
Asia is Earth's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the Eastern and Northern Hemispheres. It shares the continental landmass of Eurasia with the continent of Europe and the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. Asia covers an area of 44,579,000 square kilometres (17,212,000 sq mi), about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Asia is notable for not only its overall large size and population, but also dense and large settlements, as well as vast barely populated regions. Its 4.5 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population.

The Berlin Wall was a guarded concrete barrier that physically and ideologically divided Berlin from 1961 to 1989. Construction of the Wall was commenced by the German Democratic Republic on 13 August 1961. The Wall cut off West Berlin from surrounding East Germany, including East Berlin. The barrier included guard towers placed along large concrete walls, accompanied by a wide area that contained anti-vehicle trenches, beds of nails, and other defenses. The Eastern Bloc portrayed the Wall as protecting its population from fascist elements conspiring to prevent the "will of the people" from building a socialist state in East Germany.

EastEnders is a British soap opera created by Julia Smith and Tony Holland which has been broadcast on BBC One since 1985. Set in Albert Square in the East End of London in the fictional borough of Walford, the programme follows the stories of local residents and their families as they go about their daily lives. Initially there were two 30-minute episodes per week, later increasing to three, but since 2001, episodes have been broadcast on every weekday except Wednesday. On 18 March 2020, BBC made the decision to suspend production of the programme until further notice, in addition to reducing the broadcast frequency to two 30-minute episodes per week. This was due to the 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic with the reduced broadcast frequency being a temporary measure to preserve the ongoing broadcast of filmed episodes.

East Pakistan was the eastern provincial wing of Pakistan between 1955 and 1971, covering the territory of the modern country Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Burma, with a coastline on the Bay of Bengal. East Pakistanis were popularly known as 'Pakistani Bengalis' and also to differ this region from India's state West Bengal East Pakistan was known as 'Pakistani Bengal'.

East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic, was a state that existed from 1949 to 1990, the period when the eastern portion of Germany was part of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state in English usage, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state". It consisted of territory that was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR.

Jerusalem is a city in the Middle East, located on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the oldest cities in the world, and is considered holy to the three major Abrahamic religions—Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israel and the Palestinian Authority claim Jerusalem as their capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power; however, neither claim is widely recognized internationally.

The Levant is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, it is equivalent to the historical region of Syria, which included present-day Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Palestine and most of Turkey south-east of the middle Euphrates. In its widest historical sense, the Levant included all of the Eastern Mediterranean with its islands; that is, it included all of the countries along the Eastern Mediterranean shores, extending from Greece to Cyrenaica in eastern Libya.

The Middle East is a transcontinental region which includes most of Western Asia, Iran and all of Egypt. The term has come into wider usage as a replacement of the term Near East beginning in the early 20th century. The broader concept of the "Greater Middle East" also adds the Maghreb, Sudan, Djibouti, Somalia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and sometimes even Central Asia and Transcaucasia into the region. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions.

Southeast Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the regions that are geographically south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent and north-west of Australia. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia and the Indian Ocean. The region is the only part of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere, although the majority of it is in the Northern Hemisphere. In contemporary definition, Southeast Asia consists of two geographic regions:
- Mainland Southeast Asia, also known historically as Indochina, comprising Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam.
- Maritime Southeast Asia, also known historically as Nusantara, the East Indies, or the Malay Archipelago, comprising the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (India), Ashmore and Cartier Islands (Australia), Brunei, Christmas Island (Australia), the Cocos (Keeling) Islands (Australia), East Malaysia, East Timor, Indonesia, the Philippines and Singapore.

West Berlin was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. There was no specific date on which the sectors of Berlin occupied by the Western Allies became "West Berlin", but 1949 is widely accepted as the year in which the name was adopted. West Berlin aligned itself politically with the Federal Republic of Germany and was directly or indirectly represented in its federal institutions.

The East India Company (EIC), also known as the Honourable East India Company (HEIC), East India Trading Company (EITC), the English East India Company or the British East India Company, and informally known as John Company, Company Bahadur, or simply The Company, was an English and later British joint-stock company. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the Moghuls of India and the East Indies, and later with Qing China. The company ended up seizing control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent - and briefly Afghanistan, colonised parts of Southeast Asia, and colonised Hong Kong after the First Opium War.

East Anglia is a geographical area in the East of England. The area included has varied but the legally defined NUTS 2 statistical unit comprises the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, including the City of Peterborough unitary authority area. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a tribe whose name originated in Anglia, northern Germany.

German reunification was the process in 1990 in which the German Democratic Republic became part of the Federal Republic of Germany to form the reunited nation of Germany, as provided by Article 23 of the FRG's then constitution. The end of the unification process is officially referred to as German unity, celebrated each year on 3 October as German Unity Day. Berlin was reunited into a single city, and was once again designated as the capital of united Germany.

The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Eastern United States meets the North Atlantic Ocean. Regionally, the term refers to the coastal states and area east of the Appalachian Mountains that have shoreline on the Atlantic Ocean, from north to south, Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida.

The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages, a sub-family of the Indo-European languages, along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is also referred to as the "Nordic languages", a direct translation of the most common term used among Danish, Faroese, Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish scholars and laypeople.

Assyrians are an ethnic group indigenous to Mesopotamia, a region in the Middle East. Some self-identify as Syriacs, Arameans, and Chaldeans. Speakers of the Neo-Aramaic branch of Semitic languages as well as the primary languages in their countries of residence, modern Assyrians are Syriac Christians who claim descent from Assyria, one of the oldest civilizations in the world, dating back to 2500 BC in ancient Mesopotamia.
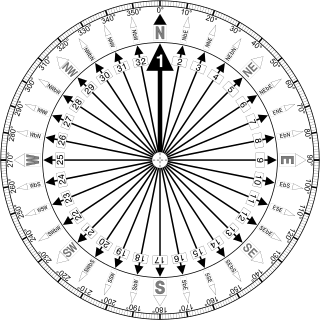
The points of the compass are the vectors by which planet-based directions are conventionally defined. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional vectors. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 'points'.

The Bangladesh Liberation War, also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh, was a revolution and armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in what was then East Pakistan during the 1971 Bangladesh genocide. It resulted in the independence of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The war began after the Pakistani military junta based in West Pakistan launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971. It pursued the systematic elimination of nationalist Bengali civilians, students, intelligentsia, religious minorities and armed personnel. The junta annulled the results of the 1970 elections and arrested Prime minister-designate Sheikh Mujibur Rahman. The war ended on 16 December 1971 after West Pakistan surrendered.

East Timor or Timor-Leste, officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is a country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the nearby islands of Atauro and Jaco, and Oecusse, an exclave on the northwestern side of the island surrounded by Indonesian West Timor. Australia is the country's southern neighbour, separated by the Timor Sea. The country's size is about 15,007 km2.

East Asia is the eastern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of China, Hong Kong, Macau, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan. The East Asian states China, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan are all unrecognized by at least one other East Asian state. Hong Kong and Macau are officially highly autonomous but are under effective Chinese sovereignty. North Asia borders East Asia's north, Southeast Asia the south, South Asia the southwest, and Central Asia the west. To the east is the Pacific Ocean, and to the southeast is Micronesia.




















