Related Research Articles

Lemon balm is a perennial herbaceous plant in the mint family and native to south-central Europe, the Mediterranean Basin, Iran, and Central Asia, but now naturalised elsewhere.

Valerian is a perennial flowering plant native to Europe and Asia. In the summer when the mature plant may have a height of 1.5 metres, it bears sweetly scented pink or white flowers that attract many fly species, especially hoverflies of the genus Eristalis. It is consumed as food by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species, including the grey pug.

Calendula is a genus of about 15–20 species of annual and perennial herbaceous plants in the daisy family, Asteraceae that are often known as marigolds. They are native to southwestern Asia, western Europe, Macaronesia, and the Mediterranean. Other plants known as marigolds include corn marigold, desert marigold, marsh marigold, and plants of the genus Tagetes.

Soliga, also spelled Solega, Sholaga and Shōlaga, is an ethnic group of India. Its members inhabit the mountain ranges mostly in the Chamarajanagar district of southern Karnataka and Erode district of Tamil Nadu. Many are concentrated in the Biligiriranga Hills and associated ranges, mainly in the talukas Yelandur, Kollegal and Chamarajanagar of Karnataka. The Soliga speak Sholaga, which belongs to the Dravidian family. Under Indian law, they are recognized as a scheduled tribe, they have a population of around 40,000.

Salvia officinalis, the common sage or sage, is a perennial, evergreen subshrub, with woody stems, grayish leaves, and blue to purplish flowers. It is a member of the mint family Lamiaceae and native to the Mediterranean region, though it has been naturalized in many places throughout the world. It has a long history of medicinal and culinary use, and in modern times it has been used as an ornamental garden plant. The common name "sage" is also used for closely related species and cultivars.

Phyllanthus emblica, also known as emblic, emblic myrobalan, myrobalan, Indian gooseberry, Malacca tree, or amla, from the Sanskrit आमलकी (āmalakī), is a deciduous tree of the family Phyllanthaceae. Its native range is tropical and southern Asia.

Special Herbs, Vols. 7 & 8 is an instrumental album released by MF Doom under the moniker Metal Fingers. As with all volumes of Special Herbs released by Metal Fingers, each track is named after a herb or similar flora. Although being an instrumental album, some tracks contain sampled speech.

Sanguisorba officinalis, commonly known as great burnet, is a plant in the family Rosaceae, subfamily Rosoideae. It is native throughout the cooler regions of the Northern Hemisphere in Europe, northern Asia, and northern North America.

Calendula officinalis, the pot marigold, common marigold, ruddles, Mary's gold or Scotch marigold, is a flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae. It is probably native to southern Europe, though its long history of cultivation makes its precise origin unknown. It is also widely naturalised farther north in Europe and elsewhere in warm temperate regions of the world.
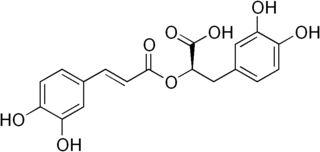
Rosmarinic acid, named after rosemary, is a polyphenol constituent of many culinary herbs, including rosemary, perilla, sage, mint, and basil.
The European Chemical Society (EuChemS) is a European non-profit organisation which promotes collaboration between non-profit scientific and technical societies in the field of chemistry.
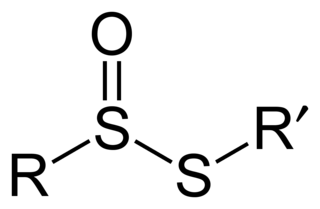
In organosulfur chemistry, thiosulfinate is a functional group consisting of the linkage R-S(O)-S-R. Thiolsulfinates are also named as alkanethiosulfinic acid esters.

Glucogallin is chemical compound formed from gallic acid and β-D-glucose. It can be found in oaks species like the North American white oak, European red oak and Amla fruit.
The ChemDB HIV, Opportunistic Infection and Tuberculosis Therapeutics Database is a publicly available tool developed by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to compile preclinical data on small molecules with potential therapeutic action against HIV/AIDS and related opportunistic infections.

Punigluconin is an ellagitannin, a polyphenol compound. It is found in the bark of Punica granatum (pomegranate) and in Emblica officinalis. It is a molecule having a hexahydroxydiphenic acid group and two gallic acids attached to a gluconic acid core.

Pedunculagin is an ellagitannin. It is formed from casuarictin via the loss of a gallate group.
Churna is a mixture of powdered herbs and or minerals used in Ayurvedic medicine. Triphala is an example of a classic Ayurvedic formula, used for thousands of years that is made from the powders of three fruits Amalaki, Haritaki and Bibhitaki.
Selepa celtis, called the hairy caterpillar as a larva, is a moth of the family Nolidae. The species was first described by Frederic Moore in 1858. It is found in Oriental tropics of India, Sri Lanka, Taiwan towards the Ryukyu Islands and Australia.
Selepa discigera is a moth of the family Nolidae first described by Francis Walker in 1864. It is found in Oriental tropics of India, Sri Lanka, New Guinea and Australia.
Selepa plumbeata is a moth of the family Nolidae first described by George Hampson in 1912. It is found in Oriental tropics of India, Sri Lanka, and Borneo.
References
- ↑ Ghosal, S.; Tripathi, V. K.; Chauhan, S. (2010). "ChemInform Abstract: Active Constituents of Emblica officinalis. Part 1. The Chemistry and Antioxidative Effects of Two New Hydrolysable Tannins, Emblicanin A ( Ia) and B (Ib)". ChemInform. 27 (47): no. doi:10.1002/chin.199647279.