In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands".

Terpyridine is a heterocyclic compound derived from pyridine. It is a white solid that is soluble in most organic solvents. The compound is mainly used as a ligand in coordination chemistry.

1,10-Phenanthroline (phen) is a heterocyclic organic compound. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The 1,10 refer to the location of the nitrogen atoms that replace CH's in the hydrocarbon called phenanthrene.

Salen refers to a tetradentate C2-symmetric ligand synthesized from salicylaldehyde (sal) and ethylenediamine (en). It may also refer to a class of compounds, which are structurally related to the classical salen ligand, primarily bis-Schiff bases. Salen ligands are notable for coordinating a wide range of different metals, which they can often stabilise in various oxidation states. For this reason salen-type compounds are used as metal deactivators. Metal salen complexes also find use as catalysts.

Cyclen (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane) is a aza-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2NH)4. It is a white solid. Being structurally simple, symmetrical, and polyfunctional, cyclen has been widely investigated.
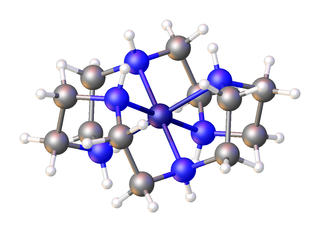
In organic chemistry, an aza-crown ether is an aza analogue of a crown ether. That is, it has a nitrogen atom in place of each oxygen atom around the ring. While the parent crown ethers have the formulae (CH2CH2O)n, the parent aza-crown ethers have the formulae (CH2CH2NH)n, where n = 3, 4, 5, 6. Well-studied aza crowns include triazacyclononane, cyclen, and hexaaza-18-crown-6.
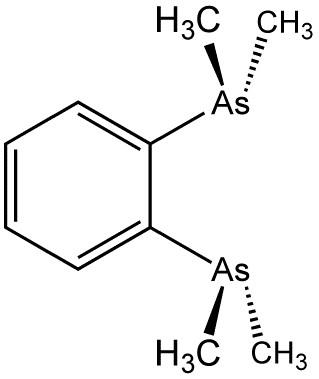
1,2-Bis(dimethylarsino)benzene (diars) is the organoarsenic compound with the formula C6H4(As(CH3)2)2. The molecule consists of two dimethylarsino groups attached to adjacent carbon centers of a benzene ring. It is a chelating ligand in coordination chemistry. This colourless oil is commonly abbreviated "diars."

Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts.

In organometallic chemistry, a metallacycle is a derivative of a carbocyclic compound wherein a metal has replaced at least one carbon center; this is to some extent similar to heterocycles. Metallacycles appear frequently as reactive intermediates in catalysis, e.g. olefin metathesis and alkyne trimerization. In organic synthesis, directed ortho metalation is widely used for the functionalization of arene rings via C-H activation. One main effect that metallic atom substitution on a cyclic carbon compound is distorting the geometry due to the large size of typical metals.

1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane (dppm), is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH2(PPh2)2. Dppm, a white, crystalline powder, is used in inorganic and organometallic chemistry as a ligand. It is more specifically a chelating ligand because it is a ligand that can bond to metals with two phosphorus donor atoms. The natural bite angle is 73°.
In coordination chemistry, a stability constant is an equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex in solution. It is a measure of the strength of the interaction between the reagents that come together to form the complex. There are two main kinds of complex: compounds formed by the interaction of a metal ion with a ligand and supramolecular complexes, such as host–guest complexes and complexes of anions. The stability constant(s) provide(s) the information required to calculate the concentration(s) of the complex(es) in solution. There are many areas of application in chemistry, biology and medicine.

DOTA (also known as tetraxetan) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2NCH2CO2H)4. The molecule consists of a central 12-membered tetraaza (i.e., containing four nitrogen atoms) ring. DOTA is used as a complexing agent, especially for lanthanide ions. Its complexes have medical applications as contrast agents and cancer treatments.
Dioxygen complexes are coordination compounds that contain O2 as a ligand. The study of these compounds is inspired by oxygen-carrying proteins such as myoglobin, hemoglobin, hemerythrin, and hemocyanin. Several transition metals form complexes with O2, and many of these complexes form reversibly. The binding of O2 is the first step in many important phenomena, such as cellular respiration, corrosion, and industrial chemistry. The first synthetic oxygen complex was demonstrated in 1938 with cobalt(II) complex reversibly bound O2.
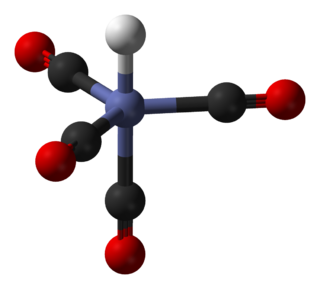
Metal acetylacetonates are coordination complexes derived from the acetylacetonate anion (CH
3COCHCOCH−
3) and metal ions, usually transition metals. The bidentate ligand acetylacetonate is often abbreviated acac. Typically both oxygen atoms bind to the metal to form a six-membered chelate ring. The simplest complexes have the formula M(acac)3 and M(acac)2. Mixed-ligand complexes, e.g. VO(acac)2, are also numerous. Variations of acetylacetonate have also been developed with myriad substituents in place of methyl (RCOCHCOR′−). Many such complexes are soluble in organic solvents, in contrast to the related metal halides. Because of these properties, acac complexes are sometimes used as catalyst precursors and reagents. Applications include their use as NMR "shift reagents" and as catalysts for organic synthesis, and precursors to industrial hydroformylation catalysts. C
5H
7O−
2 in some cases also binds to metals through the central carbon atom; this bonding mode is more common for the third-row transition metals such as platinum(II) and iridium(III).

A metal salen complex is a coordination compound between a metal cation and a ligand derived from N,N′-bis(salicylidene)ethylenediamine, commonly called salen. The classical example is salcomine, the complex with divalent cobalt Co2+, usually denoted as Co(salen). These complexes are widely investigated as catalysts and enzyme mimics.
In coordination chemistry, a macrocyclic ligand is a macrocyclic ring having at least nine atoms and three or more donor sites that serve as ligands that can bind to a central metal ion. Crown ethers and porphyrins are prominent examples. Macrocyclic ligands exhibit high affinity for metal ions.

1,5-Diaza-3,7-diphosphacyclooctanes are organophosphorus compounds with the formula [R'NCH2P(R)CH2]2, often abbreviated PR2NR'2. They are air-sensitive white solids that are soluble in organic solvents. The ligands exist as meso and d,l-diastereomers, but only the meso forms function as bidentate ligands.

In coordination chemistry and organometallic chemistry, transition metal imido complexes is a coordination compound containing an imido ligand. Imido ligands can be terminal or bridging ligands. The parent imido ligand has the formula NH, but most imido ligands have alkyl or aryl groups in place of H. The imido ligand is generally viewed as a dianion, akin to oxide.
Transition metal amino acid complexes are a large family of coordination complexes containing the conjugate bases of the amino acids, the 2-aminocarboxylates. Amino acids are prevalent in nature, and all of them function as ligands toward the transition metals. Not included in this article are complexes of the amides and ester derivatives of amino acids. Also excluded are the polyamino acids including the chelating agents EDTA and NTA.

Transition metal dithiocarbamate complexes are coordination complexes containing one or more dithiocarbamate ligand, which are typically abbreviated R2dtc−. Many complexes are known. Several homoleptic derivatives have the formula M(R2dtc)n where n = 2 and 3.

















