
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain. The general definition used is one followed by the United States Geological Survey and the Geological Survey of Canada to describe the respective countries' physiographic regions. The U.S. uses the term Appalachian Highlands and Canada uses the term Appalachian Uplands; the Appalachian Mountains are not synonymous with the Appalachian Plateau, which is one of the provinces of the Appalachian Highlands.

The Bitterroot Range is a mountain range and a subrange of the Rocky Mountains that runs along the border of Montana and Idaho in the northwestern United States. The range spans an area of 24,223 square miles (62,740 km2) and is named after the bitterroot, a small pink flower that is the state flower of Montana.

Mount Garibaldi is a dormant stratovolcano in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Pacific Ranges in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It has a maximum elevation of 2,678 metres and rises above the surrounding landscape on the east side of the Cheakamus River in New Westminster Land District. In addition to the main peak, Mount Garibaldi has two named sub-peaks. Atwell Peak is a sharp, conical peak slightly higher than the more rounded peak of Dalton Dome. Both were volcanically active at different times throughout Mount Garibaldi's eruptive history. The northern and eastern flanks of Mount Garibaldi are obscured by the Garibaldi Névé, a large snowfield containing several radiating glaciers. Flowing from the steep western face of Mount Garibaldi is the Cheekye River, a tributary of the Cheakamus River. Opal Cone on the southeastern flank is a small volcanic cone from which a lengthy lava flow descends. The western face is a landslide feature that formed in a series of collapses between 12,800 and 11,500 years ago. These collapses resulted in the formation of a large debris flow deposit that fans out into the Squamish Valley.

Crary Mountains are a group of ice-covered volcanoes in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. They consist of two or three shield volcanoes, named Mount Rees, Mount Steere and Mount Frakes, which developed during the course of the Miocene and Pliocene and last erupted about 30,000-40,000 years ago. The first two volcanoes are both heavily incised by cirques, while Mount Frakes is better preserved and has a 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) wide caldera at its summit. Boyd Ridge is another part of the mountain range and lies southeast of Mount Frakes; it might be the emergent part of a platform that underlies the mountain range.

Monte Rosa is a mountain massif in the eastern part of the Pennine Alps, on the border between Italy and Switzerland (Valais). The highest peak of the massif, amongst several peaks of over 4,000 m (13,000 ft), is the Dufourspitze, the second highest mountain in the Alps and western Europe, after Mont Blanc. The east face of the Monte Rosa towards Italy has a height of about 2,400 metres (7,900 ft) and is the highest mountain wall of the Alps.

The Snake Range is a mountain range in White Pine County, Nevada, United States. The south-central portion of the range is included within Great Basin National Park, with most of the remainder included within the Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest. The range reaches a maximum elevation of 13,065 feet (3,982 m) at the summit of Wheeler Peak, the tallest independent mountain within Nevada and the second highest point within the state. The range also contains four of the five highest mountain peaks in Nevada, including all peaks greater than 12,000 feet (3,658 m) except for Boundary Peak.

Bald Eagle Valley is a low-lying area in Pennsylvania that drains into Bald Eagle Creek between the Allegheny Front and Bald Eagle Mountain, south of the West Branch Susquehanna River, in the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians. The valley is located southwest of West Branch Susquehanna Valley and includes Williamsport, Nittany Valley, and State College in the central portion of Centre County and southern portion of Clinton County.

Bald Eagle Mountain – once known locally as Muncy Mountain – is a stratigraphic ridge in the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians of central Pennsylvania, United States, running east of the Allegheny Front and northwest of Mount Nittany. It lies along the southeast side of Bald Eagle Creek and south of the West Branch Susquehanna River, and is the westernmost ridge in its section of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians. The ridge line separates the West Branch Susquehanna Valley from the Nippenose and White Deer Hole valleys, and Bald Eagle Valley from Nittany Valley.

