
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch 3,000 miles in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in the southwestern United States. Depending on differing definitions between Canada and the U.S., its northern terminus is located either in northern British Columbia's Terminal Range south of the Liard River and east of the Trench, or in the northeastern foothills of the Brooks Range/British Mountains that face the Beaufort Sea coasts between the Canning River and the Firth River across the Alaska-Yukon border. Its southernmost point is near the Albuquerque area adjacent to the Rio Grande rift and north of the Sandia–Manzano Mountain Range. Being the easternmost portion of the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are distinct from the tectonically younger Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada, which both lie farther to its west.

The geography of Switzerland encompasses the geographical features of Switzerland, a mountainous and landlocked country located in Western and Central Europe. Switzerland's natural landscape is marked by its numerous lakes and mountains. It is surrounded by five countries: Austria and Liechtenstein to the east, France to the west, Italy to the south and Germany to the north. Switzerland has a maximum north–south length of 220 kilometres (140 mi) and an east–west length of about 350 kilometres (220 mi).

The Alpine region of Switzerland, conventionally referred to as the Swiss Alps, represents a major natural feature of the country and is, along with the Swiss Plateau and the Swiss portion of the Jura Mountains, one of its three main physiographic regions. The Swiss Alps extend over both the Western Alps and the Eastern Alps, encompassing an area sometimes called Central Alps. While the northern ranges from the Bernese Alps to the Appenzell Alps are entirely in Switzerland, the southern ranges from the Mont Blanc massif to the Bernina massif are shared with other countries such as France, Italy, Austria and Liechtenstein.

The Bernese Alps are a mountain range of the Alps, located in western Switzerland. Although the name suggests that they are located in the Berner Oberland region of the canton of Bern, portions of the Bernese Alps are in the adjacent cantons of Valais, Fribourg and Vaud, the latter being usually named Fribourg Alps and Vaud Alps respectively. The highest mountain in the range, the Finsteraarhorn, is also the highest point in the canton of Bern.
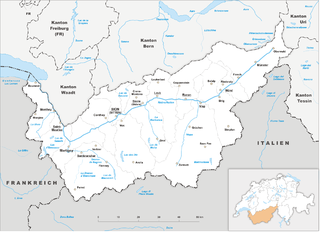
Valais, more formally the Canton of Valais, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of thirteen districts and its capital and largest city is Sion. The flag of the canton is made of thirteen stars representing the districts, on a white-red background.
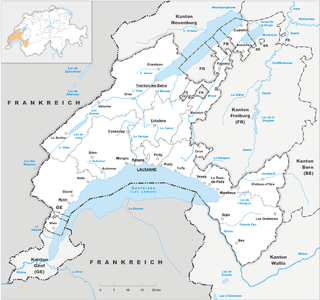
Vaud, more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts, and its capital city is Lausanne. Its coat of arms bears the motto "Liberté et patrie" on a white-green bicolour.

The Diablerets are a huge ice-covered mountain massif of the Alps, culminating at the Sommet des Diablerets (VS) at 3,216 metres (10,551 ft) above sea level and almost straddling the border between the Swiss cantons of Vaud (VD) and Valais (VS). The northeastern part of the massif stretches also into the canton of Bern (BE).

Saxon Switzerland is a hilly climbing area and national park in the Elbe Sandstone Mountains. It is located around the Elbe valley south-east of Dresden in Saxony, Germany, adjoining Bohemian Switzerland in the Czech Republic. Together with the Czech part, the region is known as Saxon-Bohemian Switzerland.

The Missisquoi River is a transboundary river of the east shore of Lake Champlain, approximately 80 miles (130 km) long, in northern Vermont in the United States and southern Quebec in Canada.

The Sierra de Guadarrama is a mountain range forming the main eastern section of the Sistema Central, the system of mountain ranges along the centre of the Iberian Peninsula. It is located between the systems Sierra de Gredos in the province of Ávila, and Sierra de Ayllón in the province of Guadalajara.

The Jacques-Cartier River is a river in the province of Quebec, Canada. It is 161 km long and its source is Jacques-Cartier Lake in Laurentides Wildlife Reserve, and flows in a predominantly southern direction before ending in the Saint Lawrence River at Donnacona, about 30 km upstream from Quebec City.

Conthey is a municipality in the district of Conthey in the canton of Valais in Switzerland.

Lac de Derborence is a mountain lake in the municipality of Conthey, Valais, Switzerland, located near the hamlet of Derborence. It was formed after rockfalls on 24 September 1714 and 23 June 1749. In 1749, an estimated 50 million m3 of rocks blocked the course of the Derbonne river and led to the formation of the lake.

Fort l'Écluse, or the Fort de l'Écluse, is a military fort in Léaz, Ain, close to Collonges in Eastern France. It commands the Rhône Valley as a natural entrance into France from Switzerland between the Vuache and the Jura Mountains.

The Scex Rouge is a mountain of the Alps, overlooking Les Diablerets in the canton of Vaud. Along with the Oldenhorn to the east, it is one of the main peaks of the Diablerets, a huge ice-covered mountain near the western end of the Bernese Alps, straddling the border between the cantons of Vaud, Valais, and Bern, and exceeding 3,000 metres (9,800 ft) above sea level. On its west side, the Scex Rouge is part of a nearly 2,000-metre-high (6,600 ft) amphitheatre of cliffs surrounding the Creux de Champ valley, south of Les Diablerets. On its southeast side, the Scex Rouge overlooks the Tsanfleuron Glacier, the largest in the massif. Administratively, the mountain is part of the municipality of Ormont-Dessus, which also includes Les Diablerets.

Mont Gond is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, overlooking Derborence in Valais. It is located between the Diablerets and the Rhone valley. Etang de Trente Pas is a small lake and bog below Mont Gond.

Les Diablerets is a village and ski resort located in the municipality of Ormont-Dessus in the canton of Vaud, Switzerland.

The Creux du Van is a natural rocky cirque approximately 1,400 metres wide and 150 metres deep, on the north side of Le Soliat, in the Val de Travers district in the Swiss canton of Neuchâtel. A very well known, amphitheatre-shaped natural attraction, it is at the heart of a nature reservation area of 15.5 km2.

The France–Switzerland border is 572 km (355 mi) long. Its current path is mostly the product of the Congress of Vienna of 1815, with the accession of Geneva, Neuchâtel and Valais to the Swiss Confederation, but it has since been modified in detail, the last time being in 2002. Although most of the border, marked with border stones, is unguarded, several checkpoints remain staffed, most notably on busy roads.
The Gemmi Fault or Gemmi Pass Fault is a geologic fault in Switzerland. It lies close to the Gemmi Pass at Leukerbad and is a strike-slip fault. This fault is at least 2.6 kilometres (1.6 mi) long and shows evidence of Holocene movement; several landslides and traces of early Holocene earthquakes found in Swiss lakes may correlate to movements along the Gemmi Fault.




















