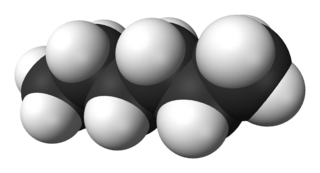
Hexane or n-hexane is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane with six carbon atoms and has the molecular formula C6H14.

Cyclohexanol is the organic compound with the formula HOCH(CH2)5. The molecule is related to cyclohexane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by a hydroxyl group. This compound exists as a deliquescent colorless solid with a camphor-like odor, which, when very pure, melts near room temperature. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.

Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida. As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an animal cell. Coccidian parasites infect the intestinal tracts of animals, and are the largest group of apicomplexan protozoa.

Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH3CO2CH2CH3, simplified to C4H8O2. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and in the decaffeination process of tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent.

Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.

p-Xylene (para-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The p- stands for para-, indicating that the two methyl groups in p-xylene occupy the diametrically opposite substituent positions 1 and 4. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, o-xylene and m-xylene. All have the same chemical formula C6H4(CH3)2. All xylene isomers are colorless and highly flammable. The odor threshold of p-xylene is 0.62 parts per million (ppm).
Coccidiosis is a parasitic disease of the intestinal tract of animals caused by coccidian protozoa. The disease spreads from one animal to another by contact with infected feces or ingestion of infected tissue. Diarrhea, which may become bloody in severe cases, is the primary symptom. Most animals infected with coccidia are asymptomatic, but young or immunocompromised animals may suffer severe symptoms and death.
Eimeria acervulina is a species of Eimeria that causes coccidiosis in poultry worldwide. Affected birds tend to appear depressed with reduced appetite, diarrhea, and depigmentation. Diagnosis is made by necropsy based on lesions in the upper third of the small intestine, and the appearance of white or grey striations along the intestinal mucosa. Scrapings of the mucosa from diseased birds can reveal oocysts.

Eimeria tenella is a species of Eimeria that causes hemorrhagic cecal coccidiosis in young poultry. It is found worldwide.

Eimeria is a genus of apicomplexan parasites that includes various species capable of causing the disease coccidiosis in animals such as cattle, poultry and smaller ruminants including sheep and goats. Eimeria species are considered to be monoxenous because the life cycle is completed within a single host, and stenoxenous because they tend to be host specific, although a number of exceptions have been identified. Species of this genus infect a wide variety of hosts. Thirty-one species are known to occur in bats (Chiroptera), two in turtles, and 130 named species infect fish. Two species infect seals. Five species infect llamas and alpacas: E. alpacae, E. ivitaensis, E. lamae, E. macusaniensis, and E. punonensis. A number of species infect rodents, including E. couesii, E. kinsellai, E. palustris, E. ojastii and E. oryzomysi. Others infect poultry, rabbits and cattle. For full species list, see below.

Hydrogen selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula H2Se. This hydrogen chalcogenide is the simplest and most commonly encountered hydride of selenium. H2Se is a colorless, flammable gas under standard conditions. It is the most toxic selenium compound with an exposure limit of 0.05 ppm over an 8-hour period. Even at extremely low concentrations, this compound has a very irritating smell resembling that of decayed horseradish or 'leaking gas', but smells of rotten eggs at higher concentrations.
Eimeria necatrix is a species of Eimeria that causes very severe intestinal coccidiosis in older poultry characterized by congestion, hemorrhage, necrosis of the intestine and bloody feces. Very large schizonts can be seen as white or yellow dots and oocysts can be found occasionally in the ceca.
Eimeria brunetti is a species of Eimeria that causes hemorrhagic intestinal coccidiosis in poultry worldwide. Lesions are limited to lower small intestine.

Ethopabate is a coccidiostat used in poultry.
Nicarbazin is a coccidiostat used on meat chickens. It is also used as a contraceptive for population control of Canada geese and feral pigeons.

Pediococcus acidilactici is a species of Gram-positive cocci that is often found in pairs or tetrads. P. acidilactici is a homofermentative bacterium that can grow in a wide range of pH, temperature, and osmotic pressure, therefore being able to colonize the digestive tract. It has emerged as a potential probiotic that has shown promising results in animal and human experiments, though some of the results are limited. They are commonly found in fermented vegetables, fermented dairy products, and meat.
Growell India is a multinational feed additive company headquartered in Pune, Maharashtra, India. Growell India manufactures and exports phytogenic feed additives for livestock. The company is a pioneer in phytogenic feed additives and has established a strong presence worldwide since its inception in 1995.
Eimeria zuernii is a species of the parasite Eimeria that causes diarrheic disease known as eimeriosis in cattle, and mainly affects younger animals. The disease is also commonly referred to as coccidiosis. The parasite can be found in cattle around the globe.
Eimeria arlongi is a species of Eimeria that causes clinical coccidiosis in goats. It and Eimeria ninakohlyakimovae are two of the most pathogenic species for goats. It is particularly prevalent in goat kids in Iran. Issues with coccidiosis specifically due to Eimeria arloingi have also been reported in Egypt and Portugal. It is unclear whether this species is present in the Americas as most of the case reports of coccidiosis in these areas do not differentiate the species causing the disease. Infections with this species are commonly compounded by infections with other Eimeria species in "mixed infections." This species is closely related to Eimeria bovis and Eimeria zuernii which are both highly pathogenic in cattle' Infections with this species are characterized by lesions specifically in the jejunum, but also the ilium and cecum which results in diarrhea. Oocysts begin shedding between 16 and 18 days after the animal is infected which is when the parasite is spread. The shedding can last as long as 15 days. This parasite causes an immune response in its host that includes accumulation of fluid in body cavities, presence of large numbers of leukocytes in the small intestine, and necrosis of the tissue of the small intestine. Pale yellow plaques can be seen on the small intestine of severely affected kids at necropsy.
Eimeria bovis is a parasite belonging to the genus Eimeria and is found globally. The pathogen can cause a diarrheic disease in cattle referred to as either eimeriosis or coccidiosis. The infection predominantly cause disease in younger animals.