The Kell antigen system is a human blood group system, that is, a group of antigens on the human red blood cell surface which are important determinants of blood type and are targets for autoimmune or alloimmune diseases which destroy red blood cells. The Kell antigens are K, k, Kpa, Kpb, Jsa and Jsb. The Kell antigens are peptides found within the Kell protein, a 93-kilodalton transmembrane zinc-dependent endopeptidase which is responsible for cleaving endothelin-3.

CD68 is a protein highly expressed by cells in the monocyte lineage, by circulating macrophages, and by tissue macrophages.

Betacellulin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BTC gene located on chromosome 4 at locus 4q13-q21. Betacellulin was initially identified as a mitogen. Betacellulin, is a part of an Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) family and functions as a ligand for the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). The role of betacellulin as an EGF is manifested differently in various tissues, and it has a great effect on nitrogen signaling in retinal pigment epithelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells. While many studies attest a role for betacellulin in the differentiation of pancreatic β-cells, the last decade witnessed the association of betacellulin with many additional biological processes, ranging from reproduction to the control of neural stem cells. Betacellulin is a member of the EGF family of growth factors. It is synthesized primarily as a transmembrane precursor, which is then processed to mature molecule by proteolytic events.

White adipose tissue or white fat is one of the two types of adipose tissue found in mammals. The other kind is brown adipose tissue. White adipose tissue is composed of monolocular adipocytes.

EGF-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor-like 2 also known as CD312 is a protein encoded by the ADGRE2 gene. EMR2 is a member of the adhesion GPCR family. Adhesion GPCRs are characterized by an extended extracellular region often possessing N-terminal protein modules that is linked to a TM7 region via a domain known as the GPCR-Autoproteolysis INducing (GAIN) domain.

Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha (IKK-α) also known as IKK1 or conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase (CHUK) is a protein kinase that in humans is encoded by the CHUK gene. IKK-α is part of the IκB kinase complex that plays an important role in regulating the NF-κB transcription factor. However, IKK-α has many additional cellular targets, and is thought to function independently of the NF-κB pathway to regulate epidermal differentiation.

T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 gamma chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD3G gene.

Cluster of differentiation 97 is a protein also known as BL-Ac[F2] encoded by the ADGRE5 gene. CD97 is a member of the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. Adhesion GPCRs are characterized by an extended extracellular region often possessing N-terminal protein modules that is linked to a TM7 region via a domain known as the GPCR-Autoproteolysis INducing (GAIN) domain.

CD82, or KAI1, is a human protein encoded by the CD82 gene.
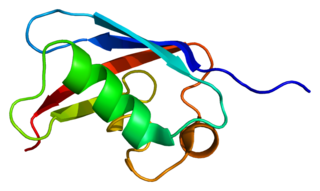
FAS-associated factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAF1 gene.

Pregnancy-specific beta-1-glycoprotein 1 (PSBG-1) also known as CD66f, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSG1 gene and is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family. Pregnancy-specific glycoproteins (PSGs) are a complex consisting of carbohydrate and protein, which is present in the mammalian body specifically during pregnancy. This glycoprotein is the most abundant protein found in the maternal bloodstream during the later stages of pregnancy and it is of vital importance in fetal development. The PSG functions primarily as an immunomodulator to protect the growing fetus.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 12 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP3K12 gene.

T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1e, membrane-associated is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD1E gene.

Myeloid cell Nuclear Differentiation Antigen is a protein that in humans is encoded as MNDA gene.

Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 85B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC85B gene.

Synapse-associated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SYAP1 gene.

Chemerin, also known as retinoic acid receptor responder protein 2 (RARRES2), tazarotene-induced gene 2 protein (TIG2), or RAR-responsive protein TIG2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RARRES2 gene.
A431 cells are a model human cell line used in biomedical research.

Adipogenesis is the formation of adipocytes from stem cells. It involves 2 phases, determination, and terminal differentiation. Determination is mesenchymal stem cells committing to the adipocyte precursor cells, also known as lipoblasts or preadipocytes which lose the potential to differentiate to other types of cells such as chondrocytes, myocytes, and osteoblasts. Terminal differentiation is that preadipocytes differentiate into mature adipocytes. Adipocytes can arise either from preadipocytes resident in adipose tissue, or from bone-marrow derived progenitor cells that migrate to adipose tissue.

T-box transcription factor TBX15 is protein that is encoded in humans by the Tbx15 gene, mapped to Chromosome 3 in mice and Chromosome 1 in humans. Tbx15 is a transcription factor that plays a key role in embryonic development. Like other members of the T-box subfamily, Tbx15 is expressed in the notochord and primitive streak, where it assists with the formation and differentiation of the mesoderm. It is steadily downregulated after segmentation of the paraxial mesoderm.



















