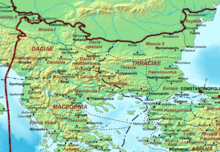
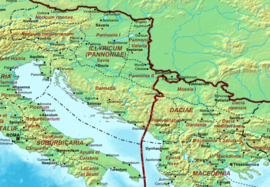
Moesia was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballia'. It included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia, Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine.

Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous province of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians and Celts, it was conquered by the Romans in the 1st century BC and subsequently became the capital of the Roman province of Pannonia Inferior. In 294 AD, Sirmium was proclaimed one of four capitals of the Roman Empire. It was also the capital of the Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum and of Pannonia Secunda. The site is protected as an archaeological Site of Exceptional Importance. The modern region of Syrmia was named after the city.

In Roman literature of the early 1st century CE, the Moesi appear as a Paleo-Balkan people who lived in the region around the Timok River to the south of the Danube. The Moesi do not appear in ancient sources before Augustus's death in 14 CE and are mentioned only by three authors dealing with the Roman warfare in the region and the ethnonymic situation between mid-1st century BC and mid-1st century CE: Ovid, Strabo and Livy. Recent research suggests that a Paleo-Balkan people known as the Moesi never actually existed but the name was transplanted from Asia Minor Mysians to the Balkans by the Romans as an alternative name for the people who lived in the later province of Moesia Superior as Dardani communities. This decision in Roman literature is linked to the appropriation of the name Dardani in official Roman ideological discourse as Trojan ancestors of the Romans and the creation of a fictive name for the actual Dardani who were seen as barbarians and antagonists of Rome in antiquity.

The praetorian prefecture of Illyricum was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided.
Justiniana Prima was an Eastern Roman city that existed from 535 to 615 CE, near modern Lebane in the Leskovac region, Serbia. It is currently an archaeological site. Founded by Emperor Justinian I (527-565), it was the metropolitan seat of the newly founded Archbishopric of Justiniana Prima, which became the main church administrative body of the central Dardania with jurisdiction from Praevalitana to Dacia Ripensis. Justinian Prima was originally designed to become the capital of the prefecture of Illyricum, but for reasons likely related with its status near the Roman frontiers of the 6th century CE, Thessaloniki was preferred. It was abandoned less than 100 years after its foundation.

Pannonia Secunda was one of the provinces of the Roman Empire. It was formed in 296 AD, during the reign of Emperor Diocletian. The capital of the province was Sirmium. Pannonia Secunda comprised parts of present-day Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina.

Dacia Ripensis was the name of a Roman province in the northern Balkan peninsula, immediately south of the Middle Danube. Its capital was Ratiaria. It was a district less urban than neighbouring Dacia Mediterranea and more militarized; "military camps and forts, rather than cities, were typical of the province". Besides Ratiaria, Oescus was the major settlement.

Dacia Mediterranea was a late antique Roman province, whose capital city was Serdica.

Dacia Aureliana was a province in the eastern half of the Roman Empire established by Roman Emperor Aurelian in the territory of former Moesia Superior after his evacuation of Dacia Traiana beyond the Danube in 271. Between 271/275 and 285, it occupied most of what is today northwestern Bulgaria and eastern Serbia. Its capital was in Serdica.

Praevalitana was a Late Roman province that existed between c. 284 and c. 600. It included parts of present-day Montenegro, Albania, and part of present-day Kosovo. Its capital city was Doclea, later Scodra.
Maurice's Balkan campaigns were a series of military expeditions conducted by Roman Emperor Maurice in an attempt to defend the Balkan provinces of the Roman Empire from the Avars and the South Slavs. Maurice was the only East Roman emperor, other than Anastasius I, who did his best to implement determined Balkan policies during Late Antiquity by paying adequate attention to the safety of the northern frontier against barbarian incursions. During the second half of his reign, the Balkan campaigns were the main focus of Maurice's foreign policies, as a favourable peace treaty with Persian Empire in 591 enabled him to shift his experienced troops from the Persian front to the region. The refocusing of Roman efforts soon paid off: the frequent Roman failures before 591 were succeeded by a string of successes afterwards.

Dardania was a Roman province in the Central Balkans, initially an unofficial region in Moesia (87–284), and then a province administratively part of the Diocese of Moesia (293–337). It was named after the tribe of the Dardani who inhabited the region in classical antiquity prior to the Roman conquest. During the late Imperial period the Dardanian territory was the homeland of many Roman emperors, notably Constantine the Great and Justinian I.

Ratiaria was a city founded by the Moesians, a Daco-Thracian tribe, in the 4th century BC, along the river Danube. In Roman times it was named Colonia Ulpia Traiana Ratiaria.

Much of the territory of the modern state of Serbia was part of the Roman Empire and later the Eastern Roman Empire. In particular, the region of Central Serbia was under Roman rule for about 800 years, starting from the 1st century BC, interrupted by the arrival of the Slavs into the Balkans during the 6th century, but continued after fall of the First Bulgarian Empire in the early 11th century and permanently ended with the rise of the Second Bulgarian Empire in the late 12th century. The territories were administratively divided into the provinces of Moesia, Pannonia and Dardania. Moesia Superior roughly corresponds to modern Serbia proper; Pannonia Inferior included the eastern part of Serbia proper; Dardania included the western part of Serbia proper. After its reconquest from the Bulgarians by Emperor Basil II in 1018, it was reorganized into the Theme of Bulgaria.

Archbishopric of Justiniana Prima was a Christian autonomous Archbishopric with see in the city of Justiniana Prima and jurisdiction over the Late Roman Diocese of Dacia in central parts of the Southeastern Europe.

The Diocese of Moesia was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, in the area of modern western Bulgaria, central Serbia, Montenegro, Albania, North Macedonia, and Greece.

Moesia Prima was a frontier province of the Late Roman Empire, situated in the central parts of present-day Serbia, along the south bank of the Danube River. Provincial capital was Viminacium, near modern Kostolac in Serbia).

The Eparchy of Niš is an eparchy (diocese) of the Serbian Orthodox Church with its seat in Niš, in Serbia. It has jurisdiction over the south-eastern regions of Serbia. Since 2017, Serbian Orthodox Bishop of Niš is Arsenije Glavčić.

The Metropolitanate of Skopje is an Eastern Orthodox eparchy, formerly under the jurisdiction of the Orthodox Ohrid Archbishopric, an autonomous and canonical branch of the Serbian Orthodox Church in North Macedonia. Its seat is in Skopje. It is a metropolitan diocese of the Orthodox Ohrid Archbishopric, headed by Archbishop Jovan Vraniškovski of Ohrid, who is also styled Metropolitan of Skopje.