
Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump. Their beneficial medical uses are as treatments for congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias; however, their relative toxicity prevents them from being widely used. Most commonly found as secondary metabolites in several plants such as foxglove plants, these compounds nevertheless have a diverse range of biochemical effects regarding cardiac cell function and have also been suggested for use in cancer treatment.

Erysimum, or wallflower, is a genus of flowering plants in the cabbage family, Brassicaceae. It includes more than 150 species, both popular garden plants and many wild forms. The genus Cheiranthus is sometimes included here in whole or in part. Erysimum has since the early 21st century been ascribed to a monogeneric cruciferous tribe, Erysimeae, characterised by sessile, stellate (star-shaped) and/or malpighiaceous (two-sided) trichomes, yellow to orange flowers and multiseeded siliques.

Asclepias tuberosa, commonly known as butterfly weed, is a species of milkweed native to eastern and southwestern North America. It is commonly known as butterfly weed because of the butterflies that are attracted to the plant by its color and its copious production of nectar.

The monarch butterfly or simply monarch is a milkweed butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. Other common names, depending on region, include milkweed, common tiger, wanderer, and black-veined brown. It is amongst the most familiar of North American butterflies and an iconic pollinator, although it is not an especially effective pollinator of milkweeds. Its wings feature an easily recognizable black, orange, and white pattern, with a wingspan of 8.9–10.2 cm (3.5–4.0 in). A Müllerian mimic, the viceroy butterfly, is similar in color and pattern, but is markedly smaller and has an extra black stripe across each hindwing.

Asclepias is a genus of herbaceous, perennial, flowering plants known as milkweeds, named for their latex, a milky substance containing cardiac glycosides termed cardenolides, exuded where cells are damaged. Most species are toxic to humans and many other species, primarily due to the presence of cardenolides, although, as with many such plants, there are species that feed upon them and from them. Most notable are monarch butterflies, who use and require certain milkweeds as host plants for their larvae.

Cerberin is a type of cardiac glycoside, a steroidal class found in the seeds of the dicotyledonous angiosperm genus Cerbera; including the suicide tree and the sea mango. This class includes digitalis-like agents, channel-blockers that as a group have found historic uses as cardiac treatments, but which at higher doses are extremely toxic; in the case of cerberin, consumption of the C. odollam results in poisoning with presenting nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, often leading to death. The natural product has been structurally characterized, its toxicity is clear—it is often used as an intentional human poison in third-world countries, and accidental poisonings with fatalities have resulted from individuals even indirectly consuming the agent—but its potentially therapeutic pharmacologic properties are very poorly described.

Danaus chrysippus, also known as the plain tiger, African queen, or African monarch, is a medium-sized butterfly widespread in Asia, Australia and Africa. It belongs to the Danainae subfamily of the brush-footed butterfly family Nymphalidae. Danainae primarily consume plants in the genus Asclepias, more commonly called milkweed. Milkweed contains toxic compounds, cardenolides, which are often consumed and stored by many butterflies. Because of their emetic properties, the plain tiger is unpalatable to most predators. As a result, its coloration is widely mimicked by other species of butterflies. The plain tiger inhabits a wide variety of habitats, although it is less likely to thrive in jungle-like conditions and is most often found in drier, wide-open areas.

The queen butterfly is a North and South American butterfly in the family Nymphalidae with a wingspan of 80–85 mm. It is orange or brown with black wing borders and small white forewing spots on its dorsal wing surface, and reddish ventral wing surface fairly similar to the dorsal surface. The ventral hindwings have black veins and small white spots in a black border. The male has a black androconial scent patch on its dorsal hindwings. It can be found in meadows, fields, marshes, deserts, and at the edges of forests.
A Norrish reaction in organic chemistry is a photochemical reaction taking place with ketones and aldehydes. Such reactions are subdivided into Norrish type I reactions and Norrish type II reactions. The reaction is named after Ronald George Wreyford Norrish. While of limited synthetic utility these reactions are important in the photo-oxidation of polymers such as polyolefins, polyesters, certain polycarbonates and polyketones.

A cardenolide is a type of steroid. Many plants contain derivatives, collectively known as cardenolides, including many in the form of cardenolide glycosides (cardenolides that contain structural groups derived from sugars). Cardenolide glycosides are often toxic; specifically, they are heart-arresting. Cardenolides are toxic to animals through inhibition of the enzyme Na+/K+‐ATPase, which is responsible for maintaining the sodium and potassium ion gradients across the cell membranes.
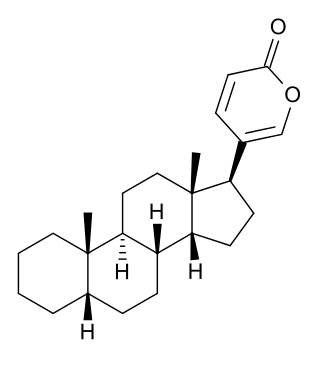
Bufadienolide is a chemical compound with steroid structure. Its derivatives are collectively known as bufadienolides, including many in the form of bufadienolide glycosides. These are a type of cardiac glycoside, the other being the cardenolide glycosides. Both bufadienolides and their glycosides are toxic; specifically, they can cause an atrioventricular block, bradycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and possibly lethal cardiac arrest.

The black-eared mouse, or black-eared deer mouse, is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae, native to North America.

Gitoformate is a cardiac glycoside, a type of drug that can be used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmia. Produced by Madaus, it is not available in the US, and does not seem to be available in Europe either.
In enzymology, a 3beta-hydroxy-5beta-steroid dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.277) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Erysimum cheiranthoides, the treacle-mustard,wormseed wallflower, or wormseed mustard is a species of Erysimum native to most of central and northern Europe and northern and central Asia. Like other Erysimum species, E. cheiranthoides accumulates two major classes of defensive chemicals, glucosinolates and cardiac glycosides.
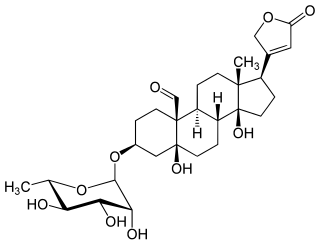
Convallatoxin is a glycoside extracted from Convallaria majalis.
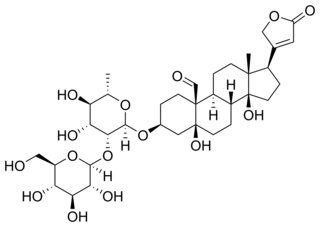
Neoconvalloside is a cardenolide glycoside extracted from Convallaria majalis.

Digitalis ciliata, commonly called hairy foxglove is a member of the genus Digitalis. It has thimble-shaped, yellow to cream colored flowers produced on perennial plants with evergreen foliage. It is native to the Caucasus and is grown as an ornamental in other parts of the world. The species name is derived from the fine hairs that cover the plants stems and flowers.

Calotropin is a toxic cardenolide found in plants in the family Asclepiadoideae. In extreme cases, calotropin poisoning can cause respiratory and cardiac failure. Accidental poisoning is common in livestock who have ingested milkweed. Calotropin is commonly stored as a defense mechanism by insects that eat milkweeds as their main food source.

Erysimum crepidifolium, the pale wallflower, is a plant species in the crucifer family, Brassicaceae. It is a member of the genus Erysimum, which includes between 150 and 350 species in the Northern Hemisphere.


















