Related Research Articles
The Desulfobacteraceae are a family of Thermodesulfobacteriota. They reduce sulfates to sulfides to obtain energy and are strictly anaerobic. They have a respiratory and fermentative type of metabolism. Some species are chemolithotrophic and use inorganic materials to obtain energy and use hydrogen as their electron donor.
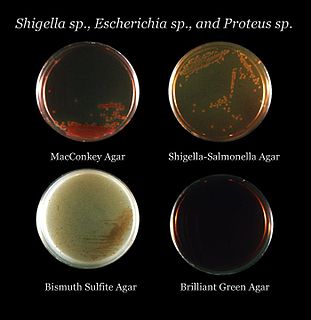
Bismuth sulfite agar is a type of agar media used to isolate Salmonella species. It uses glucose as a primary source of carbon. BLBG and bismuth stop gram-positive growth. Bismuth sulfite agar tests the ability to use ferrous sulfate and convert it to hydrogen sulfide.
Middlebrook 7H9 broth is a liquid growth medium specially used for culture of Mycobacterium species, notably Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Middlebrook 7H10 Agar is a solid growth medium specially used for culture of Mycobacterium, notably Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It has been reported that the 7H10 medium tends to grow fewer contaminants than the egg-based media commonly used for the cultivation of mycobacteria.
Desulfobacterium indolicum is an oval to rod-shaped, Gram-negative, non-sporing sulfate-reducing bacterium. Its type strain is In04. It is notable for its use of particular metabolic pathways, including desulfurization of diesel.
Desulfobacterium autotrophicum is a mesophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium. Its genome has been sequenced.
Desulfobacter curvatus is a sulfate-reducing bacteria, with type strain AcRM3.
Desulfotomaculum halophilum is a halophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium. It is endospore-forming, long, straight to curved rod-shaped and with type strain SEBR 3139T.
Streptomyces flaveus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil.
Acetitomaculum ruminis is a Gram-positive bacterium species from the genus of Acetitomaculum which has been isolated from the rumen of a bovine in the United States. Acetitomaculum ruminis utilize formate, glucose and CO2.
Methylorubrum thiocyanatum is a facultative methylotroph bacteria from the genus Methylorubrum which has been isolated from soil around the plant Allium aflatunense in Warwickshire in the United Kingdom.
Methylocystis heyeri is a Gram-negative, aerobic, methanotrophic and non-motile bacterium species from the genus of Methylocystis that has been isolated from Sphagnum peat in the Großer Teufelssee in Germany.
Desulfobacterium is a rod-shaped bacteria genus from the family of Desulfobacteraceae. Desulfobacterium occur widespread in brackish and marine sediments.
Desulfacinum is an acetate-oxidizing bacteria genus from the family of Syntrophobacteraceae.
Hymenobacter aerophilus is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Hymenobacter which has been isolated from airborne from the Museo Correr in Venice in Italy.
Thermonema rossianum is a thermophilic and halophilic bacterium from the genus of Thermonema which has been isolated from a saline hot springs in from the Bay of Naples in Italy.
Desulfotignum is a Gram-negative and strictly anaerobic bacteria with a single polar flagellum genus from the family of Desulfobacteraceae.
Desulfobacula toluolica is a Gram-negative and sulfate-reducing bacterium from the genus of Desulfobacula which has been isolated from marine mud in the United States.
Desulfococcus biacutus is a Gram-negative and strictly anaerobic bacterium from the genus of Desulfococcus which has been isolated from anaerobic digestor sludge in Germany.
Azorhizophilus paspali is a bacterium from the genus of Azorhizophilus which has been isolated from rhizosphere soil from the plant Paspalum notatum in Brazil.