
The Scorpaeniformes are a diverse order of ray-finned fish, including the lionfishes and sculpins, but have also been called the Scleroparei. It is one of the five largest orders of bony fishes by number of species, with over 1,320.
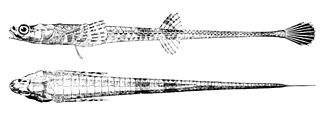
Agonidae is a family of small, bottom-dwelling, cold-water marine fish. Common names for members of this family include poachers, Irish lords, sea ravens, alligatorfishes, starsnouts, hooknoses, and rockheads. They are notable for having elongated bodies covered by scales modified into bony plates, and for using their large pectoral fins to move in short bursts. The family includes about 59 species in some 25 genera, some of which are quite widespread.

The snailfishes or sea snails are a family of marine ray-finned fishes. These fishes make up the Liparidae, which is classified within the order Scorpaeniformes.

Gasterosteoidei is a suborder of ray-finned fishes that includes the sticklebacks and relatives, the 5th edition of Fishes of the World classifies this suborder within the order Scorpaeniformes.

The Cyclopteridae are a family of marine fishes, commonly known as lumpsuckers or lumpfish, in the order Scorpaeniformes. They are found in the cold waters of the Arctic, North Atlantic, and North Pacific oceans. The greatest number of species are found in the North Pacific. The family name Cyclopteridae derives from the Greek words κύκλος (kyklos), meaning "circle", and πτέρυξ (pteryx), meaning "wing" or "fin", in reference to the circle-shaped pectoral fins of most of the fish in this family.

Anoplopomatidae, the sablefishes, are a small family of ray-finned fishes classified within the order Scorpaeniformes. This family is the only family in the monotypic superfamily Anoplopomatoidea. These fishes are found in the North Pacific Ocean.

Rhamphocottidae is a family of ray-finned fishes belonging to the superfamily Cottoidea, the sculpins. The species in this family occur in the North Pacific Ocean.

Hexagrammidae, the greenlings, is a family of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the suborder Cottoidei in the order Scorpaeniformes. These fishes are found in the North Pacific Ocean.

Anarhichadidae, the wolffishes, sea wolves or wolf eels, is a family of marine ray finned fishes belonging to the order Scorpaeniformes. These are predatory, eel shaped fishes which are native to the cold waters of the Arctic, North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans.

Pholidae is a family of marine ray-finned fishes, known as gunnels, in the scorpaeniform suborder Zoarcoidei. These are fishes of the littoral zone and are mainly found in North Pacific Ocean, with two species found in the North Atlantic Ocean and Arctic Ocean.

Stichaeidae, the pricklebacks or shannies, are a family of marine ray-finned fishes in the suborder Zoarcoidei of the order Scorpaeniformes. Most species are found in the North Pacific Ocean with a few in the North Atlantic Ocean.

The quillfish,, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, it is the only species in the genus Ptilichthys and family Ptilichthyidae. This fish occurs in the northern North Pacific Ocean.

The Hemitripterinae is a subfamily of the scorpaeniform family Agonidae, known as sea ravens or sailfin sculpins. They are bottom-dwelling fish that feed on small invertebrates, found in the northwest Atlantic and north Pacific Oceans. They are covered in small spines.

The Trichodontidae, or sandfishes, are a small family of ray-finned fishes from the order Scorpaeniformes. The species in this family are found in the North Pacific Ocean.

Zoarcoidei is a suborder of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Scorpaeniformes. The suborder includes the wolffishes, gunnels and eelpouts. The suborder includes about 400 species. These fishes predominantly found in the boreal seas of the northern hemisphere but they have colonised the southern hemisphere.
Bathylutichthys a genus of marine ray-finned fishes which is the only genus in the monotypic family Bathylutichthyidae, known as the Antarctic sculpins. These fishes are found in the Southern Ocean.

The Zaniolepididae is a family of marine ray-finned fishes classified within the suborder Cottoidei of the order Scorpaeniformes. They are found in the North Pacific Ocean.

Cryptacanthodes is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the monogeneric family Cryptacanthodidae, commonly referred to as wrymouths. Three of the four species are found in the Pacific Ocean with one species native to the western Atlantic Ocean where they are benthic fishes, tunneling through soft substrates. It is currently the only known genus in its family.

Cottoidei is a suborder of ray-finned fishes which, according to the 5th edition of Fishes of the World, is placed within the order Scorpaeniformes, alongside the scorpionfishes, flatheads, eelpouts, sticklebacks and related fishes.

Jordaniidae is a small family of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Scorpaeniformes. These fishes are found in the eastern North Pacific Ocean.



















