Hydrolase is a class of enzymes that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases.

Nitisinone, sold under the brand name Orfadin among others, is a medication used to slow the effects of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT-1).
In enzymology, a 3-hydroxycyclohexanone dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-hydroxymuconate-semialdehyde hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-diketone hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a haloalkane dehalogenase (EC 3.8.1.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phloretin hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 4-oxalmesaconate hydratase (EC 4.2.1.83) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,5-dioxopiperazine hydrolase (EC 3.5.2.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 6-aminohexanoate-cyclic-dimer hydrolase (EC 3.5.2.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
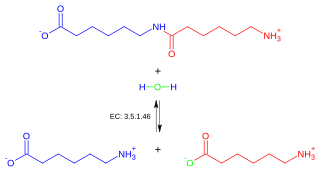
In enzymology, a 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.46) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate + H2O 2 6-aminohexanoate. Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate and H2O, whereas its product is two molecules of 6-aminohexanoate.
In enzymology, Nα-benzyloxycarbonylleucine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.64) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-malonylurea hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.95) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-methylhydantoinase (ATP-hydrolysing) (EC 3.5.2.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a riboflavinase (EC 3.5.99.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-N-acetyl-1-phenylethylamine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.85) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
L-saccharopine oxidase (EC 1.5.3.18, FAP2) is an enzyme with systematic name L-saccharopine:oxygen oxidoreductase (L-glutamate forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cyclohexane-1,2-dione hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.11) is an enzyme with systematic name cyclohexane-1,2-dione acylhydrolase (decyclizing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
6-oxocamphor hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.18, OCH, camK (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name bornane-2,6-dione hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

1,3-Cyclohexanedione is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(CO)2. It is one of three isomeric cyclohexanediones. It is a colorless compound that occurs naturally. It is the substrate for cyclohexanedione hydrolase. The compound exists mainly as the enol tautomer.




