
Averrhoa is a genus of trees in the family Oxalidaceae, of the order Oxalidales, named after Averroes, a 12th-century astronomer and philosopher from Al-Andalus.

Aporosa is a genus of flowering plant belonging to the family Phyllanthaceae, first described as a genus in 1825. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Papuasia, and Queensland.

Drypetes is a plant genus of the family Putranjivaceae, in the order Malpighiales.
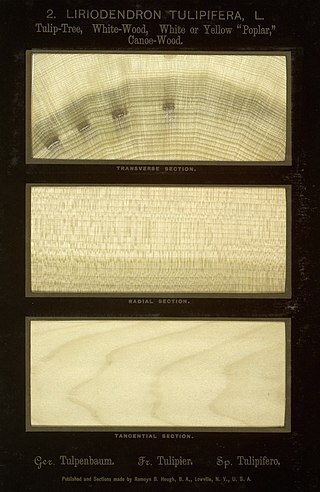
Most commonly, tulipwood is the greenish yellowish wood yielded from the tulip tree, found on the Eastern side of North America and a similar species is found in some parts of China. In the United States, it is commonly known as tulip poplar or yellow poplar, even though the tree is not related to the poplars. It is notable for its height, which can exceed 190 feet. The wood is very light, around 490 kg per cubic meter, but very strong and is used in many applications, including furniture, joinery and moldings. It can also be stained very easily and is often used as a low-cost alternative to walnut and cherry in furniture and doors.
Micronesian mythology comprises the traditional belief systems of the people of Micronesia. There is no single belief system in the islands of Micronesia, as each island region has its own mythological beings.
Changiostyrax is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the family Styracaceae. Its only member species is Changiostyrax dolichocarpus, formerly known as Sinojackia dolichocarpa.
Apurimacia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It includes two species native to South America. The species Apurimacia dolichocarpa is a shrub endemic to the Sierras de Córdoba in Argentina. The species Apurimacia boliviana is a tree native to Peru and Bolivia. It is used as an insecticide in Peru.

Drypetes deplanchei is a tree of eastern and northern Australia. It also occurs in New Caledonia and Lord Howe Island. The genus is derived from the Greek, dryppa meaning "olive fruit". The species named after Dr. Emile Deplanche, who collected this plant at New Caledonia. Common names include yellow tulip, grey boxwood, white myrtle, grey bark and yellow tulipwood.

Tabernaemontana pandacaqui, known as windmill bush and banana bush, is a species of plant in the dogbane family Apocynaceae.

Drypetes sepiaria is a species of small tree in the family Putranjivaceae. This tree is very common in India and Sri Lanka. It is known by many local names, including vellakasavu, veeramaram in Malayalam, vellilambu, veerai (வீரை), aadumilukkan, kaayalakkamaram in Tamil, and weera (වීර) in Sinhala.

Drypetes deplanchei subsp. affinis, commonly known as greybark or grey bark, is a flowering plant in the Putranjivaceae family. The subspecific epithet affinis alludes to its similarity to Drypetes sepiaria of India and Sri Lanka.

Artocarpus mariannensis, also known as the Marianas breadfruit or the seeded breadfruit, is a species of plant in the mulberry / fig family, Moraceae. It is endemic to the Mariana Islands and Guam. It has been utilised extensively by the Micronesian people, being one of the staple food crops that was introduced to other islands in Micronesia.

Drypetes arguta, commonly known as the water ironplum, is a species of small tree or large bush in the family Putranjivaceae. It is native to tropical East Africa. It was first described in 1920 by the English botanist John Hutchinson, who named it Cyclostemon argutus. It was later transferred to the genus Drypetes.
Drypetes hoaensis is an Asian tree species in the family Putranjivaceae.
Drypetes thorelii is an Asian tree species in the family Putranjivaceae; it is named after the French botanist Clovis Thorel.
Drypetes gerrardii is a species of small tree or large shrub in the family Putranjivaceae. Common names include forest ironplum, bastard white ironwood, and forest ironwood. It is native to tropical and subtropical central and eastern Africa. It was first described in 1920 by the English botanist John Hutchinson, who named it after the English botanist William Tyrer Gerrard who collected plants and seeds in southern Africa in the 1860s.

The Marianas tropical dry forests is a tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests ecoregion on the Marianas Islands in the western Pacific Ocean.

The Yap tropical dry forests is a tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests ecoregion in Micronesia. It includes the Yap Islands and neighboring atolls in the Federated States of Micronesia.

Drypetes wightii is an evergreen tree species endemic to the Western Ghats, India. The species is considered Vulnerable under the IUCN Redlist of Threatened Species.

Drypetes venusta is an evergreen tree species endemic to the Western Ghats, India. They are large trees with smooth, straight, and white trunk and horizontal branches. It can reach a height up to 35 m, and a girth up to 3 m.















