
Centipedes are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda of the subphylum Myriapoda, an arthropod group which also includes millipedes and other multi-legged creatures. Centipedes are elongated metameric creatures with one pair of legs per body segment. Most centipedes are generally venomous and can inflict painful bites, injecting their venom through pincer-like appendages known as forcipules. Despite the name, centipedes can have a varying number of legs, ranging from 30 to 354. Centipedes always have an odd number of pairs of legs. Therefore, no centipede has exactly 100 legs. Like spiders and scorpions, centipedes are predominantly carnivorous.

The Lumbricidae are a family of earthworms which doesn't include the earthworm species well-known to Europeans. About 33 lumbricid species have become naturalized around the world, but the bulk of the species are in the Holarctic region: from Canada and the United States and throughout Eurasia to Japan. An enigmatic species in Tasmania is Eophila eti. Currently, 670 valid species and subspecies in about 42 genera are recognized.

Oligochaeta is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworms, and freshwater or semiterrestrial microdrile forms, including the tubificids, pot worms and ice worms (Enchytraeidae), blackworms (Lumbriculidae) and several interstitial marine worms.

The Megascolecidae are a large family of earthworms which has native representatives in Australia, New Zealand, both Southeast and East Asia, and North America. The most ancient lineages of the family show a Gondwanan distribution and have been used as evidence of continental drift. Members of the Pheretima group of genera are widely distributed around the tropics, much as some Lumbricidae are distributed through the temperate zones. Some North American native genera – e.g., Arctiostrotus, Argilophilus and Driloleirus – also belong to this family.
Sparganophilus, the only genus in the family Sparganophilidae, is a group of long, slender, limicolous (mud-dwelling) earthworms native to North America. The number of species is unknown, most of them are undescribed, throughout the continent and into Central America. One species, S. tamesis, has been introduced into the streams of Europe, where it is now widespread; its synonyms are S. eiseni, S. benhami, S. guatemalensis, S. carnea, S. elongatus, S. cuenoti and, newly, S. langi.
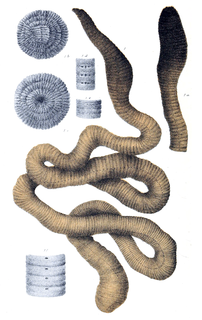
The giant Gippsland earthworm, Megascolides australis, is one of Australia's 1,000 native earthworm species. It is also commonly known as karmai, taken from the Boonwurrung language.
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, is the condition of a species that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.

Sternotherus odoratus is a species of small turtle in the family Kinosternidae. The species is native to southeastern Canada and much of the Eastern United States. It is also known commonly as the common musk turtle, eastern musk turtle, or stinkpot due to its ability to release a foul musky odor from scent glands on the edge of its shell, possibly to deter predation. This turtle is grouped in the same family as mud turtles.
The Eudrilidae are a family of earthworms, mostly of Africa. One species, Eudrilus eugeniae, is widely distributed around the warmer parts of the world and historically cultured as the "African nightcrawler".

The yellow mud turtle, also commonly known as the yellow-necked mud turtle, is a species of mud turtle in the family Kinosternidae. The species is endemic to the Central United States and Mexico.

The Magellanic oystercatcher is a species of wader in the family Haematopodidae. It is found in Argentina, Chile and the Falkland Islands in freshwater lake and sandy shore habitats.
The Oregon giant earthworm is one of the largest earthworms found in North America, growing to more than three feet in length. First described in 1937, the species is not common. Since its discovery, specimens have been documented in only fifteen locations within Oregon's Willamette Valley.

Rhamnus cathartica, the European buckthorn, common buckthorn, purging buckthorn, or just buckthorn, is a species of small tree in the flowering plant family Rhamnaceae. It is native to Europe, northwest Africa and western Asia, from the central British Isles south to Morocco, and east to Kyrgyzstan. It was introduced to North America as an ornamental shrub in the early 19th century or perhaps before, and is now naturalized in the northern half of the continent, and is classified as an invasive plant in several US states and in Ontario, Canada.

Pheretima is a genus of earthworms found mostly in New Guinea and parts of Southeast Asia.
The Acanthodrilidae are an ancient and widely distributed family of earthworms which has native representatives in Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, South America, and North America. No native species are known from India nor Asia. The family possibly shows a pre-Pangaean distribution.

Pollenia rudis, the common cluster fly, is a species of fly in the family Polleniidae. Pollenia rudis is also known as the attic fly, the loft fly, pollenie du lombric [French], and the buckwheat fly. During the autumn and winter months, Pollenia rudis can be found overwintering inside attics or lofts. This sluggish species can be found “clustering” near the interior windows of a warm structure.

An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan, are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation, and usually have setae on all segments. They occur worldwide where soil, water, and temperature allow. Earthworms are commonly found in soil, eating a wide variety of organic matter. This organic matter includes plant matter, living protozoa, rotifers, nematodes, bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms. An earthworm's digestive system runs the length of its body. It respires through its skin. It has a double transport system made of coelomic fluid that moves within the fluid-filled coelom and a simple, closed circulatory system. It has a central and peripheral nervous system. Its central nervous system consists of two ganglia above the mouth, one on either side, connected to a nerve running along its length to motor neurons and sensory cells in each segment. Large numbers of chemoreceptors concentrate near its mouth. Circumferential and longitudinal muscles edging each segment let the worm move. Similar sets of muscles line the gut, and their actions move digesting food toward the worm's anus.

Invasive species of earthworms from the suborder Lumbricina have been expanding their range in North America. Their introduction can have marked effects on the nutrient cycles in temperate forests. These earthworms increase the cycling and leaching of nutrients by breaking up decaying organic matter and spreading it into the soil. Since plants native to these northern forests are evolutionarily adapted to the presence of thick layers of decaying organic matter, the introduction of worms can lead to loss of biodiversity as young plants face less nutrient-rich conditions. Some species of trees and other plants may be incapable of surviving such changes in available nutrients. This change in the plant diversity in turn affects other organisms and often leads to increased invasions of other exotic species as well as overall forest decline. They do not require a mate to reproduce, allowing them to spread faster.
Earthworms are invasive species throughout the world. Of a total of about 6,000 species of earthworm, about 120 species are widely distributed around the globe. These are the peregrine or cosmopolitan earthworms. Some of these are invasive species in many regions.
Amynthas mekongianus, the Mekong worm or Mekong giant earthworm, previously known as Megascolex mekongianus, is a species of earthworm in the family Megascolecidae. It is native to the vicinity of the River Mekong in southeastern Asia and may have more than 500 segments and grow to a length of 2.9 m (10 ft).












