
Berlin is the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, as measured by population within city limits. The city is also one of the states of Germany, and is the third smallest state in the country in terms of area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of Brandenburg, and Brandenburg's capital Potsdam is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.5 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany. The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr region, and the sixth-biggest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union.

The Berlin Wall was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin of the Federal Republic of Germany from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and the German Democratic Republic. Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the government of the GDR on 13 August 1961. It included guard towers placed along large concrete walls, accompanied by a wide area that contained anti-vehicle trenches, beds of nails and other defenses. The primary intention for the Wall's construction was to prevent East German citizens from fleeing to the West.

East Berlin was the partially recognised capital of East Germany (GDR) from 1949 to 1990. From 1945, it was the Soviet occupation sector of Berlin. The American, British, and French sectors were known as West Berlin. From 13 August 1961 until 9 November 1989, East Berlin was separated from West Berlin by the Berlin Wall. The Western Allied powers did not recognize East Berlin as the GDR's capital, nor the GDR's authority to govern East Berlin. For most of its administrative existence, East Berlin was officially known as Berlin, capital of the GDR by the GDR government. On 3 October 1990, the day Germany was officially reunified, East and West Berlin formally reunited as the city of Berlin.

Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG), is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of 357,569 km2 (138,058 sq mi), making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.

East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic, was a country in Central Europe from its formation on 7 October 1949 until its reunification with West Germany on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was generally viewed as a communist state and described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state". The economy of the country was centrally planned and state-owned. Although the GDR had to pay substantial war reparations to the Soviets, its economy became the most successful in the Eastern Bloc.

The Ministry for State Security, commonly known as the Stasi, an abbreviation of Staatssicherheit, was the state security service and secret police of East Germany from 1950 to 1990.

World War II or the Second World War was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies and the Axis powers. Nearly all of the world's countries—including all the great powers—participated, with many investing all available economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities in pursuit of total war, blurring the distinction between military and civilian resources. Tanks and aircraft played major roles, with the latter enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and delivery of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was the deadliest conflict in history, resulting in 70 to 85 million fatalities, more than half of which were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust of European Jews, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. Following the Allied powers' victory, Germany, Austria, Japan, and Korea were occupied, and war crimes tribunals were conducted against German and Japanese leaders.
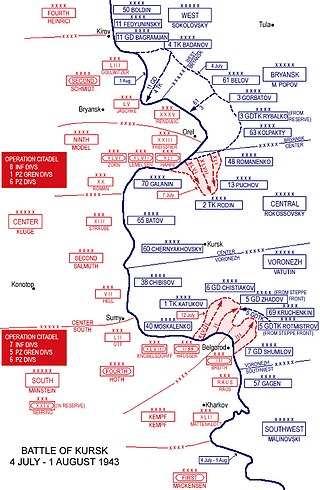
The Battle of Kursk was a major World War II Eastern Front battle between the forces of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union near Kursk in southwestern Russia during the summer of 1943, resulting in a Soviet victory. The Battle of Kursk was the single largest battle in the history of warfare. It, along with the Battle of Stalingrad several months earlier, are the two most oft-cited turning points in the European theatre of the war. It was one of the costliest and fiercest battles of the entire Second World War, and the single deadliest armoured battle in history and the opening day of the battle, 5 July, being the single costliest day in the history of aerial warfare. The battle was also marked by fierce house-to-house fighting and hand-to-hand combat.

West Germany was the Federal Republic of Germany from its formation on 23 May 1949 until its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republic after its capital city of Bonn. During the Cold War, the western portion of Germany and the associated territory of West Berlin were parts of the Western Bloc. West Germany was formed as a political entity during the Allied occupation of Germany after World War II, established from 12 states formed in the three Allied zones of occupation held by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France.

Walter Ernst Paul Ulbricht was a German communist politician. Ulbricht played a leading role in the creation of the Weimar-era Communist Party of Germany (KPD) and later in the early development and establishment of the German Democratic Republic. As the First Secretary of the Socialist Unity Party from 1950 to 1971, he was the chief decision-maker in East Germany. From President Wilhelm Pieck's death in 1960 on, he was also the East German head of state until his own death in 1973. As the leader of a significant Communist satellite, Ulbricht had a degree of bargaining power with the Kremlin that he used effectively. For example, he demanded the building of the Berlin Wall in 1961 when the Kremlin was reluctant.

