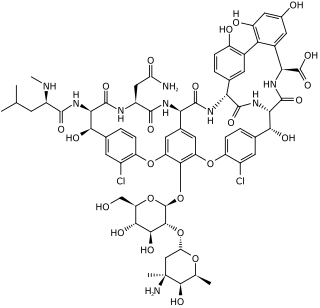
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, and meningitis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Blood levels may be measured to determine the correct dose. Vancomycin is also taken by mouth as a treatment for severe Clostridium difficile colitis. When taken by mouth it is poorly absorbed.

Enterococcus is a large genus of lactic acid bacteria of the phylum Bacillota. Enterococci are gram-positive cocci that often occur in pairs (diplococci) or short chains, and are difficult to distinguish from streptococci on physical characteristics alone. Two species are common commensal organisms in the intestines of humans: E. faecalis (90–95%) and E. faecium (5–10%). Rare clusters of infections occur with other species, including E. casseliflavus, E. gallinarum, and E. raffinosus.

Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019.

Linezolid is an antibiotic used for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. Linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The main uses are infections of the skin and pneumonia although it may be used for a variety of other infections including drug-resistant tuberculosis. It is used either by injection into a vein or by mouth.

Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) are strains of Staphylococcus aureus that have become resistant to the glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin.

Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, or vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), are bacterial strains of the genus Enterococcus that are resistant to the antibiotic vancomycin.

Enterococcus faecalis – formerly classified as part of the group D Streptococcus system – is a Gram-positive, commensal bacterium inhabiting the gastrointestinal tracts of humans. Like other species in the genus Enterococcus, E. faecalis is found in healthy humans and can be used as a probiotic. The probiotic strains such as Symbioflor1 and EF-2001 are characterized by the lack of specific genes related to drug resistance and pathogenesis. As an opportunistic pathogen, E. faecalis can cause life-threatening infections, especially in the nosocomial (hospital) environment, where the naturally high levels of antibiotic resistance found in E. faecalis contribute to its pathogenicity. E. faecalis has been frequently found in reinfected, root canal-treated teeth in prevalence values ranging from 30% to 90% of the cases. Re-infected root canal-treated teeth are about nine times more likely to harbor E. faecalis than cases of primary infections.
Century Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is an American pharmaceutical company, founded in 1966 in Indianapolis, Indiana, USA.

Dalfopristin is a semi-synthetic streptogramin antibiotic analogue of ostreogyrcin A. The combination quinupristin/dalfopristin was brought to the market by Rhone-Poulenc Rorer Pharmaceuticals in 1999. Synercid is used to treat infections by staphylococci and by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium.

Bile Esculin Agar (BEA) is a selective differential agar used to isolate and identify members of the genus Enterococcus, formerly part of the "group D streptococci".
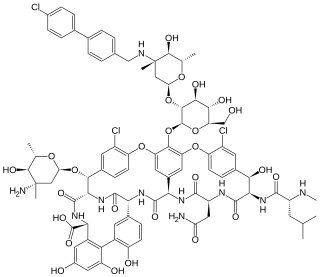
Oritavancin, sold under the brand name Orbactiv among others, is a semisynthetic glycopeptide antibiotic medication for the treatment of serious Gram-positive bacterial infections. Its chemical structure as a lipoglycopeptide is similar to vancomycin.
Enterococcus faecium is a Gram-positive, gamma-hemolytic or non-hemolytic bacterium in the genus Enterococcus. It can be commensal in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals, but it may also be pathogenic, causing diseases such as neonatal meningitis or endocarditis.
Streptogramins are a class of antibiotics.

