
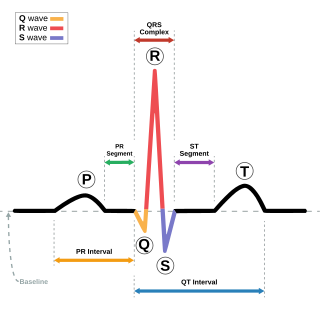
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a condition affecting repolarization (relaxing) of the heart after a heartbeat, giving rise to an abnormally lengthy QT interval. It results in an increased risk of an irregular heartbeat which can result in fainting, drowning, seizures, or sudden death. These episodes can be triggered by exercise or stress. Some rare forms of LQTS are associated with other symptoms and signs including deafness and periods of muscle weakness.
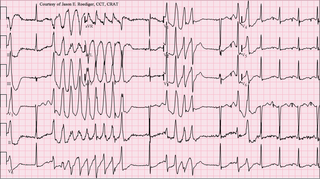
Torsades de pointes, torsade de pointes or torsades des pointes is a specific type of abnormal heart rhythm that can lead to sudden cardiac death. It is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia that exhibits distinct characteristics on the electrocardiogram (ECG). It was described by French physician François Dessertenne in 1966. Prolongation of the QT interval can increase a person's risk of developing this abnormal heart rhythm, occurring in between 1% and 10% of patients who receive QT-prolonging antiarrhythmic drugs.
Cardiac electrophysiology is a branch of cardiology and basic science focusing on the electrical activities of the heart. The term is usually used in clinical context, to describe studies of such phenomena by invasive (intracardiac) catheter recording of spontaneous activity as well as of cardiac responses to programmed electrical stimulation - clinical cardiac electrophysiology. However, cardiac electrophysiology also encompasses basic research and translational research components. Specialists studying cardiac electrophysiology, either clinically or solely through research, are known as cardiac electrophysiologists.
In cardiology, an accessory pathway is an additional electrical connection between two parts of the heart. These pathways can lead to abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) associated with symptoms of palpitations. Some pathways may activate a region of ventricular muscle earlier than would normally occur, referred to as pre-excitation, and this may be seen on an electrocardiogram. The combination of an accessory pathway that causes pre-excitation with arrhythmias is known as Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome.

The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) is an independent non-profit, non-governmental professional association that works to advance the prevention, diagnosis and management of diseases of the heart and blood vessels, and improve scientific understanding of the heart and vascular system. This is done by:

Michel Haïssaguerre is a French cardiologist and electrophysiologist. His investigations have been the basis for development of new markers and therapies for atrial and ventricular fibrillation.

Atrial fibrillation is an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by rapid and irregular beating of the atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods of abnormal beating, which become longer or continuous over time. It may also start as other forms of arrhythmia such as atrial flutter that then transform into AF.

Heart Rhythm is a peer-reviewed medical journal published by Elsevier that covers the study and management of cardiac arrhythmia. It is the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society, the Cardiac Electrophysiology Society, and the Pediatric & Congenital Electrophysiology Society. Its major focus is research and therapy of heart rhythm disorders, including mechanisms and electrophysiology, clinical and experimental, genetics, ablation, devices, drugs, and surgery. Other sections include contemporary reviews, unique case reports, viewpoints, Hands On, images, creative concepts, and editorial commentaries. New sections in 2024 include Iconic Figures and Top Stories.
A wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) is a non-invasive, external device for patients at risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). It allows physicians time to assess their patient's arrhythmic risk and see if their ejection fraction improves before determining the next steps in patient care. It is a leased device. A summary of the device, its technology and indications was published in 2017 and reviewed by the EHRA Scientific Documents Committee.

The Journal of the American College of Cardiology is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering all aspects of cardiovascular disease, including original clinical studies, translational investigations with clear clinical relevance, state-of-the-art papers, review articles, and editorials interpreting and commenting on the research presented, published by the American College of Cardiology.
An idioventricular rhythm is a cardiac rhythm characterized by a rate of <50 beats per minute (bpm), absence of conducted P waves and widening of the QRS complex. In cases where the heart rate is between 50 and 110 bpm, it is known as accelerated idioventricular rhythm and ventricular tachycardia if the rate exceeds 120 bpm. Causes of idioventricular rhythms are varied and can include drugs or a heart defect at birth. It is typically benign and not life-threatening.
The European Journal of Preventive Cardiology is a peer-reviewed medical journal that covers research on the cardiovascular system. The journal's editor-in-chief is Prof Victor Aboyans. It was established in 1994 as the European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation and obtained its current title in 2012. It is currently published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Vladimir Goldner was a Croatian physician, academic and professor at the School of Medicine, University of Zagreb.

Charles Antzelevitch is an American cardiovascular research scientist in the fields of cardiac electrophysiology and cardiac arrhythmia syndromes.

David Alfred Eisner, FRCP (Hon), FMedSci, is British Heart Foundation Professor of Cardiac Physiology at the University of Manchester and editor-in-chief of The Journal of General Physiology (JGP).
The European Heart Rhythm Association score of atrial fibrillation is a classification system for the extent of atrial fibrillation. It places patients in one of four categories based on how much they are limited during physical activity; the limitations/symptoms are in regard to normal breathing and varying degrees in shortness of breath and/or angina.
Cardiovascular Research is a medical journal published monthly by the Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. The journal publishes original and review articles from all areas of basic, translational, and clinical cardiovascular disease.

Dr. Béla Merkely is a Hungarian interventional cardiologist and sports cardiologist, a university professor, director of Semmelweis University's Heart and Vascular Centre and the current rector of Semmelweis University since 1 July 2018.
The European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing is a peer-reviewed nursing journal published by Oxford University Press. It covers cardiovascular nursing research. It is an official journal of the European Society of Cardiology and the Association of Cardiovascular Nursing and Allied Professions.

Pharmacological cardiotoxicity is defined as cardiac damage that occurs under the action of a drug. This can occur both through damage of cardiac muscle as well as through alteration of the ion currents of cardiomyocytes.