Brush Mountain is a stratigraphic ridge in the Appalachian Mountains of central Pennsylvania, United States, lying east of the Allegheny Front and west of Tussey Mountain. It runs along the southeast side of the Little Juniata River and forms a horseshoe around Sinking Run, and is the westernmost ridge in its section of the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians. The western ridge line separates the Logan Valley from the Sinking Valley.

Graystones is a fell in the English Lake District. It lies in the North Western Fells region and is one of the peaks on the ridge which encircles the valley of Aiken Beck.
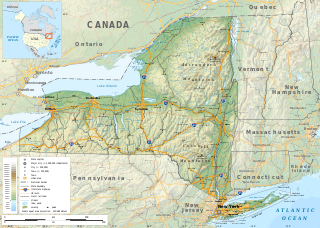
The geography of New York varies widely across the state. Most of New York is dominated by farms, forests, rivers, mountains, and lakes. New York's Adirondack Park is larger than any U.S. National Park in the contiguous United States. Niagara Falls, on the Niagara River as it flows from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario, is a popular attraction. The Hudson River begins near Lake Tear of the Clouds and flows south through the eastern part of the state without draining lakes George or Champlain. Lake George empties at its north end into Lake Champlain, whose northern end extends into Canada, where it drains into the Richelieu River and then the St. Lawrence. Four of New York City's five boroughs are on the three islands at the mouth of the Hudson River: Manhattan Island, Staten Island, and Brooklyn and Queens on Long Island.

Convoy Range is a broad range in Antarctica. It is south of the Kirkwood Range and north of the Clare Range.

The Allgäu Alps are a mountain range in the Northern Limestone Alps, located on the Austria–Germany border, which covers parts of the German states of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg and the Austrian states of Tyrol and Vorarlberg. The range lies directly east of Lake Constance.

Southwest Hunter Mountain (Leavitt Peak) is a subpeak of Hunter Mountain, located in Greene County, New York. It is considered one of the Catskills' High Peaks in its own right, because of its separation from the main summit, and its topographic prominence. Hunter Mountain is named after John Hunter, who also gave his name to the town of Hunter.

The Rattlesnake Hills, also known as Rattlesnake Ridge, is a 16-mile (26 km) long anticline mountain ridge in Yakima County and Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington. It should not be confused with the much smaller Rattlesnake Ridge located near the west end of Ahtanum Ridge just south of Yakima, Washington and west of Union Gap, Washington. The highest point in the hills is the 3,629 feet (1,106 m) Lookout Summit, which surpasses the more well-known Rattlesnake Mountain by approximately 100 ft (30 m). The Rattlesnake Hills are part of the Yakima Fold Belt of east-tending long ridges formed by the folding of Miocene Columbia River basalt flows.
Buckskin Mountain is a 16-mile (26 km) mountain ridge that spans from Coconino County, Arizona to Kane County, Utah in the United States, that is divided almost equally between the two counties.
The Perris Block is the central block of three major fault-bounded blocks of the northern part of the Peninsular Ranges. The Perris Block lies between the Santa Ana Block to the west and the San Jacinto Block to the east. The Perris Block, was named by Walter A. English in 1925 for the city of Perris, located near the center of the block.
The Plains of Leon are named for the former gold mining town, Leon once located near the middle of the plain. It is a plain in the Perris Block, contiguous on the south with the Perris Plain including within it the Domenigoni Valley and western Diamond Valley, French Valley, Auld Valley, the upper part of the valley of Warm Springs Creek and connecting tablelands.

Breccia Peak is a mountain in the southern Absaroka Range of the Rocky Mountains. It is located in Teton County in the U.S. state of Wyoming, close to the southwest border of the Teton Wilderness within the Bridger-Teton National Forest.

The Anthracite Range is a mountain range in the West Elk Mountains, a sub-range of the Rocky Mountains of North America. The range is located in Gunnison County of western Colorado and lies within the West Elk Wilderness of the Gunnison National Forest. The Anthracite Range is one of several prominent laccoliths found in the West Elk Mountains.


















