Medicare is the publicly funded universal health care insurance scheme in Australia, as well as Norfolk Island, operated by Services Australia. Medicare is the main source of funding of health care in Australia, either partially or fully covering the cost of most primary health care services for eligible citizens, residents and visitors. Residents are entitled to a rebate for treatment by medical practitioners, eligible midwives, nurse practitioners and allied health professionals who have been issued a Medicare provider number, and can also obtain free treatment in state public hospitals. The scheme was created in 1975 by the Whitlam Government under the brand Medibank, and was limited by the Fraser Government in 1976 to paying customers only. The Hawke Government reintroduced universal health care in 1984 under the brand of Medicare. Medibank continued to exist as a government-owned private health insurance provider until it was privatised by the Abbott Government in 2014.
General practice is the name given in various nations, such as the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand, to the services provided by General practitioners. In some nations, such as the US, similar services may be described as family medicine or primary care. The term Primary Care in the UK may also include services provided by community pharmacy, optometrist, dental surgery and community hearing care providers. The balance of care between primary care and secondary care - which usually refers to hospital based services - varies from place to place, and with time. In many countries there are initiatives to move services out of hospitals into the community, in the expectation that this will save money and be more convenient.
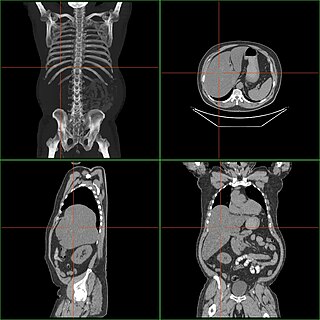
Hepatomegaly is the condition of having an enlarged liver. It is a non-specific medical sign having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, hepatic tumours, or metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly will present as an abdominal mass. Depending on the cause, it may sometimes present along with jaundice.
A personal health record (PHR) is a health record where health data and other information related to the care of a patient is maintained by the patient. This stands in contrast to the more widely used electronic medical record, which is operated by institutions and contains data entered by clinicians to support insurance claims. The intention of a PHR is to provide a complete and accurate summary of an individual's medical history which is accessible online. The health data on a PHR might include patient-reported outcome data, lab results, and data from devices such as wireless electronic weighing scales or from a smartphone.

Virginia Mason Medical Center, founded in 1920, is a private, non-profit organization located in Seattle, Washington, US.

The Cabinet of Nigeria is part of the Executive Branch of the Government of Nigeria. The Cabinet's role, as written in the Ministers' Statutory Powers and Duties Act is to serve as an advisory body to the President of Nigeria. Members of the Cabinet are appointed and report to the President, who can dismiss them at will. The Cabinet currently oversees 24 Federal Ministries, each responsible for some aspect of providing government services, as well as a number of parastatals.

AmigaOS 4 is a line of Amiga operating systems which runs on PowerPC microprocessors. It is mainly based on AmigaOS 3.1 source code developed by Commodore, and partially on version 3.9 developed by Haage & Partner. "The Final Update" was released on 24 December 2006 after five years of development by the Belgian company Hyperion Entertainment under license from Amiga, Inc. for AmigaOne registered users.
MDVIP is an American company, headquartered in Boca Raton, Florida, that operates a network of physicians. The company's physicians practice preventive medicine and personalized primary-care medicine.
The medical home, also known as the patient-centered medical home (PCMH), is a team-based health care delivery model led by a health care provider to provide comprehensive and continuous medical care to patients with a goal to obtain maximal health outcomes. It is described in the "Joint Principles" as "an approach to providing comprehensive primary care for children, youth and adults."
A sessional GP is an umbrella term for GPs whose work is organised on a sessional basis, as opposed to GP partners whose contract is generally for 24-hour care. The term was first coined by the National Association of Sessional GPs (NASGP), who at the time were called the National Association of Non-Principals (NANP). After consultation with their membership, it was perceived that the term 'non-principal' was a term that defined these GPs using a negative definition rather than a positive one.
The Shipman Inquiry was the report produced by a British governmental investigation into the activities of general practitioner and serial killer Harold Shipman. Shipman was arrested in September 1998 and the inquiry commenced shortly after he was found guilty of 15 murders in January 2000. It released its findings in various stages, with its sixth and final report being released on 27 January 2005 – by which time Shipman had died by suicide in prison. It was chaired by Dame Janet Smith DBE.
athenahealth, Inc. is a private American company that provides network-enabled services for healthcare and point-of-care mobile apps in the United States. athenahealth has a network of more than 160,000 providers and 110 million patients and offers a suite of services to manage medical records, revenue cycle, patient engagement, care coordination, and population health.
The French health care system is one of universal health care largely financed by government national health insurance. In its 2000 assessment of world health care systems, the World Health Organization found that France provided the "close to best overall health care" in the world. In 2011, France spent 11.6% of GDP on health care, or US$4,086 per capita, a figure much higher than the average spent by countries in Europe but less than in the US. Approximately 77% of health expenditures are covered by government funded agencies.
DrChrono is an American company based in Sunnyvale, California, that provides a software as a service patient care platform consisting of a Web- and cloud-based app for doctors and patients that makes electronic health records (EHR) available digitally and provides practice management and medical billing services.

Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) is any method of allowing a person in pain to administer their own pain relief. The infusion is programmable by the prescriber. If it is programmed and functioning as intended, the machine is unlikely to deliver an overdose of medication. Providers must always observe the first administration of any PCA medication which has not already been administered by the provider to respond to allergic reactions.
Lisa A. Cooper is a public health physician, and a Bloomberg Distinguished Professor at Johns Hopkins. She is the James F. Fries Professor of Medicine in the Division of General Internal Medicine, Vice President of Health Care Equity and Director of the Center to Eliminate Cardiovascular Health Disparities in the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. She is also a core faculty member in the Welch Center for Prevention, Epidemiology and Clinical Research and the Armstrong Institute for Patient Safety and Quality. She holds joint appointments in the Johns Hopkins School of Nursing and in the departments of Epidemiology, Health Policy and Management, and Health, Behavior and Society in the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. She is internationally recognized for her research on the impact of race, ethnicity and gender on the patient-physician relationship and subsequent health disparities.

Zocdoc is an online medical care appointment booking service, providing free of charge medical care search facility for end users by integrating information about medical practices and doctors' individual schedules in a central location. The company is based in New York City, with offices in Scottsdale, Arizona and Pune, India.

The Veterans Health Administration scandal of 2014 is a reported pattern of negligence in the treatment of United States military veterans. Critics charged that patients at the VHA hospitals had not met the target of getting an appointment within 14 days. In some hospitals, the staff falsified appointment records to appear to meet the 14-day target. Some patients died while they were on the waiting list; reports differ about whether they died because of the delay. Defenders agreed that it was unacceptable to falsify data, but the 14-day target was unrealistic in understaffed facilities like Phoenix, and most private insurers did not meet a 14-day target either. By most measures, the VHA system provides "excellent care at low cost," wrote Paul Krugman, who believes that the attacks on the VHA system are motivated by conservatives who want to discredit a government program that works well. Conservative legislators have proposed privatizing the VHA, and legislative reforms will make it easier for veterans to go to private doctors.
Vezeeta is an Egyptian online medical care scheduling service, providing a free of charge medical search platform for end users by integrating information about medical practices and doctors' individual schedules in a central location. The company is based in Cairo, with offices in Amman, Beirut, Dubai and Riyadh.
Luma Health is a San Francisco-based software company providing Healthcare IT solutions for the health care industry. The company’s focus is developing a web-based patient engagement platform which enables a text-first communication between health care providers and patients, referral management, and web scheduling.







