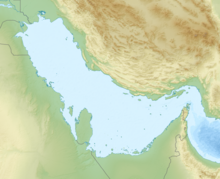
The United Arab Emirates is a country in the eastern part of the Arabian Peninsula located on the southeastern coast of the Persian Gulf and the northwestern coast of the Gulf of Oman. The UAE consists of seven emirates and was founded on 2 December 1971 as a federation, after UK armed forces left the region. Six of the seven emirates declared their union on 2 December 1971. The seventh, Ras al Khaimah, joined the federation on 10 February 1972. The seven sheikdoms were formerly known as the Trucial States, in reference to the truce treaties established with the British in the 19th century.

The United Arab Emirates is situated in the Middle East and West Asia, bordering the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf, between Oman and Saudi Arabia; it is at a strategic location along the northern approaches to the Strait of Hormuz, a vital transit point for world crude oil. The UAE lies between 22°50′ and 26° north latitude and between 51° and 56°25′ east longitude. It shares a 19 km (12 mi) border with Qatar on the northwest, a 530 km (330 mi) border with Saudi Arabia on the west, south, and southeast, and a 450 km (280 mi) border with Oman on the southeast and northeast.

The United Arab Emirates is a high-income developing market economy. The UAE's economy is the 4th largest in the Middle East, with a gross domestic product (GDP) of US$415 billion in 2021-2023.

The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a federal, elective monarchy composed of seven emirates, with Abu Dhabi as its capital. It shares land borders with Oman to the east and northeast, and with Saudi Arabia to the southwest; as well as maritime borders in the Persian Gulf with Qatar and Iran, and with Oman in the Gulf of Oman. As of 2024, the UAE has an estimated population of over 10 million, of which 11% are Emiratis; Dubai is the most populous city and is an international hub. Islam is the official religion and Arabic is the official language, while English is the most spoken language and the language of business.

Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan was an Emirati royal, politician, philanthropist and the founder of the United Arab Emirates. Zayed served as the governor of Eastern Region from 1946 until he succeeded Sheikh Shakhbut as the ruler of Abu Dhabi in 1966, and then as the first president of the United Arab Emirates while he retained his position as Abu Dhabi's ruler from 1971 until his death in 2004. He is revered in the United Arab Emirates as the Waalid al-Ummah, credited for being the principal driving force behind uniting the seven Trucial States to found the Union of the United Arab Emirates.
Sheikh Dhiyab ibn Isa Al Nahyan was the Sheikh of the Bani Yas of the Liwa Oasis from 1761 to 1793 and the founder of the Al Bu Falah dynasty, which still rules Abu Dhabi, the capital of the United Arab Emirates (UAE), today.
Bani Yas is a tribal confederation of Najdi origin in the modern United Arab Emirates. The tribal coalition, consisting of tribes from Dubai to Khor Al Adaid in southeast Qatar, was called the Bani Yas Coalition. Al Nahyan, a branch of Al Falahi, leads the tribe and is the ruling family of the Abu Dhabi. Al Maktoum, a branch of Al Falasi, is also a member and is the ruling family of Dubai. Al Nahyan and Al Maktoum are the most influential in the UAE federal government, and Abu Dhabi and Dubai have the right to veto any federal legislation. The ruler of Abu Dhabi is customarily elected as the president of the UAE, and the ruler of Dubai is traditionally elected as the vice president and prime minister of the UAE.

The Emirate of Abu Dhabi is one of seven emirates that constitute the United Arab Emirates. It is the largest emirate, accounting for 87% of the nation's total land area or 67,340 km2 (26,000 sq mi).

Now part of the United Arab Emirates, Abu Dhabi was formerly the largest of the seven sheikdoms which made up the Trucial States on the Pirate Coast of eastern Arabia between Oman and Qatar. The Trucial States as a whole had an area of some 32,000 square miles of which Abu Dhabi alone had 26,000. The capital was the town of Abu Dhabi which is on an offshore island and was first settled in 1761.

The House of Nahyan is the ruling royal family of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, and one of the six ruling families of the United Arab Emirates. The family is a branch of the House of Al Falahi, a branch of the Bani Yas tribe, and are related to the House of Al Falasi from which the ruling family of Dubai, the Al Maktoum, descends.

The United Arab Emirates Navy (UAEN) is the naval branch of the United Arab Emirates Armed Forces. It is small force of about 3,000 personnel. It maintains 12 well-equipped coastal patrol boats and eight missile boats. Although primarily concerned with coastal defense, the Navy is constructing a six-unit class of blue water corvettes in conjunction with French shipbuilder CMN. The UAE maintains a battalion-sized marine force called the UAE Marines equipped with BMP-3 armoured personnel carriers from Soviet union/Russia.

Abu Dhabi is the capital city of the United Arab Emirates. The city is the seat of the Abu Dhabi Central Capital District, the capital city of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, and the UAE's second-most populous city, after Dubai. The city is situated on a T-shaped island, extending into the Gulf from the central-western coast of the UAE.

Sir Abu Nuʽayr, also known as Sir Bu Nuʽayr, or Sir al Qawasim is an island in the Persian Gulf.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
Cultural policy in Abu Dhabi, a city within the United Arab Emirates, refers to any initiative undertaken by the Emirate government aimed at achieving goals to contribute to or shape culture. Abu Dhabi's government aims to develop a cultural infrastructure that will allow it to establish itself as a reference point for culture on three levels:
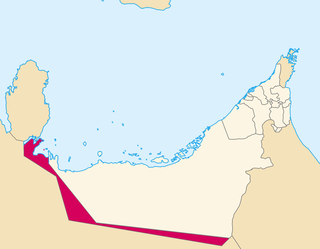
The 1974 Treaty of Jeddah was a treaty between Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates, signed in 21 August 1974 between King Faisal of Saudi Arabia and President of the United Arab Emirates Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan. The treaty intended to resolve the Saudi Arabia – United Arab Emirates border dispute. Saudi Arabia ratified the treaty in 1993, but the UAE has not yet ratified it. The legal validity of the treaty has been questioned, since Qatar was not included in the negotiations, and the proposed settlement affects the Qatari border. However, Qatar had already reached a separate agreement on its border with Saudi Arabia in December 1965.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.

Abu Dhabi Central Capital District, officially "Abu Dhabi Region", also called "Abu Dhabi Metropolitan Area", is the municipal region in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi that contains the city of Abu Dhabi, distinct from the Eastern and Western municipal regions of the Emirate. Abu Dhabi City is the capital of both the Emirate and the United Arab Emirates, and has its own local government.