
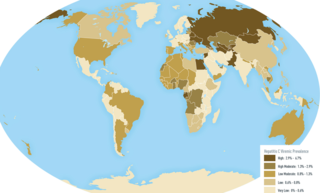
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin. The virus persists in the liver, becoming chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach.

Hepatitis A is an infectious disease of the liver caused by Hepatovirus A (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is 2–6 weeks. When symptoms occur, they typically last 8 weeks and may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain. Around 10–15% of people experience a recurrence of symptoms during the 6 months after the initial infection. Acute liver failure may rarely occur, with this being more common in the elderly.

Hepatitis E is inflammation of the liver caused by infection with the hepatitis E virus (HEV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Hepatitis E has mainly a fecal-oral transmission route that is similar to hepatitis A, although the viruses are unrelated. In retrospect, the earliest known epidemic of hepatitis E occurred in 1955 in New Delhi, but the virus was not isolated until 1983 by Russian scientists investigating an outbreak in Afghanistan. HEV is a positive-sense, single-stranded, nonenveloped, RNA icosahedral virus and one of five known human hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.

Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a 30 nm icosahedral capsid. The viruses in this family can cause a range of diseases including the common cold, poliomyelitis, meningitis, hepatitis, and paralysis.
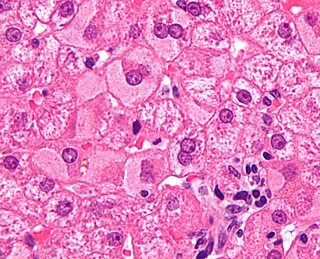
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute form as a recent infection with relatively rapid onset, or in chronic form, typically progressing from a long-lasting asymptomatic condition up to a decompensated hepatic disease and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).

The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small, enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer and lymphomas in humans.

Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term "oncornaviruses" was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the letters "RNA" removed, it now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with "tumor virus" or "cancer virus". The vast majority of human and animal viruses do not cause cancer, probably because of longstanding co-evolution between the virus and its host. Oncoviruses have been important not only in epidemiology, but also in investigations of cell cycle control mechanisms such as the retinoblastoma protein.
Marek's disease is a highly contagious viral neoplastic disease in chickens. It is named after József Marek, a Hungarian veterinarian who described it in 1907. Marek's disease is caused by an alphaherpesvirus known as "Marek's disease virus" (MDV) or Gallid alphaherpesvirus 2 (GaHV-2). The disease is characterized by the presence of T cell lymphoma as well as infiltration of nerves and organs by lymphocytes. Viruses related to MDV appear to be benign and can be used as vaccine strains to prevent Marek's disease. For example, the related herpesvirus found in turkeys (HVT), causes no apparent disease in the birds, and continues to be used as a vaccine strain for prevention of Marek's disease.
GB virus C (GBV-C), formerly known as hepatitis G virus (HGV) and also known as human pegivirus – HPgV is a virus in the family Flaviviridae and a member of the Pegivirus, is known to infect humans, but is not known to cause human disease. Reportedly, HIV patients coinfected with GBV-C can survive longer than those without GBV-C, but the patients may be different in other ways. Research is active into the virus' effects on the immune system in patients coinfected with GBV-C and HIV.
Infectious canine hepatitis (ICH) is an acute liver infection in dogs caused by Canine mastadenovirus A, formerly called Canine adenovirus 1 (CAV-1). Canine mastadenovirus A also causes disease in wolves, coyotes, and bears, and encephalitis in foxes. The virus is spread in the feces, urine, blood, saliva, and nasal discharge of infected dogs. It is contracted through the mouth or nose, where it replicates in the tonsils. The virus then infects the liver and kidneys. The incubation period is 4 to 9 days.

Feline calicivirus (FCV) is a virus of the family Caliciviridae that causes disease in cats. It is one of the two important viral causes of respiratory infection in cats, the other being Felid alphaherpesvirus 1. FCV can be isolated from about 50% of cats with upper respiratory infections. Cheetahs are the other species of the family Felidae known to become infected naturally.

Murine coronavirus (M-CoV) is a virus in the genus Betacoronavirus that infects mice. Belonging to the subgenus Embecovirus, murine coronavirus strains are enterotropic or polytropic. Enterotropic strains include mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) strains D, Y, RI, and DVIM, whereas polytropic strains, such as JHM and A59, primarily cause hepatitis, enteritis, and encephalitis. Murine coronavirus is an important pathogen in the laboratory mouse and the laboratory rat. It is the most studied coronavirus in animals other than humans, and has been used as an animal disease model for many virological and clinical studies.
Parechovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Picornaviridae. Humans, ferrets, and various rodents serve as natural hosts. The genus currently consists of six accepted species. Human parechoviruses may cause gastrointestinal or respiratory illness in infants, and they have been implicated in cases of myocarditis and encephalitis.

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.

Enterovirus E is a picornavirus of the genus Enterovirus. The virus may also be referred to as enteric cytopathic bovine orphan virus (ECBO). It is endemic in cattle populations worldwide, and although normally fairly nonpathogenic, it can cause reproductive, respiratory, or enteric disease – particularly when the animal is concurrently infected with another pathogen.

Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus Orthohepadnavirus and a member of the Hepadnaviridae family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B.
Dabie bandavirus, also called SFTS virus, is a tick-borne virus in the genus Bandavirus in the family Phenuiviridae, order Bunyavirales. The clinical condition it caused is known as severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS). SFTS is an emerging infectious disease that was first described in northeast and central China 2009 and now has also been discovered in Japan, South Korea, Vietnam and Taiwan in 2015. SFTS has a fatality rate of 12% and as high as over 30% in some areas. The major clinical symptoms of SFTS are fever, vomiting, diarrhea, multiple organ failure, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and elevated liver enzyme levels. Another outbreak occurred in East China in the early half of 2020.
Tremovirus, also known epidemic tremor, is a virus genus belonging to the Picornaviridae family. The genus has two species, Tremovirus A, which is also called Avian encephalomyelitis virus, and Tremovirus B. The first avian picornavirus to have its genome sequenced, it causes epidemic tremor in chickens.

Picornain 3C is a protease found in picornaviruses, which cleaves peptide bonds of non-terminal sequences. Picornain 3C’s endopeptidase activity is primarily responsible for the catalytic process of selectively cleaving Gln-Gly bonds in the polyprotein of poliovirus and with substitution of Glu for Gln, and Ser or Thr for Gly in other picornaviruses. Picornain 3C are cysteine proteases related by amino acid sequence to trypsin-like serine proteases. Picornain 3C is encoded by enteroviruses, rhinoviruses, aphtoviruses and cardioviruses. These genera of picoviruses cause a wide range of infections in humans and mammals.












