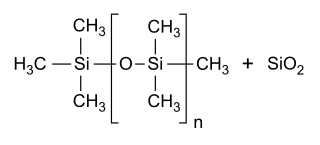
Simeticone (INN), also known as simethicone (USAN), is an anti-foaming agent used to reduce bloating, discomfort or pain caused by excessive gas.

Ergometrine, also known as ergonovine and sold under the brand names Ergotrate, Ergostat, and Syntometrine among others, is a medication used to cause contractions of the uterus to treat heavy vaginal bleeding after childbirth. It can be used either by mouth, by injection into a muscle, or injection into a vein. It begins working within 15 minutes when taken by mouth and is faster in onset when used by injection. Effects last between 45 and 180 minutes.
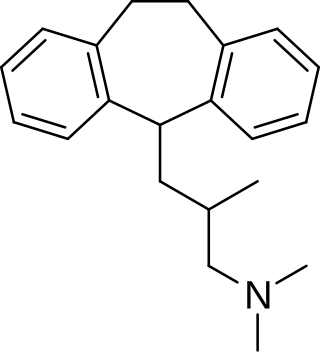
Butriptyline, sold under the brand name Evadyne among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used in the United Kingdom and several other European countries for the treatment of depression but appears to no longer be marketed. Along with trimipramine, iprindole, and amoxapine, it has been described as an "atypical" or "second-generation" TCA due to its relatively late introduction and atypical pharmacology. It was very little-used compared to other TCAs, with the number of prescriptions dispensed only in the thousands.
Plasma protein binding refers to the degree to which medications attach to proteins within the blood. A drug's efficiency may be affected by the degree to which it binds. The less bound a drug is, the more efficiently it can traverse or diffuse through cell membranes. Common blood proteins that drugs bind to are human serum albumin, lipoprotein, glycoprotein, and α, β‚ and γ globulins.

Fluprednidene, also known as fluprednylidene, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid which was never marketed. An acetate ester of fluprednidene, fluprednidene acetate, in contrast, has been marketed.

Melitracen is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA), for the treatment of depression and anxiety. In addition to single drug preparations, it is also available as Deanxit, marketed by Lundbeck, a combination product containing both melitracen and flupentixol.

Berberine is a quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids found in such plants as Berberis vulgaris (barberry), Berberis aristata, Mahonia aquifolium, Hydrastis canadensis (goldenseal), Xanthorhiza simplicissima (yellowroot), Phellodendron amurense, Coptis chinensis, Tinospora cordifolia, Argemone mexicana, and Eschscholzia californica. Berberine is usually found in the roots, rhizomes, stems, and bark.

Isoconazole is an azole antifungal drug and could inhibit gram positive bacteria. For foot and vaginal infections, isoconazole has a similar effectiveness to clotrimazole. Isoconazole nitrate may be used in combination with corticosteroid diflucortolone to increase its bioavailability.
Addiction is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1903 by the Society for the Study of Addiction to Alcohol and other Drugs as the British Journal of Inebriety. It was renamed British Journal of Addiction to Alcohol & Other Drugs in 1947, then renamed to British Journal of Addiction in 1980, before finally obtaining its current name in 1993. It covers research relating to the abuse of alcohol, illicit drugs, and tobacco, as well as behavioural addictions. The editor-in-chief is John Marsden.

Chlormadinone is a progestin which was never marketed. An acylated derivative, chlormadinone acetate, is used clinically as a pharmaceutical drug.

Sultopride (trade names Barnetil, Barnotil, Topral) is an atypical antipsychotic of the benzamide chemical class used in Europe, Japan, and Hong Kong for the treatment of schizophrenia. It was launched by Sanofi-Aventis in 1976. Sultopride acts as a selective D2 and D3 receptor antagonist. It has also been shown to have clinically relevant affinity for the GHB receptor as well, a property it shares in common with amisulpride and sulpiride.
Clifford 'Cliff' Wiley is a former American track and field athlete, who competed in the sprints events during his career. He is best known for winning the men's 400 metres event at the 1981 Athletics World Cup in Rome and the 1983 Pan American Games in Caracas.

