Related Research Articles
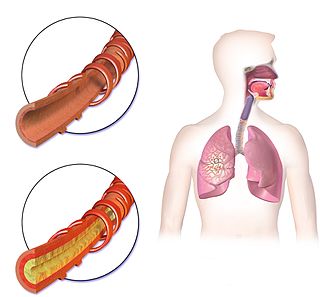
Hemoptysis or haemoptysis is the discharge of blood or blood-stained mucus through the mouth coming from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs. It does not necessarily involve coughing. In other words, it is the airway bleeding. This can occur with lung cancer, infections such as tuberculosis, bronchitis, or pneumonia, and certain cardiovascular conditions. Hemoptysis is considered massive at 300 mL. In such cases, there are always severe injuries. The primary danger comes from choking, rather than blood loss.

Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways. In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections and cytological investigations of respiratory systems. It is crucial that the specimen does not include any mucoid material from the nose or oral cavity.

Tuberculosis is diagnosed by finding Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria in a clinical specimen taken from the patient. While other investigations may strongly suggest tuberculosis as the diagnosis, they cannot confirm it.

Tuberculosis management describes the techniques and procedures utilized for treating tuberculosis (TB).

Enterobacter is a genus of common Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Cultures are found in soil, water, sewage, feces and gut environments. It is the type genus of the order Enterobacterales. Several strains of these bacteria are pathogenic and cause opportunistic infections in immunocompromised hosts and in those who are on mechanical ventilation. The urinary and respiratory tracts are the most common sites of infection. The genus Enterobacter is a member of the coliform group of bacteria. It does not belong to the fecal coliforms group of bacteria, unlike Escherichia coli, because it is incapable of growth at 44.5 °C in the presence of bile salts. Some of them show quorum sensing properties.

Mycobacteroides abscessus is a species of rapidly growing, multidrug-resistant, nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) that is a common soil and water contaminant. Although M. abscessus most commonly causes chronic lung infection and skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), it can also cause infection in almost all human organs, mostly in patients with suppressed immune systems. Amongst NTM species responsible for disease, infection caused by M. abscessus complex are more difficult to treat due to antimicrobial drug resistance.
Mycobacterium brumae is a rapidly growing environmental mycobacterial species identified in 1993. Aside from one 2004 report of a catheter related bloodstream infection no other infections by this organism have been reported. It was first isolated from water, soil and one human sputum sample in Spain.
Mycobacterium elephantis, a bacterium of the family Mycobacteriaceae, was discovered and isolated from a deceased elephant near India and may be linked to respiratory dysfunction. Organisms in the genus Mycobacterium are known to be aerobic and non-motile. Organisms within Mycobacterium belong to either the rapid growing group or the slow growing group. M. elephantis is classified as a rapid grower and relates most closely to Mycobacterium confluentis and Mycobacterium phlei.
Mycobacterium intermedium is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.

Mycobacterium kansasii is a bacterium in the Mycobacterium genus. It is an environmental bacteria that causes opportunistic infections in humans, and is one of the leading mycobacterial causes of human disease after tuberculosis and leprosy.
Mycobacterium malmoense is a Gram-positive bacterium from the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium moriokaense
Etymology: moriokaense, from Morioka, Japan where the organism was first isolated.
Mycobacterium nebraskense is a slow growing, yellow, pigmented mycobacterium that was first isolated from human sputum at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, in Omaha, Nebraska, USA. Mycobacterium species are common causes of pulmonary infections in both humans and animals.
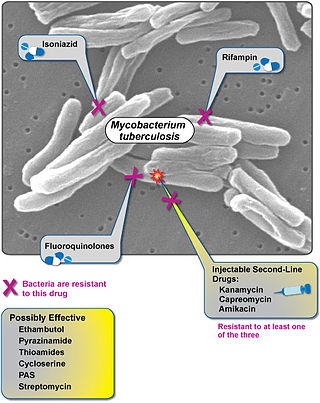
Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) is a form of tuberculosis caused by bacteria that are resistant to some of the most effective anti-TB drugs. XDR-TB strains have arisen after the mismanagement of individuals with multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a form of tuberculosis (TB) infection caused by bacteria that are resistant to treatment with at least two of the most powerful first-line anti-TB medications (drugs): isoniazid and rifampin. Some forms of TB are also resistant to second-line medications, and are called extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB).
Pilibacter is a genus of bacteria of the Enterococcaceae. This genus contains a single species, Pilibacter termitis, strains of which were isolated from a termite.
Gordonia araii is a Gram-positive and aerobic bacterium from the genus of Gordonia which has been isolated from human sputum in Japan.
Tsukamurella pulmonis is a Gram-positive and aerobic bacterium from the genus Tsukamurella which has been isolated from the sputum from a patient with lung tuberculosis in Germany.
Desmospora is a bacterial genus from the family of Thermoactinomycetaceae.
Gladiolin is a polyketide natural product produced by Burkholderia gladioli BCC0238 which is isolated from sputum of cystic fibrosis patients. It was found to be a novel macrolide antibiotic which presented an activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Gladiolin is structurally much more stable than its analogue etnangien as an efficient myxobacterial RNA polymerase inhibitor due to the lack of highly labile hexaene moiety in gladiolin. The good activity and high stability of gladiolin offers it the potential for further development as an antibiotic against antibiotic-resistant M. tuberculosis.
References
- 1 2 Parte, A.C. "Desmospora". LPSN .
- ↑ "Desmospora activa Taxon Passport - StrainInfo". www.straininfo.net. Archived from the original on 2016-11-14. Retrieved 2016-11-14.
- 1 2 "Desmospora activa". www.uniprot.org.
- ↑ "Details: DSM-45169". www.dsmz.de.
- ↑ Yassin, A. F.; Hupfer, H.; Klenk, H.-P.; Siering, C. (1 March 2009). "Desmospora activa gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermoactinomycete isolated from sputum of a patient with suspected pulmonary tuberculosis, and emended description of the family Thermoactinomycetaceae Matsuo et al. 2006". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 59 (3): 454–459. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.001362-0. PMID 19244421.
- ↑ Stephen, Dr. Berger (2015). GIDEON Guide to Medically Important Bacteria. GIDEON Informatics Inc. ISBN 978-1-4988-0429-5.