
Phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—occur naturally in wine. These include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.
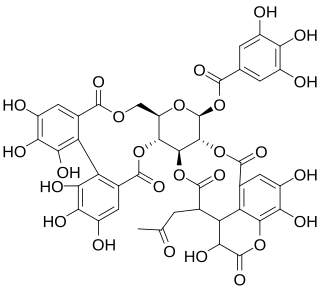
Chebulagic acid is a benzopyran tannin and an antioxidant that has many potential uses in medicine.

Ethyl gallate is a food additive with E number E313. It is the ethyl ester of gallic acid. Ethyl gallate is added to food as an antioxidant.

Chebulinic acid is an ellagitannin found in the seeds of Euphoria longana, in the fruits of Terminalia chebula or in the leaves of T. macroptera.

Castalagin is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolyzable tannin, found in oak and chestnut wood and in the stem barks of Terminalia leiocarpa and Terminalia avicennoides.

The ellagitannins are a diverse class of hydrolyzable tannins, a type of polyphenol formed primarily from the oxidative linkage of galloyl groups in 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl glucose. Ellagitannins differ from gallotannins, in that their galloyl groups are linked through C-C bonds, whereas the galloyl groups in gallotannins are linked by depside bonds.

Grandinin is an ellagitannin. It can be found in Melaleuca quinquenervia leaves and in oaks species like the North American white oak and European red oak. It shows antioxydant activity. It is an astringent compound. It is also found in wine, red or white, aged in oak barrels.

Gallagic acid is a polyphenolic chemical compound that can be found in the ellagitannins, a type of tannin, found in Punica granatum (pomegranate). It is a building block of the corresponding tannin punicalagin, punicalin, punicacortein C and 2-O-galloyl-punicalin.

Casuarictin is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolysable tannin. It can be found in Casuarina and Stachyurus species.

Terflavin B is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolysable tannin. It can be found in Myrobalanus chebula, the black chebulic, and in Terminalia catappa, the Indian almond.
Tergallic acids are trimers of gallic acid, often found naturally in the form of glycosides. Tergallic acid O- or C-glucosides that can be found in acorns of several Quercus (oak) species. The dehydrated tergallic acid C-glucoside and tergallic acid O-glucoside can be characterised in the acorns of Quercus macrocarpa. Dehydrated tergallic-C-glucoside can be found in the cork from Quercus suber.
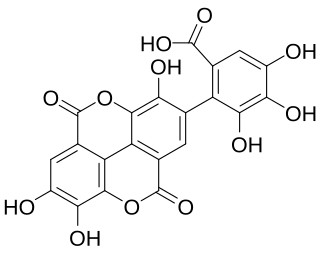
Flavogallonic acid dilactone is a hydrolysable tannin that can be found in Rhynchosia volubilis seeds, in Shorea laevifolia, in Anogeissus leiocarpus and Terminalia avicennoides.
Terminalia avicennioides is a tree species in the genus Terminalia found in West Africa.

The pomegranate ellagitannins, which include punicalagin isomers, are ellagitannins found in the sarcotestas, rind (peel), bark or heartwood of the pomegranate fruit.

Terminalia myriocarpa, the East Indian almond, is a tree species in the genus Terminalia found in Southeast Asia.

Casuarinin is an ellagitannin. It is found in the pericarp of pomegranates. It is also found in Casuarina and Stachyurus species and in Alnus sieboldiana.
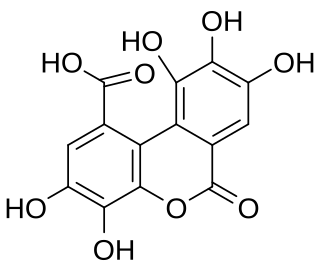
Luteic acid is a natural phenol found in numerous fruits. It is a monolactonized tergalloyl group. Maximilian Nierenstein showed in 1945 that luteic acid was a molecule present in the myrobalanitannin, a tannin found in the fruit of Terminalia chebula and is an intermediary compound in the synthesis of ellagic acid. It can form from hexahydroxydiphenic acid. It is also present in the structure of the tannins alnusiin and bicornin.

Bicornin is an ellagitannin found in plants of the order Myrtales, including Trapa bicornis and Syzygium aromaticum (clove).

Terminalia macroptera is a species of flowering plant in the Combretaceae known by the Hausa common name kwandari. It is native to Africa, where it can be found in Benin, Burkina Faso, Ghana, Senegal, Sudan, Uganda, and Nigeria.

Methyl gallate is a phenolic compound. It is the methyl ester of gallic acid.

















