
Rheidae is a family of flightless ratite birds which first appeared in the Paleocene. It is today represented by the sole living genus Rhea, but also contains several extinct genera.

The Octopodidae comprise the family containing the majority of known octopus species.

Alcide Charles Victor Marie Dessalines d'Orbigny was a French naturalist who made major contributions in many areas, including zoology, palaeontology, geology, archaeology and anthropology.
Baron Nöel Frédéric Armand André de Lafresnaye was a French ornithologist and collector.
The Toarcian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, an age and stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic. It spans the time between 182.7 Ma and 174.1 Ma. It follows the Pliensbachian and is followed by the Aalenian.
In the geologic timescale, the Sinemurian is an age and stage in the Early or Lower Jurassic epoch or series. It spans the time between 199.3 ± 2 Ma and 190.8 ± 1.5 Ma. The Sinemurian is preceded by the Hettangian and is followed by the Pliensbachian.

Octopus is the largest genus of octopuses, comprising more than 100 species. These species are widespread throughout the world's oceans. Many species formerly placed in the genus Octopus are now assigned to other genera within the family Octopodidae.

Trochus is a genus of medium-sized to large, top-shaped sea snails with an operculum and a pearly inside to their shells, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Chlorostoma is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Tegulidae.

Rissoinidae is a large family of very small and minute sea snails with an operculum, marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Littorinimorpha. Several genera that were previously part of Rissoinidae have been assigned to the Zebinidae family.
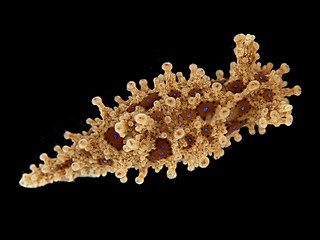
Aegires punctilucens is a species of sea slug. It is a dorid nudibranch, a shell-less marine gastropod mollusc in the family Aegiridae.

Cupulina is an extinct genus of sea sponges belonging to the class Demospongiae.

Montlivaltiidae is an extinct family of stony corals.

Louis Édouard Gourdan de Fromentel was a French physician and paleontologist known for his study of fossil coral polyps and sponges.
Comophyllia is an extinct genus of prehistoric stony corals in the family Latomeandridae. Species are known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous. C. elegans, the type species, is from the Jurassic of France.

Cuneolina is an extinct genus of prehistoric foraminifera in the family Cuneolinidae with species from the Jurassic and Cretaceous.

Cupulospongia is an extinct genus of sea sponges from the Cretaceous of France.
Mitra subscrobiculata is an extinct species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk, in the family Mitridae, the miters or miter snails.
