Oxaflozane (INN) (brand name Conflictan) is an antidepressant and anxiolytic drug that was introduced by Solvay in France in 1982 for the treatment of depression but has since been discontinued. It is a prodrug of flumexadol (N-dealkyloxaflozane; 2-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)morpholine; CERM-1841 or 1841-CERM), which is reported to act as an agonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A (pKi = 7.1) and 5-HT2C (pKi = 7.5) receptors and, to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT2A (pKi = 6.0) receptor. In addition to its serotonergic properties, oxaflozane may also produce anticholinergic side effects at high doses, namely in overdose.
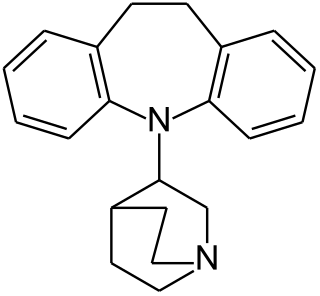
Quinupramine is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) used in Europe for the treatment of depression.

Amitriptylinoxide, or amitriptyline N-oxide, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) which was introduced in Europe in the 1970s for the treatment of depression.
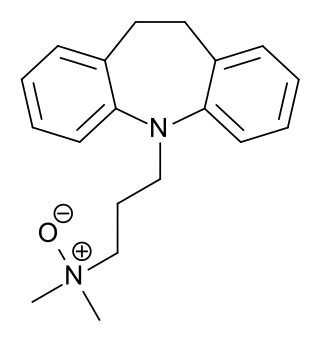
Imipraminoxide, or imipramine N-oxide, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that was introduced in Europe in the 1960s for the treatment of depression.
Tetrabamate is a combination drug formulation of febarbamate, difebarbamate, and phenobarbital which was marketed in France and Spain and was used to treat anxiety and alcohol withdrawal-associated muscle tremors, agitation, and depression. It was largely, but not completely discontinued on April 4, 1997 after over 30 years of use due to reports of hepatitis and acute liver failure. The decision to restrict the use of the drug had been long-awaited.

The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology is a peer-reviewed medical journal that covers the field of pharmacology. The editor-in-chief is Joseph S. Bertino, Jr.. It was established in 1961 and is currently published by John Wiley & Sons in association with the American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
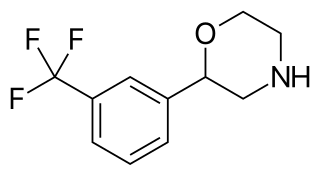
Flumexadol (INN) is a drug described and researched as a non-opioid analgesic which was never marketed. It has been found to act as an agonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT2C receptors and, to a much lesser extent, of the 5-HT2A receptor. According to Nilsson (2006) in a paper on 5-HT2C receptor agonists as potential anorectics, "The (+)-enantiomer of this compound showed [...] affinity for the 5-HT2C receptor (Ki) 25 nM) [...] and was 40-fold selective over the 5-HT2A receptor in receptor binding studies. Curiously, the racemic version [...], also known as 1841 CERM, was originally reported to possess analgesic properties while no association with 5-HT2C receptor activity was mentioned." It is implied that flumexadol might be employable as an anorectic in addition to analgesic. Though flumexadol itself has never been approved for medical use, oxaflozane is a prodrug of the compound that was formerly used clinically in France as an antidepressant and anxiolytic agent.
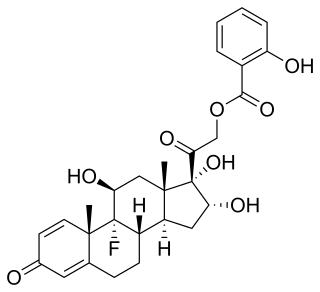
Cortobenzolone, also known as betamethasone salicylate, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and corticosteroid ester which is marketed in Spain.















