Related Research Articles

An explosive is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances.

Mining is the extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. The ore must be a rock or mineral that contains valuable constituent, can be extracted or mined and sold for profit. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water.

Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula HNO3. It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% HNO3, it is referred to as fuming nitric acid. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%.

A shaped charge is an explosive charge shaped to focus the effect of the explosive's energy. Different types of shaped charges are used for various purposes such as cutting and forming metal, initiating nuclear weapons, penetrating armor, or perforating wells in the oil and gas industry.

Thermite is a pyrotechnic composition of metal powder and metal oxide. When ignited by heat or chemical reaction, thermite undergoes an exothermic reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction. Most varieties are not explosive, but can create brief bursts of heat and high temperature in a small area. Its form of action is similar to that of other fuel-oxidizer mixtures, such as black powder.

Reactive armour is a type of vehicle armour used in protecting vehicles, especially modern tanks, against shaped charges and hardened kinetic energy penetrators. The most common type is explosive reactive armour (ERA), but variants include self-limiting explosive reactive armour (SLERA), non-energetic reactive armour (NERA), non-explosive reactive armour (NxRA), and electric armour. NERA and NxRA modules can withstand multiple hits, unlike ERA and SLERA.
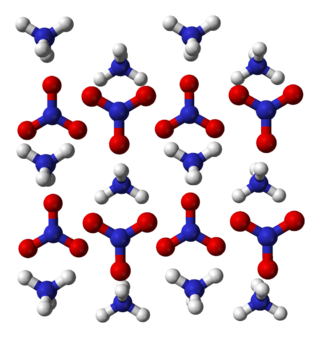
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula NH4NO3. It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer.

A shell, in a military context, is a projectile whose payload contains an explosive, incendiary, or other chemical filling. Originally it was called a bombshell, but "shell" has come to be unambiguous in a military context. A shell can hold a tracer.

Molybdenite is a mineral of molybdenum disulfide, MoS2. Similar in appearance and feel to graphite, molybdenite has a lubricating effect that is a consequence of its layered structure. The atomic structure consists of a sheet of molybdenum atoms sandwiched between sheets of sulfur atoms. The Mo-S bonds are strong, but the interaction between the sulfur atoms at the top and bottom of separate sandwich-like tri-layers is weak, resulting in easy slippage as well as cleavage planes. Molybdenite crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system as the common polytype 2H and also in the trigonal system as the 3R polytype.

A center-fire is a type of metallic cartridge used in firearms, where the primer is located at the center of the base of its casing. Unlike rimfire cartridges, the centerfire primer is typically a separate component seated into a recessed cavity in the case head and is replaceable by reloading the cartridge.
This article is a list of terms commonly used in the practice of metalworking – the science, art, industry, and craft of shaping metal.

IMI plc, formerly Imperial Metal Industries, is a British-based engineering company headquartered in Birmingham, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
Aging is a process by which an artwork, typically a painting or sculpture, is made to appear old. It is meant to emulate the natural deterioration that can occur over many decades or centuries. Although there may be "innocent" reasons for it, ageing is a technique very often used in art forgery.

Silver mining is the extraction of silver from minerals, starting with mining. Because silver is often found in intimate combination with other metals, its extraction requires elaborate technologies. In 2008, ca. 25,900 metric tons were consumed worldwide, most of which came from mining.

Worley Limited is an Australian engineering professional services company which provides project delivery and consulting services to the resources and energy sectors, and complex process industries.
Explosive forming is a metalworking technique in which an explosive charge is used instead of a punch or press. It can be used on materials for which a press setup would be prohibitively large or require an unreasonably high pressure, and is generally much cheaper than building a large enough and sufficiently high-pressure press; on the other hand, it is unavoidably an individual job production process, producing one product at a time and with a long setup time. There are various approaches; one is to place metal plate over a die, with the intervening space evacuated by a vacuum pump, place the whole assembly underwater, and detonate a charge at an appropriate distance from the plate. For complicated shapes, a segmented die can be used to produce in a single operation a shape that would require many manufacturing steps, or to be manufactured in parts and welded together with an accompanying loss of strength at the welds. There is often some degree of work hardening from the explosive-forming process, particularly in mild steel.
Evelyn Rosenberg is a New Mexico-based sculptor.

An explosion is a rapid expansion in volume of a given amount of matter associated with an extreme outward release of energy, usually with the generation of high temperatures and release of high-pressure gases. Explosions may also be generated by a slower expansion that would normally not be forceful, but is not allowed to expand, so that when whatever is containing the expansion is broken by the pressure that builds as the matter inside tries to expand, the matter expands forcefully. An example of this is a volcanic eruption created by the expansion of magma in a magma chamber as it rises to the surface. Supersonic explosions created by high explosives are known as detonations and travel through shock waves. Subsonic explosions are created by low explosives through a slower combustion process known as deflagration.

Explosion welding (EXW) is a solid state (solid-phase) process where welding is accomplished by accelerating one of the components at extremely high velocity through the use of chemical explosives. This process is often used to clad carbon steel or aluminium plate with a thin layer of a harder or more corrosion-resistant material. Due to the nature of this process, producible geometries are very limited. Typical geometries produced include plates, tubing and tube sheets.

Jerome Ackerman (1920–2019) and Evelyn Ackerman (1924–2012) were American industrial designers who jointly contributed to the aesthetic of California mid-century modern with their ceramics, wood carvings, mosaics, textiles, and enamels in home furnishings and architectural elements. The Ackermans sold their products through their companies Jenev and ERA Industries. Evelyn was an accomplished artist and an author of books on antique toys and dolls.
References
- ↑ Abatemarco, Michael (October 11, 2013). "Incendiary art: Evelyn Rosenberg's detonography". santafenewmexican.com. Retrieved 12 June 2017.