite a remarkable morphological similarity to their modern cousins, they fall outside of the priapulid crown group, which is not unambiguously represented in the fossil record until the Carboniferous. They are probably closely related or paraphyletic to the palaeoscolecids; the relationship between these basal worms is somewhat unresolved.

The palaeoscolecids are a group of extinct ecdysozoan worms resembling armoured priapulids. They are known from the Lower Cambrian to the late Silurian; they are mainly found as disarticulated sclerites, but are also preserved in many of the Cambrian lagerstätten. They take their name from the typifying genus Palaeoscolex. Other genera include Cricocosmia from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang biota.
Cambrorhytium is an enigmatic fossil genus known from the Latham Shale (California), and the Chengjiang (China) and Burgess Shale lagerstätte. 350 specimens of Cambrorhytium are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.7% of the community.

Selkirkia is a genus of predatory, tubicolous priapulid worms known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale, Ogygopsis Shale and Puncoviscana Formation. 142 specimens of Selkirkia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.27% of the community. In the Burgess Shale, 20% of the tapering, organic-walled tubes are preserved with the worm inside them, whereas the other 80% are empty. Whilst alive, the tubes were probably vertical, whereas trilobite-occupied tubes are horizontal.
Eolympia is interpreted as an extinct monospecific genus of sea anemone which existed in what is now Ningqiang, Shaanxi Province, China during the lower Cambrian period. Its fossils have been recovered from the Kuanchuanpu Formation. The pedicle is long, suggesting the animal engaged in sexual intercourse, though marked perforations imply that reproduction by transverse fission was also quite likely as a more primitive backup.

Omnidens amplus, meaning "large all-tooth", is an extinct species of large Cambrian animal known only from a series of large mouth apparatus, originally mistaken as the mouthparts of anomalocaridids. When first named, it was interpreted as a giant priapulid, but is now considered a panarthropod. Its mouth apparatus closely resembles that of the smaller gilled lobopodian Pambdelurion, indicating it is likely to have been a close relative of that species, with which it may be synonymous. With a maximum estimated body length of 1.5 metres (4.9 ft), Omnidens is the largest known free-living Cambrian organism. Omnidens fossils are found in the Maotianshan Shales.

Small carbonaceous fossils (SCFs) are sub-millimetric organic remains of organisms preserved in sedimentary strata.
Archotuba is a genus of elongated conical tubes that were seemingly deposited by colonial organisms. Known from the Chengjiang, its biological affinity is uncertain; it somewhat resembles the tubes of the 'priapulid' Selkirkia, but a cnidarian affinity is also possible. In the absence of soft parts, there really isn't enough data to confirm a biological affiliation.

Xiaoheiqingella is a taxon of priapulid known from the Chengjiang biota; synonymous with Yunnanpriapulus, and thought to belong to the priapulid crown group.

Sicyophorus is a genus of archaeopriapulid known from the Chengjiang biota; synonymous with Protopriapulites haikouensis.

Paraselkirkia is a genus of archaeopriapulid known from the Chengjiang biota, resembling Selkirkia.

Iotuba chengjiangensis is a Cambrian fossil with a U-shaped gut and tentacles, known from the Chengjiang biota. Originally interpreted as a phoronid marine animal, its affinity is currently disputed. It, and the possibly-synonymous taxon Eophoronis, resemble the 'priapulid' Louisella.
Olivooides is an extinct, sphere-shaped microfossil from Cambrian strata. Fossils are currently known only from China. Olivooides was approximately 600‐870 μm in diameter. It was an egg with a large yolk content. Fossils from Shaanxi, China can be found in the cleavage, gastrulation, organogenesis, cuticularization, pre‐hatching, post‐hatching and subsequent growth stages of development. This fossil is a result of soft-bodied preservation. Olivooides has pentaradial symmetry and is usually preserved by calcium phosphate endocast. The internal structure is rarely preserved. It has no larval stage, so it likely had a quick and direct development.














