Related Research Articles

An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge carriers, which may be one of several types of particles, depending on the conductor. In electric circuits the charge carriers are often electrons moving through a wire. In semiconductors they can be electrons or holes. In an electrolyte the charge carriers are ions, while in plasma, an ionized gas, they are ions and electrons.

Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons and positively charged metal ions. It may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a structure of positively charged ions (cations). Metallic bonding accounts for many physical properties of metals, such as strength, ductility, thermal and electrical resistivity and conductivity, opacity, and lustre.

Organic electronics is a field of materials science concerning the design, synthesis, characterization, and application of organic molecules or polymers that show desirable electronic properties such as conductivity. Unlike conventional inorganic conductors and semiconductors, organic electronic materials are constructed from organic (carbon-based) molecules or polymers using synthetic strategies developed in the context of organic chemistry and polymer chemistry.
A semiconductor is a material that has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity generally falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricating most electronic circuits.
Molecular electronics is the study and application of molecular building blocks for the fabrication of electronic components. It is an interdisciplinary area that spans physics, chemistry, and materials science. The unifying feature is use of molecular building blocks to fabricate electronic components. Due to the prospect of size reduction in electronics offered by molecular-level control of properties, molecular electronics has generated much excitement. It provides a potential means to extend Moore's Law beyond the foreseen limits of small-scale conventional silicon integrated circuits.

In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. The flow of negatively charged electrons generates electric current, positively charged holes, and positive or negative ions in some cases.
In physics, a charge carrier is a particle or quasiparticle that is free to move, carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric charges in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons, ions and holes. The term is used most commonly in solid state physics. In a conducting medium, an electric field can exert force on these free particles, causing a net motion of the particles through the medium; this is what constitutes an electric current. The electron and the proton are the elementary charge carriers, each carrying one elementary charge (e), of the same magnitude and opposite sign.

Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The main advantage of conductive polymers is that they are easy to process, mainly by dispersion. Conductive polymers are generally not thermoplastics, i.e., they are not thermoformable. But, like insulating polymers, they are organic materials. They can offer high electrical conductivity but do not show similar mechanical properties to other commercially available polymers. The electrical properties can be fine-tuned using the methods of organic synthesis and by advanced dispersion techniques.

In electronics, electrical breakdown or dielectric breakdown is a process that occurs when an electrically insulating material, subjected to a high enough voltage, suddenly becomes a conductor and current flows through it. All insulating materials undergo breakdown when the electric field caused by an applied voltage exceeds the material's dielectric strength. The voltage at which a given insulating object becomes conductive is called its breakdown voltage and, in addition to its dielectric strength, depends on its size and shape, and the location on the object at which the voltage is applied. Under sufficient voltage, electrical breakdown can occur within solids, liquids, or gases. However, the specific breakdown mechanisms are different for each kind of dielectric medium.
In semiconductor production, doping is the intentional introduction of impurities into an intrinsic semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical, optical and structural properties. The doped material is referred to as an extrinsic semiconductor.
Organic semiconductors are solids whose building blocks are pi-bonded molecules or polymers made up by carbon and hydrogen atoms and – at times – heteroatoms such as nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen. They exist in the form of molecular crystals or amorphous thin films. In general, they are electrical insulators, but become semiconducting when charges are either injected from appropriate electrodes, upon doping or by photoexcitation.
A polymer-based battery uses organic materials instead of bulk metals to form a battery. Currently accepted metal-based batteries pose many challenges due to limited resources, negative environmental impact, and the approaching limit of progress. Redox active polymers are attractive options for electrodes in batteries due to their synthetic availability, high-capacity, flexibility, light weight, low cost, and low toxicity. Recent studies have explored how to increase efficiency and reduce challenges to push polymeric active materials further towards practicality in batteries. Many types of polymers are being explored, including conductive, non-conductive, and radical polymers. Batteries with a combination of electrodes are easier to test and compare to current metal-based batteries, however batteries with both a polymer cathode and anode are also a current research focus. Polymer-based batteries, including metal/polymer electrode combinations, should be distinguished from metal-polymer batteries, such as a lithium polymer battery, which most often involve a polymeric electrolyte, as opposed to polymeric active materials.

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter along with liquid, gas, and plasma. The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice, or irregularly. Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed.

Solid-state ionics is the study of ionic-electronic mixed conductor and fully ionic conductors and their uses. Some materials that fall into this category include inorganic crystalline and polycrystalline solids, ceramics, glasses, polymers, and composites. Solid-state ionic devices, such as solid oxide fuel cells, can be much more reliable and long-lasting, especially under harsh conditions, than comparable devices with fluid electrolytes.

Transparent conducting films (TCFs) are thin films of optically transparent and electrically conductive material. They are an important component in a number of electronic devices including liquid-crystal displays, OLEDs, touchscreens and photovoltaics. While indium tin oxide (ITO) is the most widely used, alternatives include wider-spectrum transparent conductive oxides (TCOs), conductive polymers, metal grids and random metallic networks, carbon nanotubes (CNT), graphene, nanowire meshes and ultra thin metal films.

