Related Research Articles

An anti-ship missile (AShM) is a guided missile that is designed for use against ships and large boats. Most anti-ship missiles are of the sea skimming variety, and many use a combination of inertial guidance and active radar homing. A large number of other anti-ship missiles use infrared homing to follow the heat that is emitted by a ship; it is also possible for anti-ship missiles to be guided by radio command all the way.

The S-300 is a series of long-range surface-to-air missile systems developed by the former Soviet Union. It was produced by NPO Almaz for the Soviet Air Defence Forces to defend against air raids and cruise missiles. The S-300 is still regarded as one of the most potent anti-aircraft missile systems in active use.
The Kh-22 “Storm” is a large, long-range anti-ship missile developed by MKB Raduga in the Soviet Union. It was designed for use against aircraft carriers and carrier battle groups, with either a conventional or nuclear warhead. Kh-32 is an updated conventional variant of Kh-22 and was accepted to service in 2016; it features an improved rocket motor and a new seeker head.

The Buk is a family of self-propelled, medium-range surface-to-air missile systems developed by the Soviet Union and its successor state, the Russian Federation, and designed to counter cruise missiles, smart bombs, fixed- and rotary-wing aircraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles. In the Russian A2AD network, Buk is located between the S-200/300/400 systems above and the point defense Tor and Pantsir type systems below.

The S-400 Triumf, previously known as the S-300 PMU-3, is a mobile surface-to-air missile (SAM) system developed in the 1990s by Russia's NPO Almaz as an upgrade to the S-300 family of missiles. The S-400 was approved for service on 28 April 2007 and the first battalion of the systems assumed combat duty on 6 August 2007.

The P-800 Oniks, marketed in export as the Yakhont, is a Soviet / Russian supersonic anti-ship cruise missile developed by NPO Mashinostroyeniya as a ramjet version of P-80 Zubr. Its GRAU designation is 3M55, the air launched Kh-61 variant also exists. The missile has the NATO codename SS-N-26 "Strobile". Development commenced in 1983, and in the 1990s the anti-ship missile was tested on the Project 1234.7 ship. In 2002 the missile passed the whole range of trials and was commissioned. It is reportedly a replacement for the P-270 Moskit, and possibly also of the P-700 Granit.

The Zvezda Kh-35 is a Soviet turbojet subsonic cruise anti-ship missile. The missile can be launched from helicopters, surface ships and coastal defence batteries with the help of a rocket booster, in which case it is known as Uran or Bal. It is designed to attack vessels up to 5,000 tonnes.

The 9K720 Iskander is a mobile short-range ballistic missile system produced and deployed by the Russian military. They travel at a terminal hypersonic speed of 2100–2600 m/s and can reach an altitude of 50 km as they range up to 500 km. The missile systems (Искандер-М) were intended to replace by 2020 the supposedly-obsolete OTR-21 Tochka systems in the Russian military.

Barak 8, also known as LR-SAM or MR-SAM, is an Indo-Israeli jointly developed surface-to-air missile (SAM) system, designed to defend against any type of airborne threat including aircraft, helicopters, anti-ship missiles, and UAVs as well as ballistic missiles, cruise missiles and combat jets. Both maritime and land-based variants of the system exist.
The Zelenopillia rocket attack took place on 11 July 2014 during the war in Donbas. The rocket barrage, which was launched from inside Russian territory by Russian forces, killed 37 Ukrainian soldiers and border guards in a camp at Zelenopillia, Luhansk Oblast.

Hrіm-2, Grom or OTRK Sapsan, also known as Operational-Tactical Missile System Hrim, is a Ukrainian short-range ballistic missile system being developed by KB Pivdenne and PA Pivdenmash, designed to combine the features of a tactical missile system and a multiple rocket launcher. The original Sapsan version of the missile, for Ukraine's own use, was to have a range of 500 kilometers. The later Hrim-2 version, developed for export, has a range limited to 280 kilometers, in order to fall within the 300-kilometre limit set by the Missile Technology Control Regime, which seeks to limit the proliferation of missiles and missile technology.

The Volodymyr Velykyi class or Project 58250 is a planned class of frigates ordered by the Ukrainian Navy.

R-360 Neptune is a Ukrainian subsonic cruise missile with all-weather capabilities developed by the Luch Design Bureau in Kyiv. Originally designed as an anti-ship missile, an alternative model was fielded in 2023 with a new guidance system to support land-attack roles. With a range of over 200 kilometres, it is intended to neutralize naval targets up to 9,000 tonnes.

The defense industry of Ukraine is a strategically important sector and a large employer in Ukraine. After working for several decades mostly for the arms export markets, in 2014 it has moved significantly into increased Ukrainian military procurement since the start of the war in Donbas.
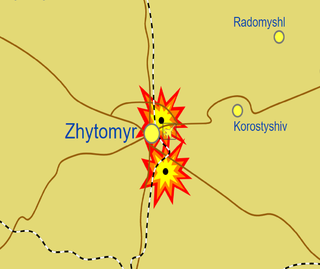
Missile attacks on the civilian airport of Zhytomyr took place on 27 February 2022 as part of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The airport is situated around 150 kilometres (93 mi) from the capital city of Ukraine — Kyiv — near the city of Zhytomyr in Zhytomyr Oblast. Attacks on the city itself followed in March. It was reported that the Russian armed forces used 9K720 Iskander missile systems that were located in Belarus.

During the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Russian Armed Forces have launched several missile attacks over the city of Dnipro in Ukraine. These have led to dozens of fatalities and over a hundred injuries among the civilian population.

During the autumn and winter of 2022–2023, Russia launched waves of missile and drone strikes against energy infrastructure as part of its invasion of Ukraine. The strikes targeted civilian areas beyond the battlefield, particularly critical power infrastructure, which is considered a war crime.

Aerial warfare in the Russian invasion of Ukraine began at dawn of 24 February 2022, with infantry divisions and armored and air support in Eastern Ukraine, and dozens of missile attacks across Ukraine. The first fighting took place in Luhansk Oblast near the village of Milove on the border with Russia at 3:40 am Kyiv time. The main infantry and tank attacks were launched in four spearhead incursions, creating a northern front launched towards Kyiv, a southern front originating in Crimea, a south-eastern front launched at the cities of Luhansk and Donbas, and an eastern front. Dozens of missile strikes across Ukraine also reached as far west as Lviv. Drones have also been a critical part of the invasion, particularly in regards to combined arms warfare. Drones have additionally been employed by Russia in striking Ukrainian critical infrastructure, and have been used by Ukraine to strike military infrastructure in Russian territory.

The 3rd Separate Assault Brigade is a brigade of the Ukrainian Ground Forces formed in 2022.
References
- ↑ Цензор.НЕТ. "Пуски керованих ракет середньої дальності на півдні України. ВIДЕО (оновлено)". Цензор.НЕТ (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 2017-04-12.