
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Turkey, Bulgaria, Romania, Ukraine, Russia and Georgia. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper and Don. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe.

Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single-celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker's five-kingdom system, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae. Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine, are photosynthetic, and exist in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean.

The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta, are a clade of algae.

Coccoliths are individual plates or scales of calcium carbonate formed by coccolithophores and cover the cell surface arranged in the form of a spherical shell, called a coccosphere.

Emiliania huxleyi is a species of coccolithophore found in almost all ocean ecosystems from the equator to sub-polar regions, and from nutrient rich upwelling zones to nutrient poor oligotrophic waters. It is one of thousands of different photosynthetic plankton that freely drift in the photic zone of the ocean, forming the basis of virtually all marine food webs. It is studied for the extensive blooms it forms in nutrient-depleted waters after the reformation of the summer thermocline. Like other coccolithophores, E. huxleyi is a single-celled phytoplankton covered with uniquely ornamented calcite disks called coccoliths. Individual coccoliths are abundant in marine sediments although complete coccospheres are more unusual. In the case of E. huxleyi, not only the shell, but also the soft part of the organism may be recorded in sediments. It produces a group of chemical compounds that are very resistant to decomposition. These chemical compounds, known as alkenones, can be found in marine sediments long after other soft parts of the organisms have decomposed. Alkenones are most commonly used by earth scientists as a means to estimate past sea surface temperatures.

Giuseppe Antonio Risso, called Antoine Risso, was a Niçard and naturalist.
Typhis tubifer is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Muricidae, the murex snails or rock snails.

Typhis is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Muricidae, the murex snails or rock snails.

Trochus tubiferus is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Marine biogenic calcification is the process by which marine organisms such as oysters and clams form calcium carbonate. Seawater is full of dissolved compounds, ions and nutrients that organisms can use for energy and, in the case of calcification, to build shells and outer structures. Calcifying organisms in the ocean include molluscs, foraminifera, coccolithophores, crustaceans, echinoderms such as sea urchins, and corals. The shells and skeletons produced from calcification have important functions for the physiology and ecology of the organisms that create them.

Syracosphaera azureaplaneta is a species of coccolithophore. This oceanic phytoplankton is not common, but is widely distributed and is known to occur in all the major seas, from tropical to sub-arctic regions. It is named after the BBC TV documentary series, The Blue Planet.
Rappephyceae, or Rappemonads, are a small family of protists first described in 2011, of uncertain phylogenic affinity. It has been discussed as a possible member of a larger clade Haptophyta. This newly identified taxonomic class of phytoplankton are named after a professor from the Hawai’i institute of marine biology, known as Michael Rappé. Rappé discovered these phytoplankton in the Atlantic Ocean and published his findings on their DNA in 1998. Current research has shown that these organisms provide an immense amount of nutritional organic molecules, such as oxygen, for other organisms using biochemical processes like photosynthesis and carbon fixation.

Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of organic compounds from atmospheric or dissolved carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are called primary producers or autotrophs.

Marine protists are defined by their habitat as protists that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. Life originated as marine single-celled prokaryotes and later evolved into more complex eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are the more developed life forms known as plants, animals, fungi and protists. Protists are the eukaryotes that cannot be classified as plants, fungi or animals. They are mostly single-celled and microscopic. The term protist came into use historically as a term of convenience for eukaryotes that cannot be strictly classified as plants, animals or fungi. They are not a part of modern cladistics because they are paraphyletic.
Ophiaster formosus is a marine, unicellular species of coccolithophore in the genus Ophiaster, first described by Gran in 1912.
Ophiaster hydroideus is a marine unicellular species of coccolithophore, an algae, in the family Syracosphaeraceae. It was first described by Hans Lohmann in 1902 as Meringosphaera hydroidea, however, this was changed to Ophiaster hydroideus in 1913. It has modified coccoliths that it can fold in or extend like arms: "These 'arms' are not actively deployed by the cell, but may function as a defensive barrier to discourage predators such as copepods".

Many protists have protective shells or tests, usually made from silica (glass) or calcium carbonate (chalk). Protists are a diverse group of eukaryote organisms that are not plants, animals, or fungi. They are typically microscopic unicellular organisms that live in water or moist environments.

Particulate inorganic carbon (PIC) can be contrasted with dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC), the other form of inorganic carbon found in the ocean. These distinctions are important in chemical oceanography. Particulate inorganic carbon is sometimes called suspended inorganic carbon. In operational terms, it is defined as the inorganic carbon in particulate form that is too large to pass through the filter used to separate dissolved inorganic carbon.
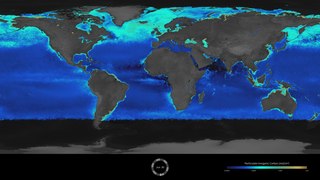
The Great Calcite Belt (GCB) refers to a region of the ocean where there are high concentrations of calcite, a mineral form of calcium carbonate. The belt extends over a large area of the Southern Ocean surrounding Antarctica. The calcite in the Great Calcite Belt is formed by tiny marine organisms called coccolithophores, which build their shells out of calcium carbonate. When these organisms die, their shells sink to the bottom of the ocean, and over time, they accumulate to form a thick layer of calcite sediment.
Siphamia tubifer, also known as the sea urchin cardinalfish, is a small (~7 cm) coral reef fish in the family Apogonidae. Its geographic range extends from East Africa to the French Polynesian Islands.












