
Sago is a starch extracted from the pith, or spongy core tissue, of various tropical palm stems, especially those of Metroxylon sagu. It is a major staple food for the lowland peoples of New Guinea and the Maluku Islands, where it is called saksak, rabia and sagu. The largest supply of sago comes from Southeast Asia, particularly Indonesia and Malaysia. Large quantities of sago are sent to Europe and North America for cooking purposes. It is traditionally cooked and eaten in various forms, such as rolled into balls, mixed with boiling water to form a glue-like paste (papeda), or as a pancake.

Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male or female. Cycads vary in size from having trunks only a few centimeters to several meters tall. They typically grow slowly and have long lifespans. Because of their superficial resemblance to palms or ferns, they are sometimes mistaken for them, but they are not closely related to either group. Cycads are gymnosperms (naked-seeded), meaning their unfertilized seeds are open to the air to be directly fertilized by pollination, as contrasted with angiosperms, which have enclosed seeds with more complex fertilization arrangements. Cycads have very specialized pollinators, usually a specific species of beetle. Both male and female cycads bear cones (strobili), somewhat similar to conifer cones.
Gyromitrin is a toxin and carcinogen present in several members of the fungal genus Gyromitra, like G. esculenta. Its formula is C4H8N2O. It is unstable and is easily hydrolyzed to the toxic compound monomethylhydrazine CH3NHNH2. Monomethylhydrazine acts on the central nervous system and interferes with the normal use and function of vitamin B6. Poisoning results in nausea, stomach cramps, and diarrhea, while severe poisoning can result in convulsions, jaundice, or even coma or death. Exposure to monomethylhydrazine has been shown to be carcinogenic in small mammals.

In excitotoxicity, nerve cells suffer damage or death when the levels of otherwise necessary and safe neurotransmitters such as glutamate become pathologically high, resulting in excessive stimulation of receptors. For example, when glutamate receptors such as the NMDA receptor or AMPA receptor encounter excessive levels of the excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate, significant neuronal damage might ensue. Excess glutamate allows high levels of calcium ions (Ca2+) to enter the cell. Ca2+ influx into cells activates a number of enzymes, including phospholipases, endonucleases, and proteases such as calpain. These enzymes go on to damage cell structures such as components of the cytoskeleton, membrane, and DNA. In evolved, complex adaptive systems such as biological life it must be understood that mechanisms are rarely, if ever, simplistically direct. For example, NMDA, in subtoxic amounts, can block glutamate toxicity and thereby induce neuronal survival.

Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exponentially to form blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they can poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning.

Zamia furfuracea is a species of cycad endemic to southeastern Veracruz state in eastern Mexico.

Cycas revoluta is a species of gymnosperm in the family Cycadaceae, native to southern Japan including the Ryukyu Islands. It is one of several species used for the production of sago, as well as an ornamental plant. The sago cycad can be distinguished by a thick coat of fibers on its trunk. The sago cycad is sometimes mistakenly thought to be a palm, although the only similarity between the two is that they look similar and both produce seeds.

Zamia is a genus of cycad of the family Zamiaceae, native to North America from the United States throughout the West Indies, Central America, and South America as far south as Bolivia. The genus is considered to be the most ecologically and morphologically diverse of the cycads, and is estimated to have originated about 68.3 million years ago.
Lytico-bodig (also Lytigo-bodig) disease, Guam disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia complex (ALS-PDC) is a neurodegenerative disease of uncertain etiology endemic to the Chamorro people of the island of Guam in Micronesia. Lytigo and bodig are Chamorro language words for two different manifestations of the same condition. ALS-PDC, a term coined by Asao Hirano and colleagues in 1961, reflects its resemblance to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease.
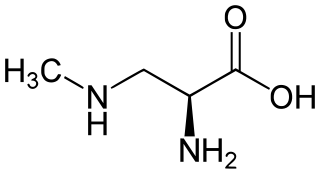
β-Methylamino-L-alanine, or BMAA, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid produced by cyanobacteria. BMAA is a neurotoxin. Its potential role in various neurodegenerative disorders is the subject of scientific research.

Cycas micronesica is a species of cycad found on the island of Yap in Micronesia, the Marianaislands of Guam and Rota, and The Republic of Palau. It is commonly known as federico nut or fadang in Chamorro. The species, previously lumped with Cycas rumphii and Cycas circinalis, was described as a unique species in 1994 by Ken Hill. Paleoecological studies have determined that Cycas micronesica has been present on the island of Guam for about 9,000 years. It has been implicated as a factor in Lytico-Bodig disease, a condition similar to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), due to the presence of the neurotoxin BMAA found in its seeds. Seeds were a traditional food source on Guam until the 1960s. The neurotoxin is present due to a symbiosis with cyanobacteria.

