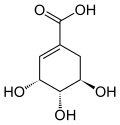
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name 1ʟ-1(OH),3,4/5-Tetrahydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid [1] | |||
| Preferred IUPAC name (1S,3R,4S,5R)-1,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxycyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.976 | ||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H12O6 | |||
| Molar mass | 192.17 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.35 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 168 °C (334 °F; 441 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 [2] [2] | |||
| Warning [2] | |||
| H319 [2] | |||
| P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313 [2] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Quinic acid is an organic compound with the formula (CHOH)3(CH2)2C(OH)CO2H. The compound is classified as a cyclitol, a cyclic polyol, and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is a colorless solid that can be extracted from plant sources. Quinic acid is implicated in the perceived acidity of coffee, where it occurs around 13% by weight. [3]