
The Gherkin, formally 30 St Mary Axe and previously known as the Swiss Re Building, is a commercial skyscraper in London's primary financial district, the City of London. It was completed in December 2003 and opened in April 2004. With 41 floors, it is 180 metres (591 ft) tall and stands on the sites of the former Baltic Exchange and Chamber of Shipping, which were extensively damaged in 1992 in the Baltic Exchange bombing by a device placed by the Provisional IRA in St Mary Axe, a narrow street leading north from Leadenhall Street.
In structural engineering, a tensile structure is a construction of elements carrying only tension and no compression or bending. The term tensile should not be confused with tensegrity, which is a structural form with both tension and compression elements. Tensile structures are the most common type of thin-shell structures.

The Shukhov Radio Tower, also known as the Shabolovka Tower, is a broadcasting tower deriving from the Russian avant-garde in Moscow designed by Vladimir Shukhov. The 160-metre-high (520 ft) free-standing steel diagrid structure was built between 1920 and 1922, during the Russian Civil War.

The Hearst Tower is a building at the southwest corner of 57th Street and Eighth Avenue, near Columbus Circle, in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City, United States. It is the world headquarters of media conglomerate Hearst Communications, housing many of its publications and communications companies. The Hearst Tower consists of two sections, with a total height of 597 feet (182 m) and 46 stories. The six lowest stories form the Hearst Magazine Building, designed by Joseph Urban and George B. Post & Sons, which was completed in 1928. Above it is the Hearst Tower addition, which was completed in 2006 and designed by Norman Foster.
The year 2006 in architecture involved some significant architectural events and new buildings.

Vladimir Grigoryevich Shukhov was a Russian and Soviet engineer-polymath, scientist and architect renowned for his pioneering works on new methods of analysis for structural engineering that led to breakthroughs in industrial design of the world's first hyperboloid structures, diagrid shell structures, tensile structures, gridshell structures, oil reservoirs, pipelines, boilers, ships and barges. He is also the inventor of the first cracking method.

The Canton Tower, formally Guangzhou TV Astronomical and Sightseeing Tower, is a 604-meter (1,982 ft)-tall multipurpose observation tower in the Haizhu District of Guangzhou. The tower was topped out in 2009 and it became operational on 29 September 2010 for the 2010 Asian Games. The tower briefly held the title of tallest tower in the world, replacing the CN Tower, before being surpassed by the Tokyo Skytree. It was the tallest structure in China prior to the topping out of the Shanghai Tower on 3 August 2013, and is now the second-tallest tower and the fifth-tallest freestanding structure in the world.

Hyperboloid structures are architectural structures designed using a hyperboloid in one sheet. Often these are tall structures, such as towers, where the hyperboloid geometry's structural strength is used to support an object high above the ground. Hyperboloid geometry is often used for decorative effect as well as structural economy. The first hyperboloid structures were built by Russian engineer Vladimir Shukhov (1853–1939), including the Shukhov Tower in Polibino, Dankovsky District, Lipetsk Oblast, Russia.

High-tech architecture, also known as structural expressionism, is a type of late modernist architecture that emerged in the 1970s, incorporating elements of high tech industry and technology into building design. High-tech architecture grew from the modernist style, utilizing new advances in technology and building materials. It emphasizes transparency in design and construction, seeking to communicate the underlying structure and function of a building throughout its interior and exterior. High-tech architecture makes extensive use of aluminium, steel, glass, and to a lesser extent concrete, as these materials were becoming more advanced and available in a wider variety of forms at the time the style was developing – generally, advancements in a trend towards lightness of weight.

The Shukhov Tower on the Oka River is the world’s only diagrid hyperboloid transmission tower. It is located in Russia, in the western suburbs of Nizhny Novgorod, on the left bank of the Oka River near Dzerzhinsk. The tower is one of several structures designed by Russian engineer and scientist Vladimir Shukhov; its power lines, however, were decommissioned in 1989.

The All-Russia industrial and art exhibition 1896 in Nizhny Novgorod was held from May 28 till October 1, 1896. The 1896 exhibition was the largest pre-revolution exhibition in the Russian Empire and was organized with money allotted by Nicholas II, Emperor of Russia. The All-Russia industrial conference was held together with the exhibition.

A gridshell is a structure which derives its strength from its double curvature, but is constructed of a grid or lattice.

The Shukhov Tower in Polibino, designed in 1896 by Russian engineer and architect Vladimir Shukhov, is the world's first diagrid hyperboloid structure. The tower is today located in the former estate of Yury Nechaev-Maltsov in the selo of Polibino in Lipetsk Oblast in Russia.
Tekla Structures is a building information modeling software able to model structures that incorporate different kinds of building materials, including steel, concrete, timber and glass. Tekla allows structural drafters and engineers to design a building structure and its components using 3D modeling, generate 2D drawings and access building information. Tekla Structures was formerly known as Xsteel.

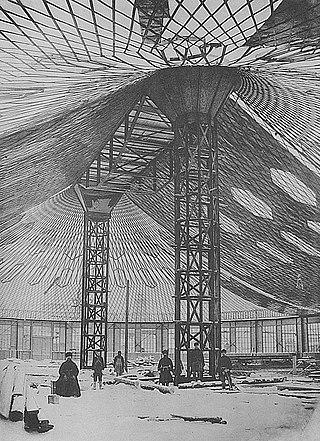
Shukhov Rotunda was a round exhibition pavilion built for All-Russia Exhibition 1896 in Nizhny Novgorod, Russia. It was built in 1896 with a diagrid hanging cover and was the world's first Hyperboloid structure. It is named after Vladimir Shukhov, who designed it in 1895.

Capital Gate, also known as the Leaning Tower of Abu Dhabi, is a skyscraper in Abu Dhabi that is over 160 meters (520 ft) tall, 35 stories high, with over 16,000 square meters (170,000 sq ft) of usable office space. Capital Gate is one of the tallest buildings in the city and was designed to incline 18° west, more than four times the lean of the Leaning Tower of Pisa. The building is owned and was developed by the Abu Dhabi National Exhibitions Company. The tower is the focal point of Capital Centre.

The Aldar Headquarters building is the first circular building of its kind in the Middle East. It is located in Al Raha, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.

A shell is a three-dimensional solid structural element whose thickness is very small compared to its other dimensions. It is characterized in structural terms by mid-plane stress which is both coplanar and normal to the surface. A shell can be derived from a plate in two steps: by initially forming the middle surface as a singly or doubly curved surface, then by applying loads which are coplanar to the plate's plane thus generating significant stresses. Materials range from concrete to fabric.



















