| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
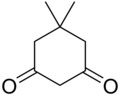
| Preferred IUPAC name 5,5-Dimethylcyclohexane-1,3-dione | |||
| Other names Cyclomethone, 5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione, Dimethyldihydroresorcinol, Methone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.369 | ||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H12O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 140.182 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Melting point | 147 to 150 °C (297 to 302 °F; 420 to 423 K) (decomposes) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Dimedone is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C(CH2)2(CO)2(CH2). Classified as a cyclic diketone, it is a derivative of 1,3-cyclohexanedione. It is a white solid that is soluble in water, as well as ethanol and methanol. It once was used as a reagent to test for the aldehyde functional group.