
N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC or DCCD) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (C6H11N)2C. It is a waxy white solid with a sweet odor. Its primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. The low melting point of this material allows it to be melted for easy handling. It is highly soluble in dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile and dimethylformamide, but insoluble in water.

Melanogaster is a genus of fungus that resemble truffles, and are often mistaken for them. However, they do not have the characteristic aroma and value of truffles, although some have been used culinarily. None are known to be poisonous. The genus contains 25 species that collectively have a widespread distribution.

Serpula lacrymans is one of the fungi that cause damage to timber referred to as dry rot. It is a basidiomycete in the order Boletales. The Serpula lacrymans has the ability to rapidly colonise sites through unique and highly specialised mycelium which also leads to greater degradation rates of wood cellulose.

Wolfgang Steglich is a German chemist.

Pulvinone, an organic compound belonging to the esters, lactones, alcohols and butenolides classes, is a yellow crystalline solid. Although the pulvinone is not a natural product, several naturally occurring hydroxylated derivatives are known. These hydroxylated pulvinones are produced by fungal species, such as the in Europe common Larch Bolete, or by moulds such as Aspergillus terreus.

Vulpinic acid is a natural product first found in and important in the symbiosis underlying the biology of lichens. It is a simple methyl ester derivative of its parent compound, pulvinic acid, and a close relative of pulvinone, both of which derive from aromatic amino acids such as phenylalanine via secondary metabolism. The roles of vulpinic acid are not fully established, but may include properties that make it an antifeedant for herbivores. The compound is relatively toxic to mammals.

Xanthoria elegans, commonly known as the elegant sunburst lichen, is a lichenized species of fungus in the genus Xanthoria, family Teloschistaceae. Recognized by its bright orange or red pigmentation, this species grows on rocks, often near bird or rodent perches. It has a circumpolar and alpine distribution. It was one of the first lichens to be used for the rock-face dating method known as lichenometry.

Thelephoric acid is a terphenylquinone pigment that is found in several fungi, such as Omphalotus subilludens and Polyozellus multiplex. Thelephoric acid has been shown to inhibit prolyl endopeptidase, an enzyme that has a role in processing proteins in Alzheimer's disease. Chemicals that inhibit prolyl endopeptidase have attracted research interest due to their potential therapeutic effects. It is derived from atromentin, and its precursor can be from cyclovariegatin. Fragmentation patterns have suggested that polymers of thelephoric acid exists.

Haematopodin is the more stable breakdown product of Haematopodin B. Both compounds are found in the mushroom Mycena haematopus, although haematopodin only occurs in trace amounts in fresh fruit bodies. Similar pigments, known as batzellins and damirones, have been found in sea sponges. A chemical synthesis for haematopodin was reported in 1996. Key steps in the synthesis involved the addition of 3-[(2,4-dimethoxybenzyl)amino]-1-propanol to the indolo-6,7-quinone and cyclization of the resulting adduct with trifluoroacetic acid.

Calostomal is an organic compound that has a carboxylic acid and an aldehyde group. It is an orange solid that is extracted from the mushroom Calostoma cinnabarinum, hence its name. The structure of this compound was confirmed by NMR and mass spectrometry of the methyl ester derivative. This compound is a polyene; its conjugated system accounts for its intense color, similar to lycopene found in tomatoes.
Boletocrocin is any one of a group of seven closely related organic compounds, individually named boletocrocin A through boletrocrocin G. These compounds are polyene dicarboxylic acids that include both lipophilic and polar amino acids. They were extracted from the brightly colored mushrooms Boletus laetissimus and B. rufoaureus. The boletocrocins' conjugated systems account for the intense color.
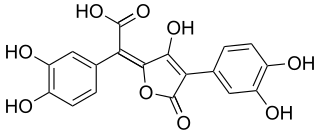
Variegatic acid is an orange pigment found in some mushrooms. It is responsible for the bluing reaction seen in many bolete mushrooms when they are injured. When mushroom tissue containing variegatic acid is exposed to air, the chemical is enzymatically oxidized to blue quinone methide anions, specifically chinonmethid anions. It is derived from xerocomic acid, which is preceded by atromentic acid and atromentin, and its genetic basis is unknown. In its oxidized form is variegatorubin, similar to xerocomorubin.

