
2C-N (2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenethylamine) is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.
Trimethoxyamphetamines (TMAs) are a family of isomeric psychedelic hallucinogenic drugs. There exist six different TMAs that differ only in the position of the three methoxy groups: TMA, TMA-2, TMA-3, TMA-4, TMA-5, and TMA-6. The TMAs are analogs of the phenethylamine cactus alkaloid mescaline. The TMAs are substituted amphetamines, however, their mechanism of action is more complex than that of the unsubstituted compound amphetamine, probably involving agonist activity on serotonin receptors such as the 5HT2A receptor in addition to the generalised dopamine receptor agonism typical of most amphetamines. This action on serotonergic receptors likely underlie the psychedelic effects of these compounds. It is reported that some TMAs elicit a range of emotions ranging from sadness to empathy and euphoria. TMA was first synthesized by Hey, in 1947. Synthesis data as well as human activity data has been published in the book PiHKAL.

2C-G is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. First synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, it is sometimes used as an entheogen. It has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to 2C-D and Ganesha. Like many of the phenethylamines in PiHKAL, 2C-G and its homologs have only been taken by Shulgin and a small test group, making it difficult to ensure completeness when describing effects.
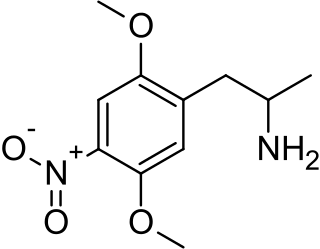
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitroamphetamine (DON) is a psychedelic drug and amphetamine. It is an analog of DOM and DOB. It is also closely related to 2C-N.

2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylamphetamine is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, and was described in his book PiHKAL.

DMMDA-2 is a psychedelic phenethylamine discussed by Alexander Shulgin in his book PiHKAL ; however, he was not the first to synthesize it. Shulgin comments in his book that a 50 milligram dose of DMMDA-2 produces similar effects to MDA. DMMDA-2 can be synthetized from dillapiole.
Ganesha (2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethylamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is also a substituted amphetamine. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 24–32 mg. The drug is usually taken orally, although other routes such as rectally may also be used. Ganesha is synthesized from 2,5-dimethoxy-3,4-dimethylbenzaldehyde. Ganesha is the amphetamine analog of 2C-G. It is a particularly long lasting drug, with the duration listed in PiHKAL as being 18–24 hours, which might make it undesirable to some users. It is named after the Hindu deity, Ganesha. Very little is known about the dangers or toxicity of ganesha. Effects of ganesha include:

Aleph is a psychedelic hallucinogenic drug and a substituted amphetamine of the phenethylamine class of compounds, which can be used as an entheogen. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, Shulgin lists the dosage range as 5–10 mg. According to Shulgin, the effects of aleph typically last for 6 to 8 hours.

2C-T-15 or 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(β-cyclopropylthio)phenethylamine is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was presumably first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and reported in his book PiHKAL .

3C-BZ (4-benzyloxy-3,5-dimethoxyamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. 3C-BZ was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 25–200 mg and the duration as 18–24 hours. According to anecdotal reports from the substance's entry in PiHKAL, 3C-BZ's effects can vary significantly, ranging from intensified emotions and strange dreams, to effects similar to those of LSD or TMA. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 3C-BZ.
Dimethoxyamphetamine (DMA) is a series of six lesser-known psychedelic drugs similar in structure to the three isomers of methoxyamphetamine and six isomers of trimethoxyamphetamine. The isomers are 2,3-DMA, 2,4-DMA, 2,5-DMA, 2,6-DMA, 3,4-DMA, and 3,5-DMA. Three of the isomers were characterized by Alexander Shulgin in his book PiHKAL. Little is known about their dangers or toxicity.
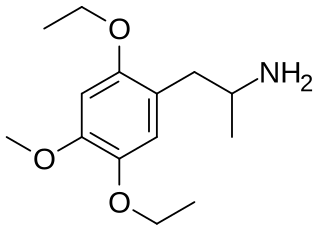
EME (2,5-diethoxy-4-methoxyamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is a diethoxy-methoxy analog of TMA-2. EME was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, both the dosage and duration are unknown. EME produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of EME.
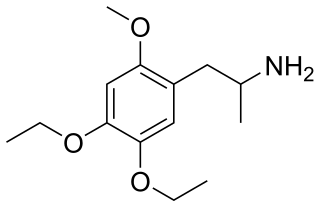
MEE (2-methoxy-4,5-diethoxyamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug of the amphetamine class. It is a diethoxy-methoxy analog of TMA-2. MEE was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, both the dosage and duration are unknown. MEE produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MEE.

F-2, or 6-(2-aminopropyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. F-2 was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 15 mg, and the duration unknown. F-2 produces few to no effects at this dose in humans. Animal studies showed it to substitute for the psychedelic drug DOM, but with less than one tenth the potency.

Thioescaline (TE) is a pair of lesser-known psychedelic drugs with the chemical formula C12H19NO2S. They structural analogs of escaline in which an oxygen atom has been replaced with a sulfur atom. They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and reported in his book PiHKAL. Very little is known about their dangers or toxicity.
TOM, or methylthio-methyl-methoxyamphetamine, is a series of lesser-known psychedelic drugs and substituted amphetamines with the molecular formula C12H19NOS. 2-TOM and 5-TOM are the 2- and 5-methylthio analogs of 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine (DOM), respectively. They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and described in his book PiHKAL. Very little is known about their dangers or toxicity.
TOET (methylthio-ethyl-methoxyamphetamines) is a pair of lesser-known psychedelic drugs and substituted amphetamines. 2-TOET and 5-TOET are the 2- and 5-methylthio analogs of DOET, respectively. They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and written up in his book PiHKAL. Very little is known about their dangers or toxicity.

2,3-Methylenedioxyamphetamine (2,3-MDA) or ORTHO-MDA is an amphetamine derivative which is mentioned in PIHKAL as a fairly potent and long-lasting stimulant drug, but with little or none of the entactogenic effects associated with its better-known structural isomer MDA.

2CD-5EtO is a homologue of the psychedelic phenethylamine 2C-D, where the 5-methoxy group of 2C-D has been lengthened to an ethoxy group. 2CD-5EtO is a representative example of the so-called "tweetio" compounds discovered by Alexander Shulgin and briefly mentioned in his book PiHKAL. They are homologues of the 2C family of drugs, where either one or both of the methoxy groups at the 2,5-positions of the aromatic ring have been replaced by ethoxy. The term tweetio was derived phonetically from the sound of the "2-ETO" derivatives.

2C-Se is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It was originally named by Alexander Shulgin as described in his book PiHKAL. Shulgin considered 2C-Se to be around three times the potency of mescaline, but was too concerned about toxicity to test it extensively, though he considered it noteworthy as the only psychedelic drug to contain a selenium atom.
















