
Drosera peltata, commonly called the shield sundew or pale sundew, is a climbing or scrambling perennial tuberous species in the carnivorous plant genus Drosera. Among the tuberous sundews, D. peltata has the largest distribution, which includes eastern and western Australia, New Zealand, India, and most of Southeast Asia including the Philippines. The specific epithet is Latin for "shield shaped", a reference to the shape of the cauline leaves. It is either a single extremely variable species, or a complex of several closely related species of uncertain taxonomic boundaries. In Australia at least four forms have had or still have specific taxonomic recognition: Drosera peltata subsp. peltata, D. peltata subsp. auriculata, D. foliosa and D. gracilis.

Fuchsia magellanica, commonly known as the hummingbird fuchsia or hardy fuchsia, is a species of flowering plant in the evening primrose family Onagraceae, native to the lower Southern Cone of southern South America.
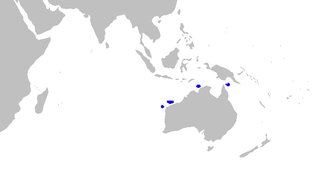
The slender sawtail catshark is a little-known species of catshark, part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to northern Australia. It is found over the continental slope in 290–470 m (950–1,540 ft) on water. Growing to 34 cm (13 in) long, this shark has a slim gray body with four dark saddle markings below the dorsal fins and on the caudal fin, as well as a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the dorsal edge of the caudal fin. The slender sawtail catshark is not valued by fisheries but is taken as bycatch. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) presently lacks enough information to assess its conservation status.

The western spotted skunk is a spotted skunk of western North America.
The slender rainbowfish is a species of rainbowfish in the subfamily Melanotaeniinae which is endemic to Australia. It occurs in the extreme north of Western Australia in the systems of the Drysdale and King Edward Rivers.

Stirlingia, commonly known as blueboy, is a genus of 7 species in the family Proteaceae, all of which are endemic to Western Australia.

Stirlingia latifolia, commonly known as blueboy, is a plant endemic to Western Australia.
Citrus gracilis, the Humpty Doo lime or Kakadu lime, is a straggly shrub endemic to eucalypt savannah woodlands of Northern Territory, Australia.

Wahlenbergia gracilis, common name Australian bluebell, is an Asian wildflower from the family Campanulaceae. It also grows on western Pacific Ocean islands.
The northern yellow-black triplefin, also known as the northern Australian yellow-black triplefin, is a species of triplefin blenny in the genus Enneapterygius. It was described by German Ichthyologist Ronald Fricke in 1994. It is a tropical blenny, endemic to northern Australia, in the western Pacific and southeastern Indian Oceans. It is a non-migratory species which dwells in shallow tidal pools on coralline rock and in seagrass, and has been recorded swimming at a depth range of 0–15 m (0–50 ft). Male northern yellow-black triplefins can reach a maximum length of 2.8 centimetres.

Cyathostemon is a genus of flowering plants in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. The genus is endemic to southwestern Western Australia. The genus was first described by Nikolai Turczaninow in 1852. Species include:

Eucalyptus gracilis, commonly known as yorrell or white mallee, is a species of mallee or small tree endemic to Australia, where it is found in south-western New South Wales], Victoria, South Australia and Western Australia. It has smooth white bark, usually with rough, fibrous or flaky bark on the lower stems, linear to narrow lance-shaped adult leaves, flower buds in group of between seven and eleven and cup-shaped, cylindrical or barrel-shaped fruit.
Verticordia gracilis is a flowering plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a low shrub with small leaves and rounded groups of fluffy pale to deep pink flowers in late spring or early summer, following rain.

Cyathostemon ambiguus is a member of the family Myrtaceae endemic to Western Australia.

Cyathostemon blackettii is a member of the family Myrtaceae endemic to Western Australia.
Cyathostemon divaricatus is a member of the family Myrtaceae endemic to Western Australia.

Cyathostemon heterantherus is a member of the family Myrtaceae endemic to Western Australia.
Cyathostemon verrucosus is a member of the family Myrtaceae endemic to Western Australia.

Xanthorrhoea gracilis, commonly known as the graceful grasstree, grassboy or mimidi, is a species of grasstree of the genus Xanthorrhoea native to Western Australia.

Leucopogon gracilis is a shrub in the family Ericaceae found in Western Australia.