Pseudocapacitance is the electrochemical storage of electricity in an electrochemical capacitor known as a pseudocapacitor. This faradaic charge transfer originates by a very fast sequence of reversible faradaic redox, electrosorption or intercalation processes on the surface of suitable electrodes. Pseudocapacitance is accompanied by an electron charge-transfer between electrolyte and electrode coming from a de-solvated and adsorbed ion. One electron per charge unit is involved. The adsorbed ion has no chemical reaction with the atoms of the electrode since only a charge-transfer takes place.
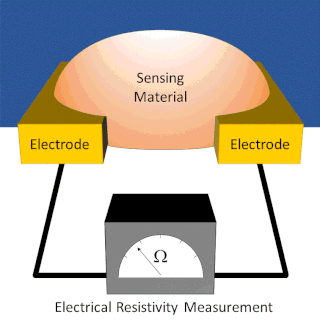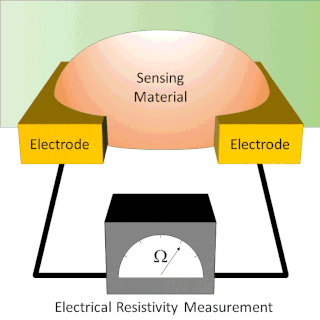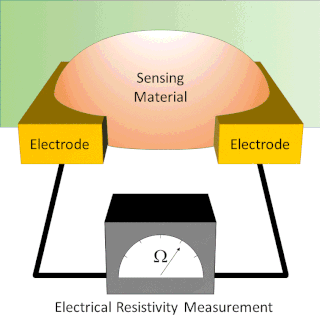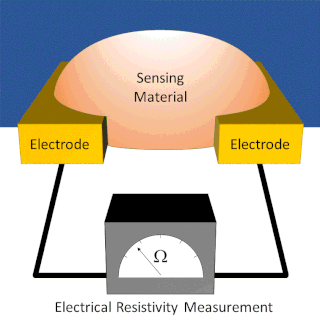
A chemiresistor is a material that changes its electrical resistance in response to changes in the nearby chemical environment. Chemiresistors are a class of chemical sensors that rely on the direct chemical interaction between the sensing material and the analyte. The sensing material and the analyte can interact by covalent bonding, hydrogen bonding, or molecular recognition. Several different materials have chemiresistor properties: metal-oxide semiconductors, some conductive polymers, and nanomaterials like graphene, carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles. Typically these materials are used as partially selective sensors in devices like electronic tongues or electronic noses.

Mixed conductors, also known as mixed ion-electron conductors(MIEC), are a single-phase material that has significant conduction ionically and electronically. Due to the mixed conduction, a formally neutral species can transport in a solid and therefore mass storage and redistribution are enabled. Mixed conductors are well known in conjugation with high-temperature superconductivity and are able to capacitate rapid solid-state reactions.
A polymer electrolyte is a polymer matrix capable of ion conduction. Much like other types of electrolyte—liquid and solid-state—polymer electrolytes aid in movement of charge between the anode and cathode of a cell. The use of polymers as an electrolyte was first demonstrated using dye-sensitized solar cells. The field has expanded since and is now primarily focused on the development of polymer electrolytes with applications in batteries, fuel cells, and membranes.

Lithium aluminium germanium phosphate, typically known with the acronyms LAGP or LAGPO, is an inorganic ceramic solid material whose general formula is Li
1+xAl
xGe
2-x(PO
4)
3. LAGP belongs to the NASICON family of solid conductors and has been applied as a solid electrolyte in all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. Typical values of ionic conductivity in LAGP at room temperature are in the range of 10–5 - 10–4 S/cm, even if the actual value of conductivity is strongly affected by stoichiometry, microstructure, and synthesis conditions. Compared to lithium aluminium titanium phosphate (LATP), which is another phosphate-based lithium solid conductor, the absence of titanium in LAGP improves its stability towards lithium metal. In addition, phosphate-based solid electrolytes have superior stability against moisture and oxygen compared to sulfide-based electrolytes like Li
10GeP
2S
12 (LGPS) and can be handled safely in air, thus simplifying the manufacture process. Since the best performances are encountered when the stoichiometric value of x is 0.5, the acronym LAGP usually indicates the particular composition of Li
1.5Al
0.5Ge
1.5(PO
4)
3, which is also the typically used material in battery applications.
References
- ↑ Surville, R. D. et al. Electrochemical chains using protolytic organic semiconductors. Electrochimica Acta 13, 1451–1458 (1968). .
- ↑ Handbook of Conducting Polymers, 2 Volume Set. (2007). .
- ↑ Sariciftci, N. S., Smilowitz, L., Heeger, A. J. & Wudl, F. Photoinduced electron transfer from a conducting polymer to buckminsterfullerene. Science 258, 1474–1476 (1992). .