The Modified Mercalli intensity scale measures the effects of an earthquake at a given location. This is in contrast with the seismic magnitude usually reported for an earthquake.

An earthquake occurred at on 8 October 2005 in Azad Jammu and Kashmir, a territory under Pakistan. It was centred near the city of Muzaffarabad, and also affected nearby Balakot in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and some areas of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It registered a moment magnitude of 7.6 and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme). The earthquake was also felt in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, India and the Xinjiang region. The severity of the damage caused by the earthquake is attributed to severe upthrust. Over 86,000 people died, a similar number were injured, and millions were displaced. It is considered the deadliest earthquake in South Asia, surpassing the 1935 Quetta earthquake.
The 1980 Irpinia earthquake took place in Italy on 23 November 1980, with a moment magnitude of 6.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme). It left at least 2,483 people dead, at least 7,700 injured, and 250,000 homeless.

The 1999 Athens earthquake occurred on September 7 at near Mount Parnitha in Greece with a moment magnitude of 6.0 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). The proximity to the Athens metropolitan area resulted in widespread structural damage, mainly to the nearby suburban towns of Ano Liosia, Acharnes, Fyli, Thrakomakedones, Kifissia, Metamorfosi, Kamatero and Nea Filadelfeia. More than 100 buildings across those areas collapsed trapping scores of victims under their rubble while dozens more were severely damaged. With damage estimated at $3–4.2 billion, 143 people were killed, and up to 1,600 were treated for injuries in Greece's deadliest natural disaster in almost half a century.

In seismology, an isoseismal map is used to show lines of equally felt seismic intensity, generally measured on the Modified Mercalli scale. Such maps help to identify earthquake epicenters, particularly where no instrumental records exist, such as for historical earthquakes. They also contain important information on ground conditions at particular locations, the underlying geology, radiation pattern of the seismic waves, and the response of different types of buildings. They form an important part of the macroseismic approach, i.e. that part of seismology dealing with noninstrumental data. The shape and size of the isoseismal regions can be used to help determine the magnitude, focal depth, and focal mechanism of an earthquake.
The 1694 Irpinia–Basilicata earthquake occurred on 8 September. It caused widespread damage in the Basilicata and Apulia regions of what was then the Kingdom of Naples, resulting in more than 6,000 casualties. The earthquake occurred at 11:40 UTC and lasted between 30 and 60 seconds.

The 1909 Provence earthquake occurred on June 11 in Provence. Measuring 6.2 on the surface wave magnitude scale, it is the largest ever recorded earthquake in metropolitan France.

Earthquake environmental effects are the effects caused by an earthquake, including surface faulting, tsunamis, soil liquefactions, ground resonance, landslides and ground failure, either directly linked to the earthquake source or provoked by the ground shaking. These are common features produced both in the near and far fields, routinely recorded and surveyed in recent events, very often remembered in historical accounts and preserved in the stratigraphic record. Both surface deformation and faulting and shaking-related geological effects not only leave permanent imprints in the environment, but also dramatically affect human structures. Moreover, underwater fault ruptures and seismically-triggered landslides can generate tsunami waves.
The 1805 Molise earthquake occurred on July 26 at 21:01 UTC. It has an estimated magnitude of 6.6 on the equivalent magnitude scale (Me) and a maximum perceived intensity of X on the Mercalli intensity scale. The area of greatest damage was between the towns of Isernia and Campobasso, while the area of intense damage extended over about 2,000 square kilometres. There were an estimated 5,573 deaths resulting from this earthquake and two of the aftershocks.
The 2017 Ischia earthquake occurred in the island of Ischia, Campania, in southern Italy. The main shock occurred at 20:57 CEST on 21 August 2017, and was rated 3.9 Mw or 4.2 mb on the moment magnitude scale.
The 1992 Murindó earthquake occurred on October 18 at 15:11 UTC with an epicenter in the Department of Chocó, northern Colombia. The shallow magnitude 7.2 earthquake struck northwest of the town of Murindó, killing ten and injured more than a hundred. Thirty-three municipalities were severely damaged.
In early 1981 the eastern Gulf of Corinth, Greece was struck by three earthquakes with a magnitude greater than 6 over a period of 11 days. The earthquake sequence caused widespread damage in the Corinth–Athens area, destroying nearly 8,000 houses and causing 20–22 deaths.
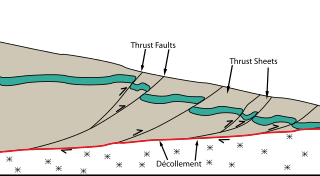
The Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT) is a décollement under the Himalaya Range. This thrust fault follows a NW-SE strike, reminiscent of an arc, and gently dips about 10 degrees towards the north, beneath the region. It is the largest active continental megathrust fault in the world.

The 1883 Casamicciola earthquake, also known as the Ischia earthquake occurred on 28 July at 20:25 local time on the island of Ischia in the Gulf of Naples in Italy. Although the earthquake had an estimated moment magnitude of 4.2–5.5, considered moderate in size, it caused intense ground shaking that was assigned XI (Extreme) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale. Between 2,313 and 3,100 people lost their lives. The city also suffered great property losses, with 80 percent of all homes destroyed. This earthquake was exceptionally destructive for its magnitude mainly due to its shallow focal depth.
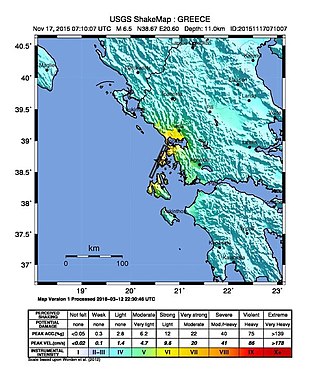
The 2015 Lefkada earthquake occurred on November 17, 2015, 10:40:07 (EEST) with a moment magnitude of 6.5 located 19 km Southwest of the Greek island of Lefkada along with a depth of 11 km and intensities reaching as high as VIII (Severe) on the Modified Mercalli Scale. Two people lost their lives in the event and 4–8 others were hospitalized with injuries.
The 1954 Sofades earthquake struck central Greece on April 30, 1954 at 16:02 (UTC+3). It was estimated to be 6.7–7.0 Mw and had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme). More than 25 people died, 717 were injured and about 28,000 structures were damaged or destroyed.
The 1885 Kashmir earthquake, also known as the Baramulla earthquake occurred on 30 May in Srinagar. It had an estimated moment magnitude of Mw 6.3–6.8 and maximum Medvedev–Sponheuer–Karnik scale intensity of VIII (Damaging). At least 3,081 people died and severe damage resulted.
The 1743 Salento earthquake affected the Apulian region of southwestern Italy on 20 February at 23:30 IST. The ~7.1 Mw earthquake had an epicenter in the Adriatic and Ionian seas, off the coast of modern-day Lecce and Brindisi provinces in Salento. It had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent), causing heavy damage in Nardò. Damage was also reported across the sea, in the Balkans. The earthquake also generated a tsunami of up to 11 meters in run-up. Between 180 and 300 people were killed in the disaster.

The 1867 Central Java earthquake occurred on June 10 at between 04:20 and 04:30 local time. It struck off the southern coast of the Indonesian island with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.8 (Mw ). Widespread devastation occurred in Central Java, where as many as 700 people were killed. The intermediate-depth intraslab earthquake did not cause a tsunami.