Pulvinic acids are natural chemical pigments found in some lichens, derived biosynthetically from the aromatic amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine, via dimerization and oxidative ring-cleavage of arylpyruvic acids, a process that also produces the related pulvinones.

Norbadione A is a pigment found in the bay bolete mushroom. A polyphenol, norbadione A is related to a family of mushroom pigments known as pulvinic acids. The molecule has also been reported as a potassium salt from the mushrooms Pisolithus tinctorius and Chalciporus piperatus.

Albatrellus cristatus is a species of fungus in the family Albatrellaceae. It is found in Asia, Europe, and North America, where it grows singly or in fused clumps on the ground in deciduous and coniferous forests. Fruit bodies contain cristatic acid, a benzoic acid derivative that has cytotoxic activity and antibiotic activity against Bacillus species in laboratory tests. Another compound known only from the fungus, cristatomentin, is a green pigment with a meroterpene chemical structure.
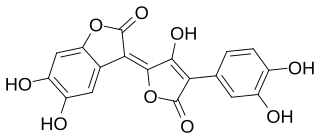
Variegatorubin is a pulvinic acid derivative. It is a red pigment that is present in many members of the Boletales, an order of the division Basidiomycota. It is generated from the oxidation of variegatic acid. Bolete species that contain variegatorubin include Neoboletus luridiformis, Chalciporus piperatus, Rhizopogon roseolus, Exsudoporus frostii, Suillellus luridus, Rubroboletus rhodoxanthus, and R. satanas. Variegatorubin was discovered by Wolfgang Steglich and colleagues, and described as a new compound in 1970.
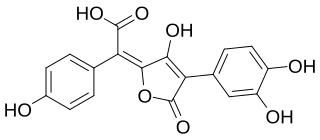
Xerocomic acid is a red-orange pigment found in fungi of the order Boletales. It is the precursor to variegatic acid, and is preceded by atromentic acid and atromentin. As an example, it is isolated from Serpula lacrymans. It is soluble in methanol. An oxidase acting on xerocomic acid is responsible for the "bluing" reaction seen in mushrooms.

Atromentic acid is a red-organge pigment found in fungi within the Boletales group. It is the precursor to variegatic acid and xerocomic acid, and is preceded by atromentin. As an example, it is isolated from Serpula lacrymans. It is soluble in methanol. Variants include homoatromentic acid. This pigment has been studied and elucidated by Wolfgang Steglich and colleagues over decades. When atromentin is oxidised with hydrogen peroxide a yellow product is produced. A sodium hydroxide solution is also yellow, but when this is neutralized with acid the red atromentic acid crystallises. Concentrated potassium hydroxide breaks up the compound to p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid and oxalic acid.

Xerocomorubin is a pigment from the fungus order Boletales. It is the oxidized form of isoxerocomic acid. Air oxidation is responsible its formation, and it oxidizes faster to a similar pulvinic acid type pigment oxidized variant, variegatorubin. The long wavelength has an absorption at 497 nm, 106 nm higher than its precursor isoxerocomic acid. Synthesis experiments have shown tetra-acetylation by acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid. Although xerocomorubin and variegatorubin give off the same deep red color and could simultaneously occur in a mushroom, extracts from the deep red colored mushroom Boletus rubellus Krombh. identified only variegatorubin by thin layer chromatography (TLC), leading to the question the natural abundance of xerocomorubin.
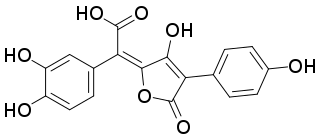
Isoxerocomic acid is a red-orange pigment found in Boletales. It is the precursor to variegatic acid, and is preceded by atromentic acid and atromentin. As an example, it is isolated from Serpula lacrymans. It is soluble in methanol. It is the isomer of xerocomic acid and precursor to xerocomorubin.



















