
The Chicago Transit Authority (CTA) is the operator of mass transit in Chicago, Illinois, and some of its surrounding suburbs, including the trains of the Chicago 'L' and CTA bus service.

The Oyster card is a payment method for public transport in London in the United Kingdom. A standard Oyster card is a blue credit-card-sized stored-value contactless smart card. It is promoted by Transport for London (TfL) and can be used on travel modes across London including London Underground, London Buses, the Docklands Light Railway (DLR), London Overground, Tramlink, some river boat services, and most National Rail services within the London fare zones. Since its introduction in June 2003, more than 86 million cards have been used.

A ticket machine, also known as a ticket vending machine (TVM), is a vending machine that produces paper or electronic tickets, or recharges a stored-value card or smart card or the user's mobile wallet, typically on a smartphone. For instance, ticket machines dispense train tickets at railway stations, transit tickets at metro stations and tram tickets at some tram stops and in some trams. Token machines may dispense the ticket in the form of a token which has the same function as a paper or electronic ticket. The typical transaction consists of a user using the display interface to select the type and quantity of tickets and then choosing a payment method of either cash, credit/debit card or smartcard. The ticket(s) are then printed on paper and dispensed to the user, or loaded onto the user's smartcard or smartphone.
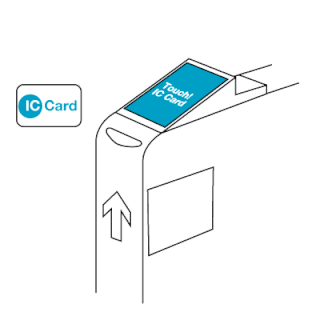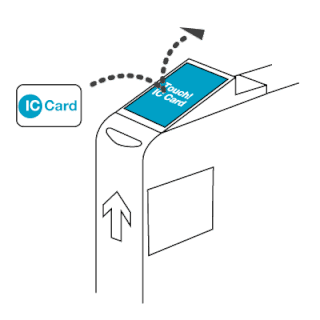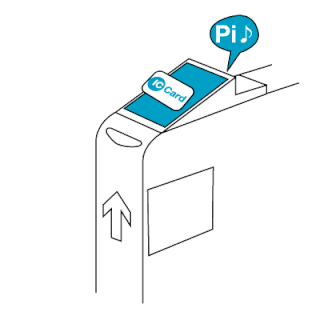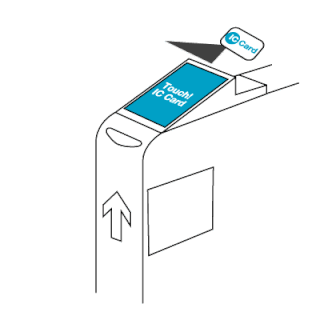
The EZ-Link card is a rechargeable contactless smart card and electronic money system that is primarily used as a payment method for public transport such as bus and rail lines in Singapore. A standard EZ-Link card is a credit-card-sized stored-value contact-less smart-card that comes in a variety of colours, as well as limited edition designs. It is sold by TransitLink Pte Ltd, a subsidiary of the Land Transport Authority (LTA), and can be used on travel modes across Singapore, including the Mass Rapid Transit (MRT), the Light Rapid Transit (LRT), public buses which are operated by SBS Transit, SMRT Buses, Tower Transit Singapore and Go-Ahead Singapore, as well as the Sentosa Express.

The Clipper card is a reloadable contactless smart card used for automated fare collection in the San Francisco Bay Area. First introduced as TransLink in 2002 by the Metropolitan Transportation Commission (MTC) as a pilot program, it was rebranded in its current form on June 16, 2010. Like other transit smart cards such as the Oyster card, the Clipper card is a credit card-sized stored-value card capable of holding both cash value and transit passes for the participating transit agencies. In addition to the traditional plastic card, Clipper is available as a virtual card in Google Pay and Apple Wallet. Clipper is accepted by nearly all public transit services in the Bay Area, including Muni, BART, Caltrain, AC Transit, SamTrans, Golden Gate Transit, Golden Gate Ferry, San Francisco Bay Ferry, VTA, and many others.