Ceftobiprole (Zevtera/Mabelio) is a fifth-generation cephalosporin for the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia and community-acquired pneumonia. It is marketed by Basilea Pharmaceutica in the United Kingdom, Germany, Switzerland and Austria under the trade name Zevtera, in France and Italy under the trade name Mabelio. Like other cephalosporins, ceftobiprole exerts its antibacterial activity by binding to important penicillin-binding proteins and inhibiting their transpeptidase activity which is essential for the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. Ceftobiprole has high affinity for penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and retains its activity against strains that express divergent mecA gene homologues. Ceftobiprole also binds to penicillin-binding protein 2b in Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-intermediate), to penicillin-binding protein 2x in Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-resistant), and to penicillin-binding protein 5 in Enterococcus faecalis.
Enterococcus gallinarum is a species of Enterococcus. E. gallinarum demonstrates an inherent, low-level resistance to vancomycin. Resistance is due to a chromosomal gene, vanC, which encodes for a terminal D-alanine-D-serine instead of the usual D-alanine-D-alanine in cell wall peptidoglycan precursor proteins. That is a separate mechanism than the vancomycin resistance seen in VRE isolates of E. faecium and E. faecalis which is mediated by vanA or vanB. This species is known to cause clusters of infection, although it considered very rare. It is the only other known enterococcal species besides E. faecium and E. faecalis known to cause outbreaks and spread in hospitals.

Sophoraflavanone G is a volatile phytoncide, released into the atmosphere, soil and ground water, by members of the Sophora genus. Due to an increase in the rates of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, scientific efforts have focused on finding either naturally-made or genetically modified compounds that can treat and or prevent these harmful and sometimes deadly bacteria. Sophoraflavanone G, due to its use as a phytoncide, has been found to impact the growth of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and enhance the effect of currently used antibiotics.
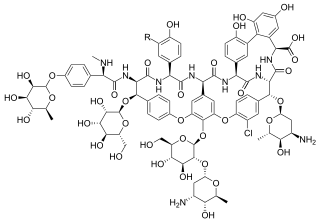
Avoparcin is a glycopeptide antibiotic effective against Gram-positive bacteria. It has been used in agriculture as an additive to livestock feed to promote growth in chickens, pigs, and cattle. It is also used as an aid in the prevention of necrotic enteritis in poultry.
D-alanine—(R)-lactate ligase is an enzyme with systematic name D-alanine:(R)-lactate ligase (ADP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
ESKAPE is an acronym comprising the scientific names of six highly virulent and antibiotic resistant bacterial pathogens including: Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp. This group of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria can evade or 'escape' commonly used antibiotics due to their increasing multi-drug resistance (MDR). As a result, throughout the world, they are the major cause of life-threatening nosocomial or hospital-acquired infections in immunocompromised and critically ill patients who are most at risk. P. aeruginosa and S. aureus are some of the most ubiquitous pathogens in biofilms found in healthcare. P. aeruginosa is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium, commonly found in the gut flora, soil, and water that can be spread directly or indirectly to patients in healthcare settings. The pathogen can also be spread in other locations through contamination, including surfaces, equipment, and hands. The opportunistic pathogen can cause hospitalized patients to have infections in the lungs, blood, urinary tract, and in other body regions after surgery. S. aureus is a Gram-positive, cocci-shaped bacterium, residing in the environment and on the skin and nose of many healthy individuals. The bacterium can cause skin and bone infections, pneumonia, and other types of potentially serious infections if it enters the body. S. aureus has also gained resistance to many antibiotic treatments, making healing difficult. Because of natural and unnatural selective pressures and factors, antibiotic resistance in bacteria usually emerges through genetic mutation or acquires antibiotic-resistant genes (ARGs) through horizontal gene transfer - a genetic exchange process by which antibiotic resistance can spread.
Kerry L. LaPlante is an American pharmacist, academic and researcher. She is a Professor of Pharmacy and the Chair of the Department of Pharmacy Practice at the University of Rhode Island, an Adjunct Professor of Medicine at Brown University, an Infectious Diseases Pharmacotherapy Specialist, and the Director of the Rhode Island Infectious Diseases Fellowship and Research Programs at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Providence, Rhode Island.












