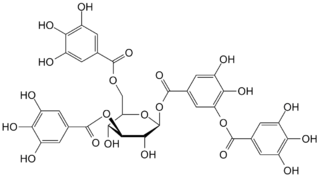
Tannins are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
A hydrolyzable tannin or pyrogallol-type tannin is a type of tannin that, on heating with hydrochloric or sulfuric acids, yields gallic or ellagic acids.
The ellagitannins are a diverse class of hydrolyzable tannins, a type of polyphenol formed primarily from the oxidative linkage of galloyl groups in 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl glucose. Ellagitannins differ from gallotannins, in that their galloyl groups are linked through C-C bonds, whereas the galloyl groups in gallotannins are linked by depside bonds.
B. japonica may refer to:

Condensed tannins are polymers formed by the condensation of flavans. They do not contain sugar residues.

Quercus infectoria, the Aleppo oak, is a species of oak, bearing galls that have been traditionally used for centuries in Asia medicinally. Manjakani is the name used in Malaysia for the galls; these have been used for centuries in softening leather and in making black dye and ink. In India the galls are called majuphal among many other names.

Rhus chinensis, the Chinese sumac, or nutgall tree, is a plant species in the genus Rhus.

Luteic acid is a natural phenol found in numerous fruits. It is a monolactonized tergalloyl group. Maximilian Nierenstein showed in 1945 that luteic acid was a molecule present in the myrobalanitannin, a tannin found in the fruit of Terminalia chebula and is an intermediary compound in the synthesis of ellagic acid. It can form from hexahydroxydiphenic acid. It is also present in the structure of the tannins alnusiin and bicornin.
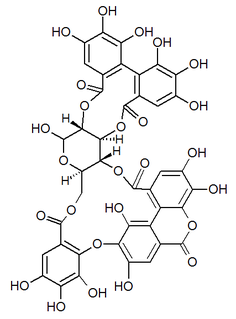
Alnusiin is an ellagitannin found in Alnus sieboldiana.

Bicornin is an ellagitannin found in the Myrtales Trapa bicornis and Syzygium aromaticum (clove).

2,3-(S)-Hexahydroxydiphenoyl-d-glucose is an hydrolyzable tannin that can be found in Eucalyptus delegatensis, the Alpine ash (Myrtaceae), in Terminalia catappa, the Bengal almond, and Combretum glutinosum.

Nuphar japonica, known as East Asian yellow water-lily, is an aquatic plant species in the genus Nuphar found in Japan and the Korean Peninsula. It is endangered in Russia. The species was not accepted by The Plant List as of November 2013, which regarded it as an "unresolved name".

Mallotus japonicus, known as East Asian mallotus, the food wrapper plant or Akamegashiwa in Japanese, is a plant species in the genus Mallotus native to China. It is also found in Japan and Korea.
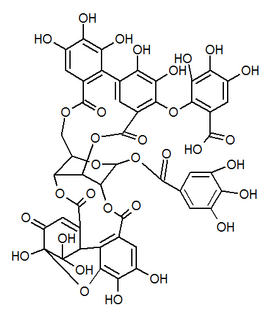
Mallotusinic acid is a hydrolysable tannin found in the bark of Mallotus japonicus. It is more generally present in Geraniales.

Balanophonin is a neo-lignan. It is a bioactive compound which can be isolated from Dipteryx odorata and Balanophora japonica.
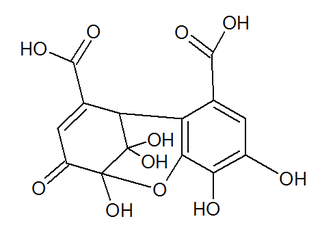
Dehydrohexahydroxydiphenic acid is a group found in dehydroellagitannins. It is formed from hexahydroxydiphenic acid (HHDP) through oxidation of the plant hydrolysable tannins. It is found in ellagitannins such as euphorbin A, geraniin or mallotusinic acid.

Mallojaponin is a hydrolysable tannin found in the bark of Mallotus japonicus. This compound contains the moiety elaeocarpusinic acid, an oxidized hexahydroxydiphenic acid group which reacted with a dehydroascorbic acid molecule. It also contains a valoneic acid and a gallic acid moieties linked to a glucose molecule.

Strictinin is a bioactive chemical of the ellagitannin family of hydrolyzable tannins. This compound shows activity against influenza virus.
