Macrozamia glaucophylla is a species of cycad from the genus Macrozamia and the family Zamiaceae. Endemic to New South Wales, Australia, this species has features that resembles palms, although both species are taxonomically quite different. The current population trend of Macrozamia glaucophylla is stable with 2,500 to 10,000 mature individuals. The species are found in several habitats including forest and savanna. Ecologically, Macrozamia glaucophylla lives in terrestrial system, a land-based community of organisms where the biotic and abiotic components interact in the given area.

Macrozamia heteromera is a species of cycad in the family Zamiaceae initially discovered by Charles Moore in 1858 and is endemic to New South Wales, Australia. It can be found in the north-western region of New South Wales within the Warrumbungle mountains and further south west towards the Coonabarabran district. It is a low trunked cycad usually at a height below 1 metre and can be found in dry sclerophyll woodlands. M. heteromera can be distinguished from the rest of the Macrozamia genus by its mid-green, narrow, usually divided pinnae and divided seedling pinnae. It is a plant that has toxic seeds and leaves, a characteristic common to cycads. However, after proper preparation and procedure, the seeds are fine for consumption.

Macrozamia miquelii, is a species of cycad in the plant family Zamiaceae. It is endemic to Queensland and New South Wales in Eastern Australia. Located within sclerophyll forests dominated by eucalyptus trees, the cycad grows on nutrient-poor soils. It is recognised within the Zamiaceae family for its, medium height at 1 m, intermediate size of male and female cones and lighter green leaves compared to other cycads within the plant family of Zamiaceae. The seeds have an orange red sarcotesta which attracts fauna consumption, allowing a mutualistic seed dispersal for the cycad. These seeds are also edible for human consumption if prepared correctly to remove the toxins.

Macrozamia riedlei, commonly known as a zamia or zamia palm, is a species of cycad in the plant family Zamiaceae. It is endemic to southwest Australia and often occurs in jarrah forests. It may only attain a height of half a metre or form an above trunk up to two metres with long arching fronds of a similar length. The giant cones amidst the crown of palm-like fronds contain edible seeds surrounded by red sarcotesta. The seeds are consumed by birds and animals, and can be a favoured part of the human diet when prepared correctly. M. riedlei benefits from a close association with bacteria that fix nitrogen, which also produce substances found throughout the plant that are toxic to some animals when consumed. The species is cultivated for ornamental use in urban and domestic environments.
In enzymology, a methyl-ONN-azoxymethanol beta-D-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Microbial toxins are toxins produced by micro-organisms, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, dinoflagellates, and viruses. Many microbial toxins promote infection and disease by directly damaging host tissues and by disabling the immune system. Endotoxins most commonly refer to the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or lipooligosaccharide (LOS) that are in the outer plasma membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. The botulinum toxin, which is primarily produced by Clostridium botulinum and less frequently by other Clostridium species, is the most toxic substance known in the world. However, microbial toxins also have important uses in medical science and research. Currently, new methods of detecting bacterial toxins are being developed to better isolate and understand these toxins. Potential applications of toxin research include combating microbial virulence, the development of novel anticancer drugs and other medicines, and the use of toxins as tools in neurobiology and cellular biology.
Zamia staggers is a fatal nervous disease affecting cattle in areas where they browse on the leaves or fruit of cycads—in particular, those of the genus Zamia. It is characterised by irreversible paralysis of the hind legs because of the degeneration of the spinal cord. It is caused by the toxins cycasin and macrozamin, β-glycosides of methylazoxymethanol (MAM), and which are found in all cycad genera.

Encephalartos ghellinckii Lem. or Drakensberg cycad is endemic to South Africa, and is one of about 70 species found in sub-Saharan Africa. Strongly associated with the Natal Drakensberg, this 3m tall evergreen species is found from the foothills to fairly high altitudes, growing on stream banks, steep grassy slopes and sandstone outcrops. Its preferred habitat lying within grassveld, it has developed resistance to veldfires, and also the intense cold brought on by snow and frost.

Zamia integrifolia, also known as coontie, is a small, tough, woody cycad native to the southeastern United States, the Bahamas, Cuba, the Cayman Islands, and Puerto Rico.

















