
Mayetiola are a genus of flies from the family Cecidomyiidae. Most species are pests of cereal crops.

Lophodermium is a genus of fungi within the family Rhytismataceae. The genus contains 145 species and has a global distribution. Species of this genus are usually observed producing zone lines, conidiomata and ascomata on dead fallen leaves, but at least some are known to colonize living leaves. In many cases they then live inside the colonized leaf as a symptomless endobiont, where they are regarded as detritivores utilising dead plant matter. In a few cases they may kill all or part of the leaf prematurely, and there is a substantial literature dealing with those species as plant pathogens. The genus infects many different plant families but with a notable concentration in the family Pinaceae; many Lophodermium species are restricted to a single host genus, but some, particularly those infecting grasses, may infect several genera. Some are economically important plant pathogens, such as those that cause needlecast disease in European Black Pine, Scots Pine and Red Pine in forestry and christmas tree plantations. In these species, notably L. pinastri and L. seditiosum, the fungal spores disperse and infect the pine needles in late summer, which turn brown by the following spring and then fall off.
Barria is a genus of fungi in the family Phaeosphaeriaceae. This is a monotypic genus, containing the single species Barria piceae. It was named after mycologist Margaret E. Barr.
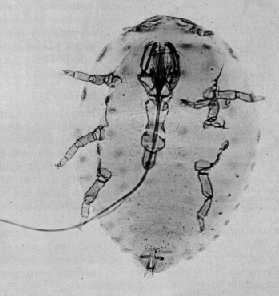
The balsam woolly adelgid is small wingless insect that infests and kills firs. In their native Europe they are a minor parasite on silver fir and Sicilian fir, but they have become a threat especially to balsam fir and Fraser fir after they were introduced to the United States around the beginning of the 20th century. Because this species is not native to North America, the Fraser fir has not evolved any type of defense against it.

Adelges is a genus of insects which feed on conifers. They have complex life cycles, some species feeding exclusively on spruce, others feeding on spruce and an alternate conifer. However, galls characteristic of each species are formed only on spruce. Six generations are usually needed to complete the 2-year cycle, and in the case of species having an alternate host, winged adults about 2 mm long are formed only in the generations that move from one host to the other.

Chrysomyxa is a genus of rust fungi in the family Coleosporiaceae. The genus, widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, contains about 23 species. Rust fungi in the genus Chrysomyxa occur in boreal forests of the northern hemisphere on Pinaceae,, and most species alternate to angiosperm hosts in the Ericaceae.

Cinara, the conifer aphids or giant conifer aphids, is a genus of aphids in the family Aphididae. They are widespread in the Northern Hemisphere.

Megastigmus atedius is a species of minute wasp that feeds on white spruce seed and cones. The damage it causes is largely undetected because the larvae complete their development hidden inside the seeds, which reveal no external indication of this. Although species of Megastigmus are said to be host-specific, the spruce seed chalcid found near Fairbanks, Alaska, was identified by E.H. Holsten and others in 1980 as M. piceae, while A.H. Rose and O.H. Lindquist applied the name Megastigmus piceae, but gave the authority as Rohwer.
Mayetiola piceae, the spruce gall midge, is a species of gall-forming flies in the Cecidomyiidae family.
Dystomorphus is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae.

Peridermium is a genus of rust fungi in the family Cronartiaceae.
Ophiostoma breviusculum is a species of fungus in the family Ophiostomataceae, associated with bark beetles infesting larch in Japan. It belongs in the Ophiostoma piceae complex. It was also found in insect galleries of Larix kaempferi. The length of its perithecial necks and synnemata are shorter than in O. piceae. The synnemata also differ from the latter morphologically.
Dystomorphus nigrosignatus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Pu, Wang and Li in 1998.
Dystomorphus notatus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Maurice Pic in 1926.

Mulsantina hudsonica, the Hudsonian lady beetle, is a species of lady beetle in the family Coccinellidae. It is found in North America. It measures 3.5–5 mm (0.1–0.2 in) in length. It has been recorded from various conifers and from willow; it is a predator of the balsam woolly adelgid.
Phloeotribus piceae is a species of crenulate bark beetle in the family Curculionidae. It is found in North America.
Dreyfusia is a genus of true bugs belonging to the family Adelgidae.
Melarthonis is fungal genus in the family Chrysotrichaceae. It is a monotypic genus, containing the single species Melarthonis piceae, a corticolous lichen. Both the genus and species were described as new to science in 2014 by Andreas Frisch and Göran Thor. The type specimen was collected from Mount Oakan at an altitude of 420 m (1,380 ft); there, it was found growing on the bark of a spruce tree in an old-growth forest. It is only known to occur in the type locality. The genus name alludes to the black ascomata that are similar to those in genus Arthonia, while the species epithet refers to the genus of the host tree (Picea).

Cryphalus piceae, the small fir bark beetle, is a tiny bark beetle, about 1.7 mm long that is found in central and southern Europe. It infests mainly fir (Abies) and spruce trees (Picea) and occasionally can cause damage to branches and young trees, including tree death.