The Presto card is a contactless smart card automated fare collection system used on participating public transit systems in the province of Ontario, Canada, specifically in Greater Toronto, Hamilton, and Ottawa. Presto card readers were implemented on a trial basis from June 25, 2007, to September 30, 2008. Full implementation began in November 2009 and it was rolled out across rapid transit stations, railway stations, bus stops and terminals, and transit vehicles on eleven different transit systems.
The Chicago Card and the Chicago Card Plus were contactless smart cards used by riders of the Chicago Transit Authority (CTA) and Pace to electronically pay for bus and train fares in the city of Chicago, Illinois, USA and the surrounding suburbs. On June 1, 2014, CTA and Pace stopped accepting these cards as part of a transition to Ventra.

Contactless payment systems are credit cards and debit cards, key fobs, smart cards, or other devices, including smartphones and other mobile devices, that use radio-frequency identification (RFID) or near field communication for making secure payments. The embedded integrated circuit chip and antenna enable consumers to wave their card, fob, or handheld device over a reader at the point of sale terminal. Contactless payments are made in close physical proximity, unlike other types of mobile payments which use broad-area cellular or WiFi networks and do not involve close physical proximity.

get me there is an electronic ticketing scheme under development by Transport for Greater Manchester (TfGM) for use on public transport services in Greater Manchester, England. It was first announced and confirmed as an integrated travel card, comparable to London's Oyster card, for Greater Manchester in June 2012, following a bid from the Greater Manchester Combined Authority.
A transit pass or travel card, often referred to as a bus pass or train pass etc., is a ticket that allows a passenger of the service to take either a certain number of pre-purchased trips or unlimited trips within a fixed period of time.
The go card is an electronic smartcard ticketing system developed by Cubic Corporation, which is currently used on the TransLink public transport network in South East Queensland. To use the go card, users hold the card less than 10 cm away from the reader to "touch on" before starting a journey, and must do the same to "touch off" the service at the end of the journey. The cost of each journey is deducted from the go card balance.

The EASY Card system is a series of linked contactless smartcard systems used by Miami-Dade Transit and South Florida Regional Transportation Authority in the South Florida area. The Easy Card allows for electronic payment on multiple public transport systems including Miami Metrorail, rapid transit rail system; Tri-Rail, commuter rail system; and Metrobus. Other public transportation agencies in the South Florida area which may eventually join the system include Broward County Transit as well as Palm Tran.

Opal is a contactless fare collection system for public transport services in the greater Sydney area and most other urban areas of New South Wales, Australia. Operation of the Opal system is managed by the New South Wales Government's transport authority, Transport for NSW. First launched in late 2012, Opal is valid on Transport for NSW's metro, train, bus, ferry and light rail services that operate in Sydney and the neighbouring Central Coast, Hunter Region, Blue Mountains, Illawarra and Southern Highlands areas. Opal equipment was designed from the start to support a variety of cards, but launched with the captive Opal cards.
Cubic Corporation is an American public transportation and defense corporation. It operates two business segments, Cubic Transportation Systems and Cubic Mission and Performance Solutions, respectively.
CIPURSE is an open security standard for transit fare collection systems. It makes use of smart card technologies and additional security measures.

An automated fare collection (AFC) system is the collection of components that automate the ticketing system of a public transportation network - an automated version of manual fare collection. An AFC system is usually the basis for integrated ticketing.

Contactless smartcards are being progressively introduced as an alternative option to paper ticketing on the National Rail system of Great Britain. Tickets for use on National Rail services can be loaded onto any ITSO card.

Ventra is an electronic fare payment system for the Chicago Transit Authority (CTA), Metra, and Pace, which replaced the Chicago Card and the Transit Card automated fare collection systems. Ventra launched in August 2013, with a full system transition occurring in July 2014. The payment system includes several options of payment, including a contactless smart card powered by RFID, a single day or use ticket powered by RFID, any personal bank-issued credit card or debit card that has an RFID chip, and a compatible mobile phone. Ventra is operated by Cubic Transportation Systems. A smartphone app allows users to manage fares, buy passes, and buy mobile tickets for Metra.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) is a type of service that through a joint digital channel enables users to plan, book, and pay for multiple types of mobility services. The concept describes a shift away from personally-owned modes of transportation and towards mobility provided as a service. This is enabled by combining transportation services from public and private transportation providers through a unified gateway that creates and manages the trip, which users can pay for with a single account. Users can pay per trip or a monthly fee for a limited distance. The key concept behind MaaS is to offer travelers mobility solutions based on their travel needs. Specialist urban mobility applications are also expanding their offerings to enable MaaS, such as Transit, Uber and Lyft.













