
Mistletoe is the common name for obligate hemiparasitic plants in the order Santalales. They are attached to their host tree or shrub by a structure called the haustorium, through which they extract water and nutrients from the host plant.

The genus Arceuthobium, commonly called dwarf mistletoes, is a genus of 26 species of parasitic plants that parasitize members of Pinaceae and Cupressaceae in North America, Central America, Asia, Europe, and Africa. Of the 42 species that have been recognized, 39 and 21 of these are endemic to North America and the United States, respectively. They all have very reduced shoots and leaves with the bulk of the plant living under the host's bark. Recently the number of species within the genus has been reduced to 26 as a result of more detailed genetic analysis.

Arceuthobium americanum is a species of dwarf mistletoe known as American dwarf mistletoe and lodgepole-pine dwarf mistletoe. It is a common plant of western North America where it lives in high elevation pine forests. It is a parasitic plant which lives upon the Lodgepole Pine, particularly the subspecies Pinus contortus ssp. murrayana, the Tamarack Pine. This pine subspecies is most common in the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada. The American dwarf mistletoe is a yellow-green coral-shaped structure above the surface of the tree's bark, while most of the parasite is beneath the bark. The seeds mature in late summer and disperse to nearby trees. This species has been found to explosively-disperse its seeds through thermogenesis.
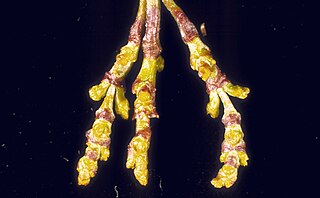
Arceuthobium campylopodum is a species of dwarf mistletoe known as western dwarf mistletoe. It is native to the low to moderate elevation coniferous forests of western North America. It is a common parasite of several species of pine tree, including Jeffrey Pine, Ponderosa Pine, and Coulter Pine. The dwarf mistletoe is a greenish-yellow structure above the bark of the tree, while most of the plant is beneath the bark. Seeds mature during the fall and disperse to nearby trees.

Arceuthobium divaricatum is a species of dwarf mistletoe known as pinyon dwarf mistletoe.
Arceuthobium littorum is a species of dwarf mistletoe known as coastal dwarf mistletoe. It is endemic to the coastline of northern California, where it lives as a parasite on Bishop Pine and Monterey Pine trees. This is a dark brown or greenish shrub which is visible as a network of scaly stems extending above the bark of its host tree. Most of the mistletoe is located inside the host tree, attached to it via haustoria, which tap the tree for water and nutrients. The leaves of the mistletoe are reduced to scales on its surface.
Arceuthobium siskiyouense is a species of dwarf mistletoe known as knobcone pine dwarf mistletoe. It is endemic to the Klamath Mountains of northern California and southern Oregon, where it lives as a parasite on knobcone pine trees. This is a brownish shrub which is visible as a network of scaly stems extending above the bark of its host tree. Most of the mistletoe is located inside the host tree, attached to it via haustoria, which tap the tree for water and nutrients. The leaves of the mistletoe are reduced to scales on its surface.
Arceuthobium monticola is a species of dwarf mistletoe known as western white pine dwarf mistletoe. It is endemic to the Klamath Mountains of northern California and southern Oregon, where it lives as a parasite on western white pine trees.

Arceuthobium oxycedri, juniper dwarf mistletoe, is a hemiparasite of the family Santalaceae. It parasitizes members of the genus Juniperus, especially Juniperus oxycedrus and Juniperus communis.
Arceuthobium gillii, common name "Chihuahua pine dwarf mistletoe," is a parasitic plant found in Arizona, New Mexico, Chihuahua, Sonora and Sinaloa. It is found mostly on the Chihuahua pine, Pinus leiophylla var. chihuahuana.
Arceuthobium microcarpum, called the "western spruce dwarf mistletoe," is a parasitic plant known only from Arizona and New Mexico. It is found mostly on spruce trees but also occasionally on Rocky Mountain bristlecone pine. The specific epithet "microcarpum" means "small fruited," in reference to the berries, which are only 3.5 mm long.

Arceuthobium vaginatum, called the "sheathed dwarf mistletoe" or "southwestern dwarf mistletoe" is a parasitic plant found in the southwestern United States and northwestern and central Mexico. It generally is found on pine trees.
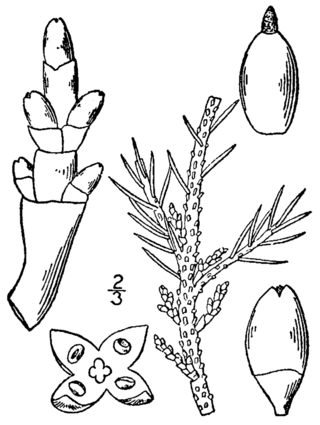
Arceuthobium pusillum is a perennial, obligate parasitic plant in the sandalwood family. Its common names include Dwarf mistletoe or Eastern dwarf mistletoe. It is one of the most widespread dwarf mistletoes within its range which covers the eastern United States and Canada, from Saskatchewan to Nova Scotia and New Jersey. The species name "pusillum" derives from Latin "pusillus", meaning very small.

The Ziarat Juniper Forest is a juniper forest in Ziarat, Balochistan, Pakistan.

Daniel Lee Nickrent is an American botanist, working in plant evolutionary biology, including the subdisciplines of genomics, phylogenetics, systematics, population genetics, and taxonomy. A major focus has been parasitic flowering plants, particularly of the sandalwood order (Santalales). His interest in photographic documentation and photographic databases has led to several photographic databases including Parasitic Plant Connection, Phytoimages, Plant Checklist for the Rocky Mountain National Park, and Plant Checklist for the Crab Orchard National Wildlife Refuge.
Lake Shore Gill was a botanist and forest pathologist for the U.S. Department of Agriculture. He was a definitive authority on the genus Arceuthobium.

Arceuthobium minutissimum, known as the Indian dwarf mistletoe or Himalayan dwarf mistletoe, is a leafless parasitic plant of Pinus wallichiana. It is considered the smallest known dicotyledonous plant.










