
The geography of Iraq is diverse and falls into five main regions: the desert, Upper Mesopotamia, the northern highlands of Iraq, Lower Mesopotamia, and the alluvial plain extending from around Tikrit to the Persian Gulf.
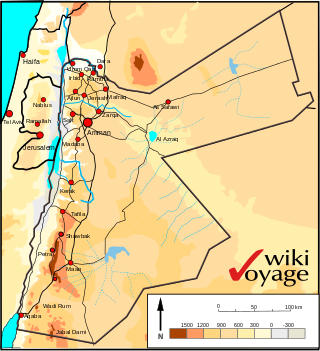
Jordan is situated geographically in West Asia, south of Syria, west of Iraq, northwest of Saudi Arabia, east of Israel and the Palestinian territory of the West Bank. The area is also referred to as the Middle or Near East. The territory of Jordan now covers about 91,880 square kilometres (35,480 sq mi).

Kuwait is a country in West Asia, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iraq and Saudi Arabia. Kuwait is located at the far northwestern corner of the Persian Gulf. Kuwait is 17,820 square kilometres in size. At its most distant points, it is about 200 km (120 mi) north to south, and 170 km (110 mi) east to west. Kuwait has 10 islands. Kuwait's area consists mostly of desert.

Qatar is a peninsula in the east of Arabia, bordering the Persian Gulf and Saudi Arabia, in a strategic location near major petroleum and natural gas deposits. The State of Qatar occupies 11,571 km2 (4,468 sq mi) on a peninsula that extends approximately to 160 km (99 mi) north into the Persian Gulf from the Arabian Peninsula.

The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is a country situated in West Asia, the largest country on the Arabian Peninsula, bordering the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea. Its extensive coastlines provide great leverage on shipping through the Persian Gulf and the Suez Canal. The kingdom occupies 80% of the Arabian Peninsula. Most of the country's boundaries with the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Oman, and the Republic of Yemen are undefined, so the exact size of the country remains unknown. The Saudi government estimate is at 2,217,949 square kilometres, while other reputable estimates vary between 2,149,690 and 2,240,000 sq. kilometres. Less than 7% of the total area is suitable for cultivation, and in the early 1960s, population distribution varied greatly among the towns of the eastern and western coastal areas, the densely populated interior oases, and the vast, almost empty deserts.

The Arabian Peninsula, or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. At 3,237,500 km2 (1,250,000 sq mi), the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.

King Khalid Military City (KKMC) is a cantonment in northeastern Saudi Arabia, approximately 60 km south of Hafar al-Batin city. Constructed during the 1970s and 1980s, the city was designed and built by the Middle East Division, a unit of the United States Army Corps of Engineers. Consulting firms involved in its construction include Brown, Daltas, and Associates, as well as LeMessurier in Cambridge, Massachusetts. KKMC was established to accommodate several brigades of Saudi troops and a population of 65,000 individuals. It is named after the former Saudi King Khalid bin Abdul Aziz.

Ras al-Khafji or Khafji (الخفجي) is a town on the border between Saudi Arabia and Kuwait. It lies in what was before 1970 the Saudi Arabian–Kuwaiti neutral zone.
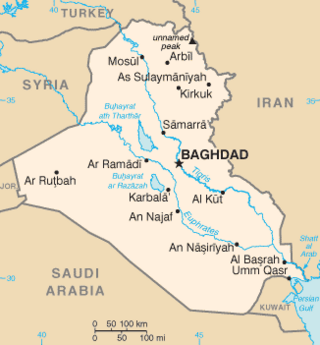
The Iraq–Saudi Arabia border is 811 km (504 mi) in length and runs from the tripoint with Jordan in the west to the tripoint with Kuwait in the east.

Wadi al-Batin is an intermittent river in Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and Kuwait. It is the lowest and final section of Wadi al-Rummah. It runs 45 mi (72 km) in a northeast–southwest direction through the Al-Dibdibah plain and has been recognized since 1913 as the border between Kuwait and Iraq.

Hafar al-Batin, also frequently spelled Hafr al-Batin, is a city in the Hafar al-Batin Governorate, Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. It is located 430 km north of Riyadh, 94.2 km from the Kuwait border, and about 74.3 from the Iraq border. The city lies in the dry valley of the Wadi al-Batin, which is part of the longer valley of the river Wadi al-Rummah, which leads inland toward Medina and formerly emptied into the Persian Gulf.

The Hijaz Mountains (Arabic: جِبَال ٱلْحِجَاز, romanized: Jibāl al-Ḥijāz or "Hejaz Range" is a mountain range located in the Hejazi region of western Saudi Arabia. The range runs north and south along the eastern coast of the Red Sea, and can thus be treated as including the Midian Mountains, and being part of the Sarawat Mountains, broadly speaking.
The Peninsula Shield Force is the military arm of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). It is intended to deter, and respond to military aggression against any of the GCC member countries: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates.

Wadi al-Rummah or ar-Rummah is one of the Arabian Peninsula's longest river valleys, at a length of almost 600 km (370 mi). Now mostly dry and partly blocked by encroaching sand dunes, the wadi rises near Medina at Jibāl al Abyaḑ. It then runs northeast, joining several smaller wadis; among them are Mohalla Wadi and Murghala Wadi to the north and Jifn Wadi and Jarir Wadi to the south. It ends at the Thuayrat Dunes of the ad-Dahna Desert in Al-Qassim Province, near Buraidah.
The geology of Saudi Arabia includes Precambrian igneous and metamorphic basement rocks, exposed across much of the country. Thick sedimentary sequences from the Phanerozoic dominate much of the country's surface and host oil.

The Iraq–Kuwait border is 254 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Saudi Arabia in the west to the Persian Gulf coast in the east.

The Kuwait–Saudi Arabia border is 221 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Iraq in the west to the Persian Gulf coast in the east.

The Arabian-Persian Gulf Coastal Plain Desert ecoregion covers the desert coastal plain of the northwest Persian Gulf, that is, on the northeast Arabian Peninsula, from Kuwait in the north to a small coastal sector in the United Arab Emirates to the southeast.



