German reunification was the process of re-establishing Germany as a single full sovereign state, which took place between 9 November 1989 and 15 March 1991. The "Unification Treaty" entered into force on 3 October 1990, dissolving the German Democratic Republic and integrating its recently re-established constituent federated states into the Federal Republic of Germany to form present-day Germany. This date has been chosen as the customary German Unity Day, and has thereafter been celebrated each year as a national holiday in Germany since 1991. As part of the reunification, East and West Berlin were also de facto united into a single city, which eventually became the capital of Germany.

East Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 ; following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's Free State of Prussia, until 1945. Its capital city was Königsberg. East Prussia was the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast.

Checkpoint Charlie was the best-known Berlin Wall crossing point between East Berlin and West Berlin during the Cold War (1947–1991), as named by the Western Allies.

The East German uprising of 1953 was an uprising that occurred in the German Democratic Republic from 16 to 17 June 1953. It began with strike action by construction workers in East Berlin on 16 June against work quotas during the Sovietization process in East Germany. Demonstrations in East Berlin turned into a widespread uprising against the Government of East Germany and the ruling Socialist Unity Party the next day, involving over one million people in about 700 localities across the country. Protests against declining living standards and unpopular Sovietization policies led to a wave of strikes and protests that were not easily brought under control and threatened to overthrow the East German government. The uprising in East Berlin was violently suppressed by tanks of the Soviet forces in Germany and the Kasernierte Volkspolizei. Demonstrations continued in over 500 towns and villages for several more days before eventually dying out.

Peaceful Revolution was the process of sociopolitical change that led to the opening of East Germany's borders to the Western world as part of the Revolutions of 1989. The peaceful revolution marks the end of the ruling by the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) in the German Democratic Republic in 1989 and the transition to a parliamentary system. This peaceful transition later enabled the German reunification in October 1990. The peaceful revolution was marked by non-violent initiatives and demonstrations. This period of change is referred to in German as Die Wende.

The Soviet occupation zone in Germany was an area of Germany that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a communist area, established as a result of the Potsdam Agreement on 1 August 1945. On 7 October 1949 the German Democratic Republic (GDR), commonly referred to in English as East Germany, was established in the Soviet occupation zone.

The Western Allied invasion of Germany was coordinated by the Western Allies during the final months of hostilities in the European theatre of World War II. In preparation for the Allied invasion of Germany east of the Rhine, a series of offensive operations were designed to seize and capture its east and west banks: Operation Veritable and Operation Grenade in February 1945, and Operation Lumberjack and Operation Undertone in March 1945; these are considered separate from the main invasion operation. The Allied invasion of Germany east of the Rhine started with the Western Allies crossing the river on 22 March 1945 before fanning out and overrunning all of western Germany from the Baltic in the north to the Alpine passes in the south, where they linked up with troops of the U.S. Fifth Army in Italy. Combined with the capture of Berchtesgaden, any hope of Nazi leadership continuing to wage war from a so-called "national redoubt" or escape through the Alps was crushed, shortly followed by unconditional German surrender on 8 May 1945. This is known as the Central Europe Campaign in United States military histories.

The German Democratic Republic (GDR), often called East Germany, founded a separate National Olympic Committee for socialist East Germany on 22 April 1951 in the Rotes Rathaus of East Berlin. This was the last of three German Olympic committees of the time. It was not recognized by the IOC for over a decade.

The fall of the Berlin Wall on 9 November 1989, during the Peaceful Revolution, marked the beginning of the destruction of the Berlin Wall and the figurative Iron Curtain, as East Berlin transit restrictions were overwhelmed and discarded. Sections of the wall were breached, and planned deconstruction began the following June. It was one of the series of events that started the fall of communism in Central and Eastern Europe. The fall of the inner German border took place shortly afterward. An end to the Cold War was declared at the Malta Summit in early December, and German reunification took place in October the following year.





















