The implementation of the Dayton Accords of 1995 has focused the efforts of policymakers in Bosnia and Herzegovina, as well as the international community, on regional stabilization in the countries-successors of the former Yugoslavia. Relations with its neighbors of Croatia and Serbia have been fairly stable since the signing of the Dayton Agreement in 1995.

The foreign relations between Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH) and Croatia are bound together by shared history, language, neighboring geography and cultural commonalties. They established diplomatic relations in 1992, following the dissolution of Yugoslavia and independence of Croatia. The two countries share a 932-kilometer (579 mi) border – the second longest external land border in the European Union (EU). Modern relations between the two states are functional but remain tense after ineffective 21st-century attempts at détente.

The relations between Bosnia and Herzegovina and North Macedonia are very good, without any open issues between them.
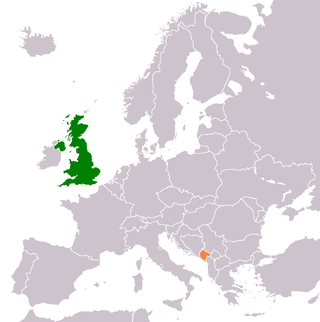
Montenegro–United Kingdom relations are the bilateral relations between Montenegro and the United Kingdom. Both nations are members of the Council of Europe and NATO and had fought on the same side in both World War I and World War II.

Bosnia and Herzegovina–Denmark relations refers to the current and historical relations between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Denmark. Bosnia and Herzegovina has an embassy in Copenhagen, and Denmark has an embassy in Sarajevo. Diplomatic relations were established on 2 June 1992. In 2010, Danish Foreign Minister Lene Espersen announced that Denmark will close their embassy in Sarajevo in 2012.

Bosnia and Herzegovina–Turkey relations are the bilateral relations between Bosnia-Herzegovina and Turkey. Bosnia and Herzegovina is a southeast European country, while Turkey is a transcontinental country with a small European part on the Balkan peninsula around Istanbul. Diplomatic relations between the two countries started on 29 August 1992. Bosnia and Herzegovina has one embassy in Ankara and two consulates in Istanbul and İzmir, while Turkey has one embassy in Sarajevo and one consulate in Mostar. The two countries enjoy very warm diplomatic relations, due to historical and cultural ties dating back to the 15th century. There is a large population of Bosniaks in Turkey and a smaller community of Turks in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The Istanbul quarter of Yenibosna is named in honour of the Bosnian community that has settled there since Ottoman times. Reflecting the close ties between the two nations, Bosnians and Turks are free to travel to each other's countries using only their national identification cards, without the need for a passport. Turkey gives full support to Bosnia and Herzegovina's NATO membership.

Bosnia and Herzegovina–Indonesia relations refers to the bilateral relations between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Indonesia. Bosnia and Herzegovina has an embassy in Jakarta, while Indonesia has an embassy in Sarajevo. The bilateral relations was initially motivated by humanity and religious solidarity. As a nation with the largest Muslim population, Indonesians were shocked by the ethnic cleansing against Muslim Bosniaks during the Bosnian War, and promptly organized and mobilized help. Indonesian support for Bosnia and Herzegovina ranged from collecting donations, sending peacekeeping forces under United Nations, to building the Istiqlal Mosque in Sarajevo.
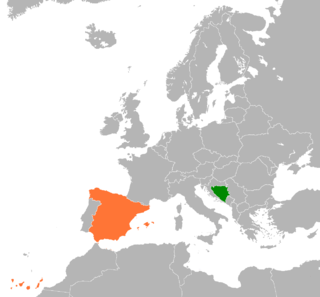
Bosnia and Herzegovina–Spain relations were formally established on 14 December 1992.

Azerbaijan-Bosnia and Herzegovina relations refer to the bilateral relations between Azerbaijan and Bosnia and Herzegovina. Azerbaijan has a diplomatic office in Sarajevo. Bosnia and Herzegovina has a non resident ambassador in Ankara, Turkey.

The Bosnia and Herzegovina–Palestine relations are the bilateral relations between Bosnia and Herzegovina and the State of Palestine. The countries recognized each other on 27 May 1992. Palestine has an embassy in Sarajevo. Bosnia does not have diplomatic representation in Palestine, but its embassy in Cairo is accredited to the Palestinian side. In the past, both countries were part of the Ottoman Empire.
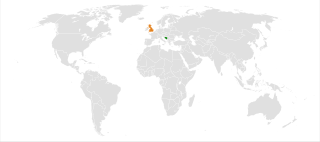
Bosnia and Herzegovina and the United Kingdom established diplomatic relations on 13 April 1992.












