
Rhizobia are diazotrophic bacteria that fix nitrogen after becoming established inside the root nodules of legumes (Fabaceae). To express genes for nitrogen fixation, rhizobia require a plant host; they cannot independently fix nitrogen. In general, they are gram negative, motile, non-sporulating rods.

Ensifer meliloti are an aerobic, Gram-negative, and diazotrophic species of bacteria. S. meliloti are motile and possess a cluster of peritrichous flagella. S. meliloti fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia for their legume hosts, such as alfalfa. S. meliloti forms a symbiotic relationship with legumes from the genera Medicago, Melilotus and Trigonella, including the model legume Medicago truncatula. This symbiosis promotes the development of a plant organ, termed a root nodule. Because soil often contains a limited amount of nitrogen for plant use, the symbiotic relationship between S. meliloti and their legume hosts has agricultural applications. These techniques reduce the need for inorganic nitrogenous fertilizers.

Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, primarily legumes, that form a symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Under nitrogen-limiting conditions, capable plants form a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of bacteria known as rhizobia. This process has evolved multiple times within the legumes, as well as in other species found within the Rosid clade. Legume crops include beans, peas, and soybeans.
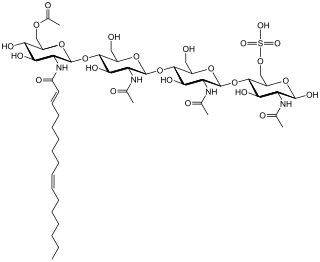
Nod factors, are signaling molecules produced by soil bacteria known as rhizobia in response to flavonoid exudation from plants under nitrogen limited conditions. Nod factors initiate the establishment of a symbiotic relationship between legumes and rhizobia by inducing nodulation. Nod factors produce the differentiation of plant tissue in root hairs into nodules where the bacteria reside and are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere for the plant in exchange for photosynthates and the appropriate environment for nitrogen fixation. One of the most important features provided by the plant in this symbiosis is the production of leghemoglobin, which maintains the oxygen concentration low and prevents the inhibition of nitrogenase activity.
Sharon Rugel Long is an American plant biologist. She is the Steere-Pfizer Professor of Biological Science in the Department of Biology at Stanford University, and the Principal Investigator of the Long Laboratory at Stanford.

Bradyrhizobium is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria, many of which fix nitrogen. Nitrogen fixation is an important part of the nitrogen cycle. Plants cannot use atmospheric nitrogen (N2); they must use nitrogen compounds such as nitrates.

Ensifer is a genus of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (rhizobia), three of which have been sequenced.
Bradyrhizobium japonicum is a species of legume-root nodulating, microsymbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The species is one of many Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria commonly referred to as rhizobia. Within that broad classification, which has three groups, taxonomy studies using DNA sequencing indicate that B. japonicum belongs within homology group II.
Pararhizobium giardinii is a Gram negative root nodule bacteria. It forms nitrogen-fixing root nodules on legumes, being first isolated from those of Phaseolus vulgaris.
Rhizobium gallicum is a Gram-negative root-nodule bacterium. It forms nitrogen-fixing root nodules on legumes, being first isolated from those of Phaseolus vulgaris.
Bradyrhizobium arachidis is a species of legume-root nodulating, microsymbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacterium. It was first isolated from Arachis hypogaea root nodules in China. Its type strain is CCBAU 051107T.
Bradyrhizobium liaoningense is a species of legume-root nodulating, microsymbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacterium. It was first isolated from Glycine soja and Glycine max root nodules in China. Its type strain is strain 2281.
Bradyrhizobium canariense is a species of legume-root nodulating, endosymbiont nitrogen-fixing bacterium. It is acid-tolerant and nodulates endemic genistoid legumes from the Canary Islands. The type strain is BTA-1T.
Rhizobium mongolense is a Gram negative root nodule bacteria, which nodulates and forms nitrogen-fixing symbioses with Medicago ruthenica. Its type strain is USDA 1844.
Mesorhizobium mediterraneum is a bacterium from the genus Mesorhizobium, which was isolated from root nodule of the Chickpea in Spain. The species Rhizobium mediterraneum was subsequently transferred to Mesorhizobium mediterraneum. This species, along with many other closely related taxa, have been found to promote production of chickpea and other crops worldwide by forming symbiotic relationships.
Rhizobium lusitanum is a Gram negative root nodule bacteria, specifically nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris. Its type strain is P1-7T.
Ensifer americanus is a bacterium first isolated from root nodules of Acacia species native of Mexico. Its type strain is CFNEI 156.
Ensifer medicae is a species of gram-negative, nitrogen-fixing, rod-shaped bacteria. They can be free-living or symbionts of leguminous plants in root nodules. E.medicae was first isolated from root nodules on plants in the genus Medicago. Some strains of E.medicae, like WSM419, are aerobic. They are chemoorganotrophic mesophiles that prefer temperatures around 28 °C. In addition to their primary genome, these organisms also have three known plasmids, sized 1,570,951 bp, 1,245,408 bp and 219,313 bp.

A symbiosome is a specialised compartment in a host cell that houses an endosymbiont in a symbiotic relationship.

Ensifer numidicus is a nitrogen fixing symbiont of Fabaceae. gram-negative, aerobic, non-spore forming, rod-shaped bacterium of the family Rhizobiaceae. First described in 2010; more biovars have since been isolated and described with ORS 1407 considered the representative organism. Most examples have been found in arid and infra-arid regions of Tunisia.






