
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the geometry, gravity, and spatial orientation of the Earth in temporally varying 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical bodies, such as planets or circumplanetary systems. Geodesy is an earth science and many consider the study of Earth's shape and gravity to be central to that science. It is also a discipline of applied mathematics.

A geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or geodetic coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest and most widely used type of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface.
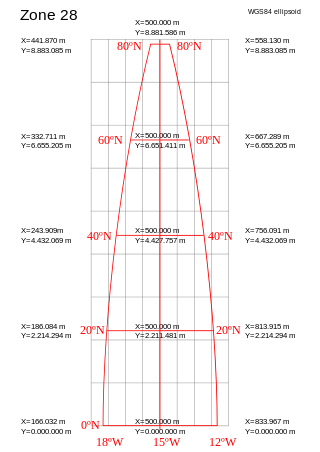
A projected coordinate system – also called a projected coordinate reference system, planar coordinate system, or grid reference system – is a type of spatial reference system that represents locations on Earth using Cartesian coordinates (x, y) on a planar surface created by a particular map projection. Each projected coordinate system, such as "Universal Transverse Mercator WGS 84 Zone 26N," is defined by a choice of map projection (with specific parameters), a choice of geodetic datum to bind the coordinate system to real locations on the earth, an origin point, and a choice of unit of measure. Hundreds of projected coordinate systems have been specified for various purposes in various regions.

The World Geodetic System (WGS) is a standard used in cartography, geodesy, and satellite navigation including GPS. The current version, WGS 84, defines an Earth-centered, Earth-fixed coordinate system and a geodetic datum, and also describes the associated Earth Gravitational Model (EGM) and World Magnetic Model (WMM). The standard is published and maintained by the United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency.

The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system (OSGB), also known as British National Grid (BNG), is a system of geographic grid references, distinct from latitude and longitude, whereby any location in Great Britain can be described in terms of its distance from the origin, which lies to the west of the Isles of Scilly.
In geodesy, conversion among different geographic coordinate systems is made necessary by the different geographic coordinate systems in use across the world and over time. Coordinate conversion is composed of a number of different types of conversion: format change of geographic coordinates, conversion of coordinate systems, or transformation to different geodetic datums. Geographic coordinate conversion has applications in cartography, surveying, navigation and geographic information systems.

A geodetic datum or geodetic system is a global datum reference or reference frame for unambiguously representing the position of locations on Earth by means of either geodetic coordinates or geocentric coordinates. Datums are crucial to any technology or technique based on spatial location, including geodesy, navigation, surveying, geographic information systems, remote sensing, and cartography. A horizontal datum is used to measure a horizontal position, across the Earth's surface, in latitude and longitude or another related coordinate system. A vertical datum is used to measure the elevation or depth relative to a standard origin, such as mean sea level (MSL). A three-dimensional datum enables the expression of both horizontal and vertical position components in a unified form. The concept can be generalized for other celestial bodies as in planetary datums.

The European Terrestrial Reference System 1989 (ETRS89) is an ECEF geodetic Cartesian reference frame, in which the Eurasian Plate as a whole is static. The coordinates and maps in Europe based on ETRS89 are not subject to change due to the continental drift.

ED50 is a geodetic datum which was defined after World War II for the international connection of geodetic networks.

A Lambert conformal conic projection (LCC) is a conic map projection used for aeronautical charts, portions of the State Plane Coordinate System, and many national and regional mapping systems. It is one of seven projections introduced by Johann Heinrich Lambert in his 1772 publication Anmerkungen und Zusätze zur Entwerfung der Land- und Himmelscharten.

A spatial reference system (SRS) or coordinate reference system (CRS) is a framework used to precisely measure locations on the surface of Earth as coordinates. It is thus the application of the abstract mathematics of coordinate systems and analytic geometry to geographic space. A particular SRS specification comprises a choice of Earth ellipsoid, horizontal datum, map projection, origin point, and unit of measure. Thousands of coordinate systems have been specified for use around the world or in specific regions and for various purposes, necessitating transformations between different SRS.

The North American Datum (NAD) is the horizontal datum now used to define the geodetic network in North America. A datum is a formal description of the shape of the Earth along with an "anchor" point for the coordinate system. In surveying, cartography, and land-use planning, two North American Datums are in use for making lateral or "horizontal" measurements: the North American Datum of 1927 (NAD 27) and the North American Datum of 1983 (NAD 83). Both are geodetic reference systems based on slightly different assumptions and measurements.

The Earth-centered, Earth-fixed coordinate system, also known as the geocentric coordinate system, is a cartesian spatial reference system that represents locations in the vicinity of the Earth as X, Y, and Z measurements from its center of mass. Its most common use is in tracking the orbits of satellites and in satellite navigation systems for measuring locations on the surface of the Earth, but it is also used in applications such as tracking crustal motion.
The International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP) is the petroleum industry's global forum in which members identify and share best practices to achieve improvements in health, safety, the environment, security, social responsibility, engineering and operations.
The State Plane Coordinate System (SPCS) is a set of 125 geographic zones or coordinate systems designed for specific regions of the United States. Each U.S. state contains one or more state plane zones, the boundaries of which usually follow county lines. There are 108 zones in the contiguous United States, with 10 more in Alaska, five in Hawaii, one for Puerto Rico and the United States Virgin Islands, and one for Guam. The system is widely used for geographic data by state and local governments. Its popularity is due to at least two factors. First, it uses a simple Cartesian coordinate system to specify locations rather than a more complex spherical coordinate system. By using the Cartesian coordinate system's simple XY coordinates, "plane surveying" methods can be used, speeding up and simplifying calculations. Second, the system is highly accurate within each zone. Outside a specific state plane zone accuracy rapidly declines, thus the system is not useful for regional or national mapping.
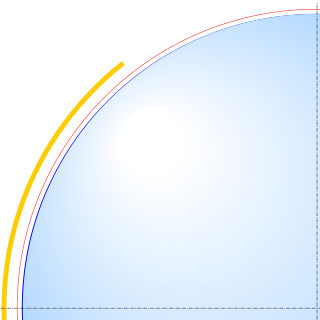
An Earth ellipsoid or Earth spheroid is a mathematical figure approximating the Earth's form, used as a reference frame for computations in geodesy, astronomy, and the geosciences. Various different ellipsoids have been used as approximations.

The Hellenic Geodetic Reference System 1987 or HGRS87 is a geodetic system commonly used in Greece (SRID=2100). The system specifies a local geodetic datum and a projection system. In some documents it is called Greek Geodetic Reference System 1987 or GGRS87.
The Gauss–Boaga projection is a map projection used in Italy that uses a Hayford ellipsoid.

Web Mercator, Google Web Mercator, Spherical Mercator, WGS 84 Web Mercator or WGS 84/Pseudo-Mercator is a variant of the Mercator map projection and is the de facto standard for Web mapping applications. It rose to prominence when Google Maps adopted it in 2005. It is used by virtually all major online map providers, including Google Maps, CARTO, Mapbox, Bing Maps, OpenStreetMap, Mapquest, Esri, and many others. Its official EPSG identifier is EPSG:3857, although others have been used historically.
Well-known text representation of coordinate reference systems is a text markup language for representing spatial reference systems and transformations between spatial reference systems. The formats were originally defined by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) and described in their Simple Feature Access and Well-known text representation of coordinate reference systems specifications. The current standard definition is ISO 19162:2019. This supersedes ISO 19162:2015.










